Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Creatine kinase (CK) is an important biomarker for the diagnosis and monitoring of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM). However, in some cases, CK levels might exhibit only minor elevation or remain normal, even in the setting of active muscle disease. The data regarding normal CK in IIM is limited. The study aimed to characterize IIM patients with normal CK levels, including demographic and clinical phenotypes, and disease activity.
Methods: Data were collected from the Rituximab in Myositis (RIM) trial, a large prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The study enrolled IIM patients with refractory disease despite glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive treatment, with each case adjudicated for diagnosis and disease activity. Data were collected on all core set measures (CSMs), including CK, manual muscle testing (MMT), physician-global disease activity (Ph-GDA), patient-global disease activity (Pt-GDA), extra-muscular disease activity (Ex-GDA) and HAQ-DI, at baseline and every 4 weeks for 44 weeks. “Normal” CK including near normal CK was defined at baseline, as a serum level within twice the ULN as per the laboratory reference range. Sub-analysis by subtypes, including dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), anti-synthetase syndrome (ASyS), and necrotizing myopathy (NM), was performed according to the myositis classification criteria and autoantibodies.
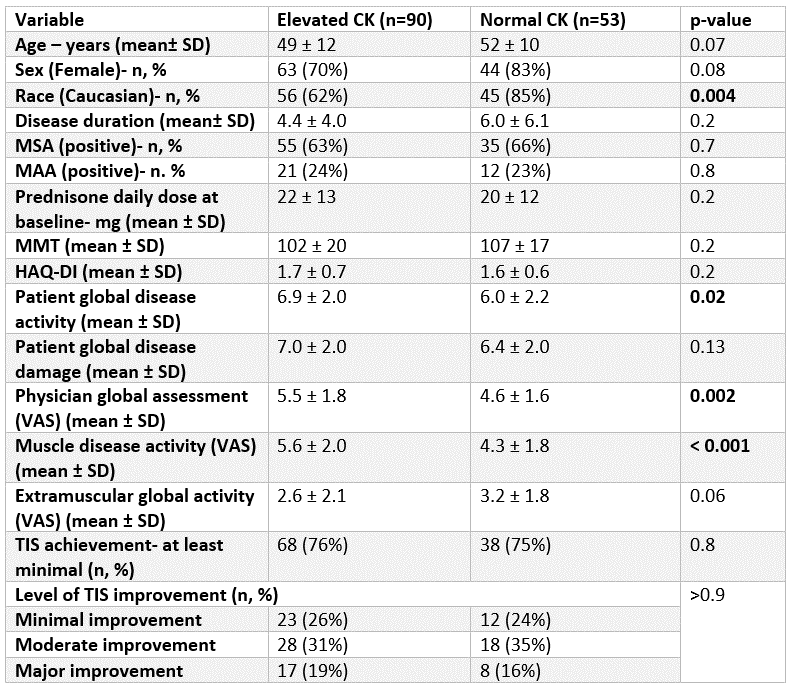
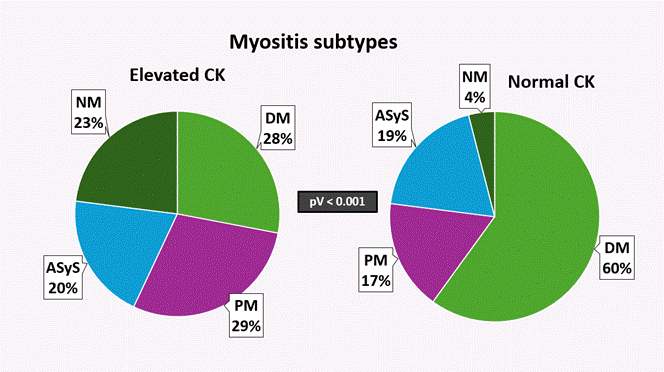
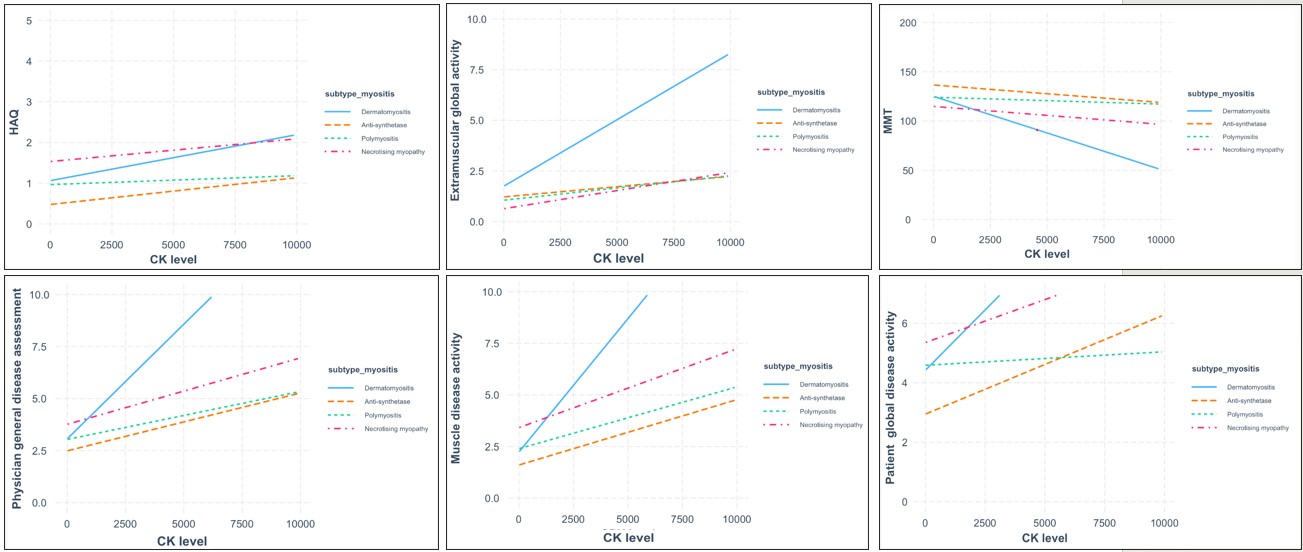
Results: 143 adult patients were analyzed, including 53 (37%) patients with normal/near normal CK and 90 (63%) with elevated CK. The former group had a significantly higher prevalence of Whites (85% vs. 62%, p=0.004), and a tendency toward female predominance (83% vs. 70%, p=0.08) and increased age (52±10 vs 49±12, p=0.07). No significant difference was observed in disease duration, the frequency of