Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an increased cardiovascular (CV) risk compared to the general population. All stages of the atherogenic process appear to be accelerated in RA. Because the presence of carotid plaque is an independent predictor of CV events and its timely treatment has been associated with beneficial effects, a screening tool is necessary in patients with RA. Inflammatory indices are simple and inexpensive biomarkers of systemic inflammation that have been used as diagnostic and prognostic markers in different types of diseases. Recently, multiple studies have used these indices in RA as biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring. These studies suggest that inflammatory indices may be a good indicator of subclinical chronic inflammation. The aim pf this study is compare and determine which is the best inflammatory index to predict the presence of carotid plaque in patients with RA.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted that included patients between 40 and 75 years of age who met the 2010 ACR/EULAR and/or 1987 ACR RA classification criteria. Patients with a history of a major CV event were excluded. Patients were questioned about traditional as well as non-traditional risk factors (such as disease activity and duration). Laboratory studies were taken, and a carotid Doppler ultrasound (US) was performed. With the results, 9 inflammatory indices were calculated (see Table 1), of which their diagnostic performance was evaluated using ROC curves, considering carotid Doppler US as the gold standard for diagnosing carotid plaque. Finally, a cut-off point was determined using the Youden index and its sensitivity, specificity, positive-negative predictive value and positive-negative probability coefficient were determined.
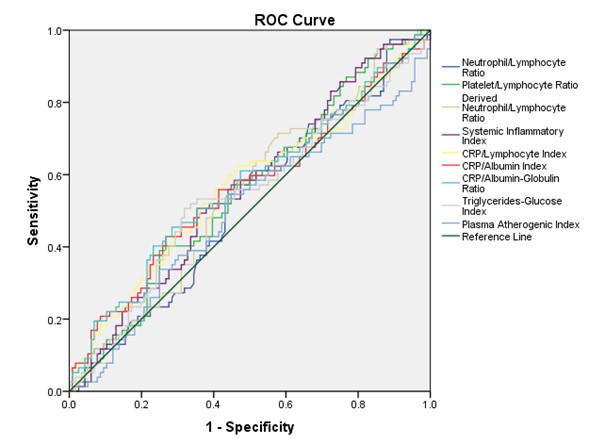
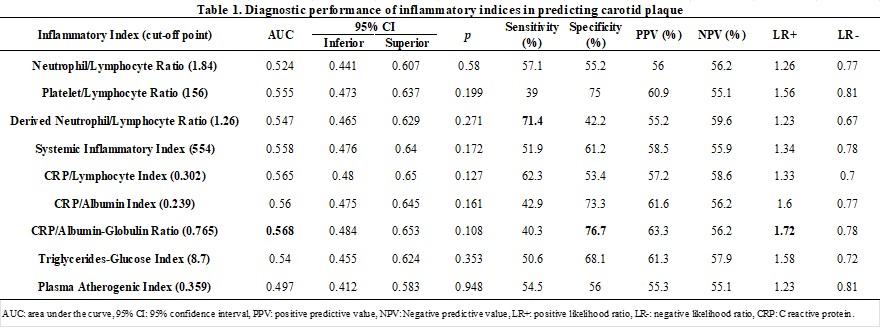
Results: A total of 193 patients with RA were studied, the majority women (90.6%), with an average age of 56 (±9.9) years and with an average DAS 28-CRP of 3.46 (±1.55). The prevalence of comorbidities was active smoking in 12.2%, type 2 diabetes mellitus in 19.7%, systemic arterial hypertension in 40.6% and obesity in 33.1%. The prevalence of carotid plaque by carotid Doppler US was 39.9%, whether unilateral or bilateral. Table 1 and Figure 1 show the results of the analysis with ROC curves as well as the parameters of the diagnostic tests. The index with the largest area under the curve was the CRP/Albumin-Globulin Ratio with 0.568. The index with the highest specificity (76.7%) and the highest positive likelihood ratio (1.7) was also CRP/Albumin-Globulin Ratio using the cut-off point of 0.76. This means that a patient with RA is 1.7 times more likely to have carotid plaque when obtaining this cut-off point. Nevertheless, when we compare areas under the curve, we can see a poor discriminatory capacity of all the indices.
Conclusion: The 9 indices touch the reference line, which invalidates them as a tool to predict carotid plaque, obtaining a non-significant p in all of them. These results suggest that inflammatory indices do not replace traditional CV risk calculators as screening to predict subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Davila Jimenez J, Galarza-Delgado D, Colunga Pedraza I, Azpiri-Lopez j, Arvizu-Rivera R, Cardenas-de la Garza J, Gonzalez Melendez A, Guajardo Aldaco A, Elizondo-Benitez M, Polina-Lugo R, Salcedo-Almanza D. Evaluation of Inflammatory Indices as Predictive Biomarkers of Carotid Plaque in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-inflammatory-indices-as-predictive-biomarkers-of-carotid-plaque-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-inflammatory-indices-as-predictive-biomarkers-of-carotid-plaque-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/