Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) there has been wide variability in terms of gender regarding disease characteristics as well as outcomes across different ethnicities and geographic regions.1,2 The Treat-to-Target (T2T) strategy in axSpA has recently been advocated in patients with axSpA.3,4 The study aimed to compare the demographic characteristics, disease activity scores at baseline, adherence, and outcome of the treat-to-target (T2T) strategy between both genders in patients with axSpA in a real-world setting.
Methods: This was the first retrospective analysis looking at gender differences in a cohort set up with the support of the Arthritis Care Foundation enrolling patients from two academic rheumatology departments and affiliated clinics in Lahore, Pakistan. All patients who were enrolled gave an informed consent. Patients were diagnosed as axSpA as per ASAS classification criteria.5 Data regarding demography, disease parameters, and outcome measures like Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and Assessment of Spondyloarthritis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS)-CRP were retrieved from electronic medical records. Adherence to the T2T strategy in both groups was assessed by adaptations to treatment as per Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) recommendations performing ASDAS-CRP scores on at least 2 visits during the follow-up period of at least 6 months. 4 The outcome was assessed by proportion of patients achieving ASDA-CRP cut off of £ 2.1 at the last available visit, for analysis data was entered into SPSS version 26.
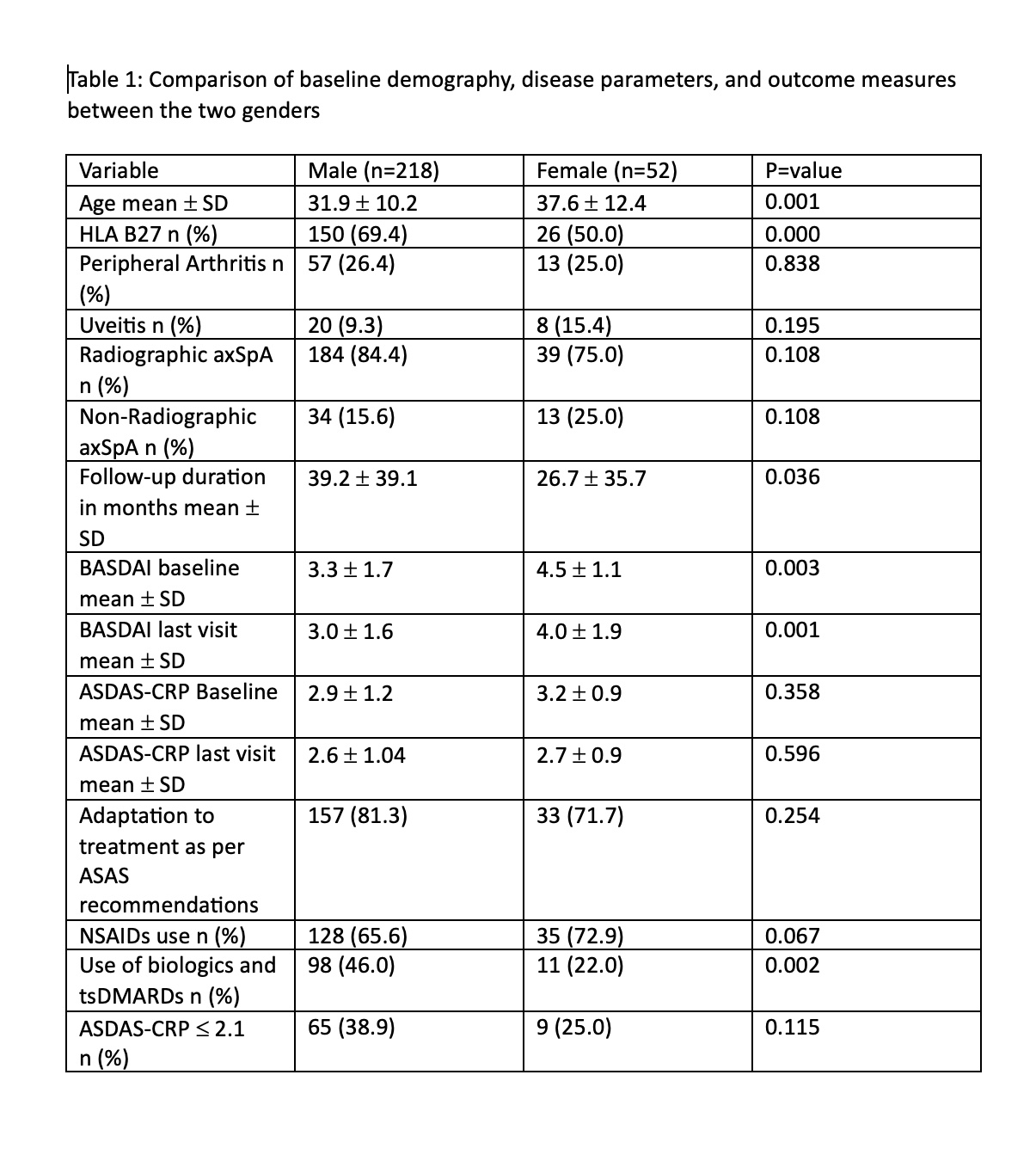
Results: There were a total of 270 axSpA patients enrolled from November 2019 to December 2023. Out of these, there were 218 (80.7 %) men and 52 (19.3 %) women. Women were found to be older than their counterparts at presentation (p=value 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference between the two genders in terms of disease duration at their first visit. However, there were more men with positive HLA-B 27 status 150 (69.4 %) vs 26 (50.0 %), p=0.000. There was no statistically significant difference In the frequency of peripheral arthritis and Uveitis. Females were reported to have higher BASDAI scores 4.5 ± 1.1 vs 3.3 ± 1.7 in men at baseline (p=0.003). ASDAS-CRP scores were also higher in women but this was not found to be statistically significant. Adherence to T2T by treating rheumatologists in terms of escalation of treatment was higher in male patients leading to higher use of biologic or targetted synthetic modifying rheumatic Drugs (tsDMARDs) in men (46 % vs 22 % p=0.002). There was no statistically significant difference in the proportion of patients achieving the target of ASDAS-CRP score of £ 2.1 i.e., 65 (38.9 %) in men vs 9 (25.0 %), (p-value=0.115). For a detailed comparison see Table 1.
Conclusion: This study highlighted that the disease burden in women was higher than in men in terms of BASDAI but there were no significant differences in ASDAS-CRP. However, despite this, there was a disparity in the use of biologics and tsDMARDs amongst both genders. However, there was no statistically significant difference in the proportion of patients achieving the target of ASDAS-CRP at 6 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saeed M, Ahmed H, Ahmed A. Gender Differences in Disease Parameters, Adherence to Treat to Target Strategy and Outcomes in Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) in Pakistani Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-differences-in-disease-parameters-adherence-to-treat-to-target-strategy-and-outcomes-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-in-pakistani-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-differences-in-disease-parameters-adherence-to-treat-to-target-strategy-and-outcomes-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-in-pakistani-cohort/