positive antibodies, or daily prednisone dosage [Table 1]. The distribution of IIM subtypes significantly differed between patients with elevated CK vs. normal CK (p < 0.001). Patients with normal CK suffered mainly from DM, whereas NM mostly had elevated CK [Figure 1]. At baseline, patients with elevated CK had significantly higher Ph-GDA, Pt-GDA, and muscle disease activity, as well as showed an association of CK levels with Ph-GDA (p=0.01) and muscle disease activity (p=0.001). Conversely, in patients with normal CK levels, no baseline associations were observed between CK levels and other CSMs. Employing a linear mixed model with adjustment for age, sex, race, and prednisone dose, CK levels exhibited a significant longitudinal association (p< 0.001) during follow-up with various CSMs, including MMT, Pt-GDA, Ph-GDA, muscle disease activity, and Ex-GDA. This correlation was strong regardless of baseline CK status (normal vs. elevated) or myositis sub-type, except in PM where it did not reach statistical significance with MMT and Pt-GDA [Figure 2].
Conclusion: Normal CK levels are common in IIM, and do not exclude the presence of active muscle disease. CK levels demonstrate a strong longitudinal correlation with other CSMs, irrespective of baseline CK levels or myositis sub-type, highlighting the importance of CK as a biomarker for monitoring disease activity in all IIM patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
keret s, Chandra T, Kaly L, Silva R, Gkiaouraki E, Pongtarakulpanit N, Sriram s, Gopalarathinam R, Mogahadam S, Oddis C, Aggarwal R. Normal Creatine Kinase in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies- Patient Characteristics and Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/normal-creatine-kinase-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-patient-characteristics-and-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/normal-creatine-kinase-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-patient-characteristics-and-disease-activity/