Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The GUARD (Genakumab in high Uric Acid-induced Arthritis/goutfor Resolution and Delay study) program was designed to investigate the efficacy and safety of Genakumab, a novel fully humanized, monoclonal anti-IL-1β antibody, developed by GenSci Co., in patients with gout through IL-1β pathway. Here, we first report the data of Genakumab vs Compound betamethasone in treatment of Chinese adult patients with gout flare(chictr.org.cn identifier: CTR20223136).
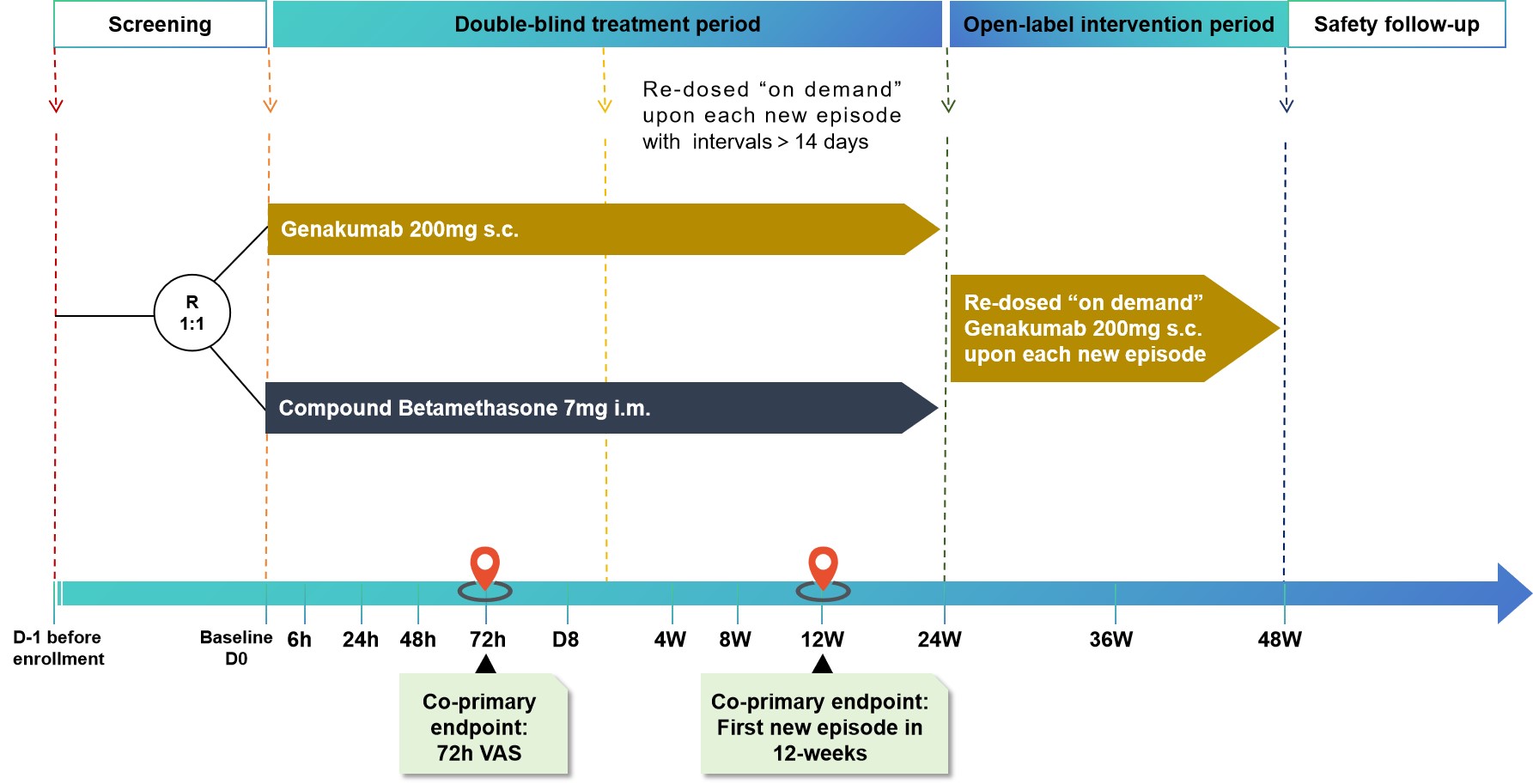
Methods: The GUARD-1 study was a prospective, randomized, multi-center, active controlled study, with a 48-week treatment period (24 weeks for double-blind treatment and 24 weeks for open-label intervention) and a 12-week safety follow-up period. In this study, patients (≥18-≤75 yrs) who met the ACR preliminary criteria for acute GA and contraindicated for, intolerance of, or unresponsiveness to NSAIDs and/or colchicine, with ≥2 episodes during the previous 12-month, were randomized with ratio 1:1 to receive a single dose of Genakumab 200 mg SC or Compound betamethasone 7 mg IM and and administered in case of new episode. Urico-lowering therapy (ULT) were kept no change during study follow up period. The co-primary endpoints were change in pain intensity at 72 hours for baseline most affected joint (noninferiority testing), measured with the 0-100 mm VAS, and the time to first new episode over 12 weeks (superiority testing). Secondary endpoints include pain at 6h, 24h, 48h, and 7 days measured with visual analogue scale (VAS); percentage of patients with at least 1 new episode; and safety during treatment period (Figure 1).
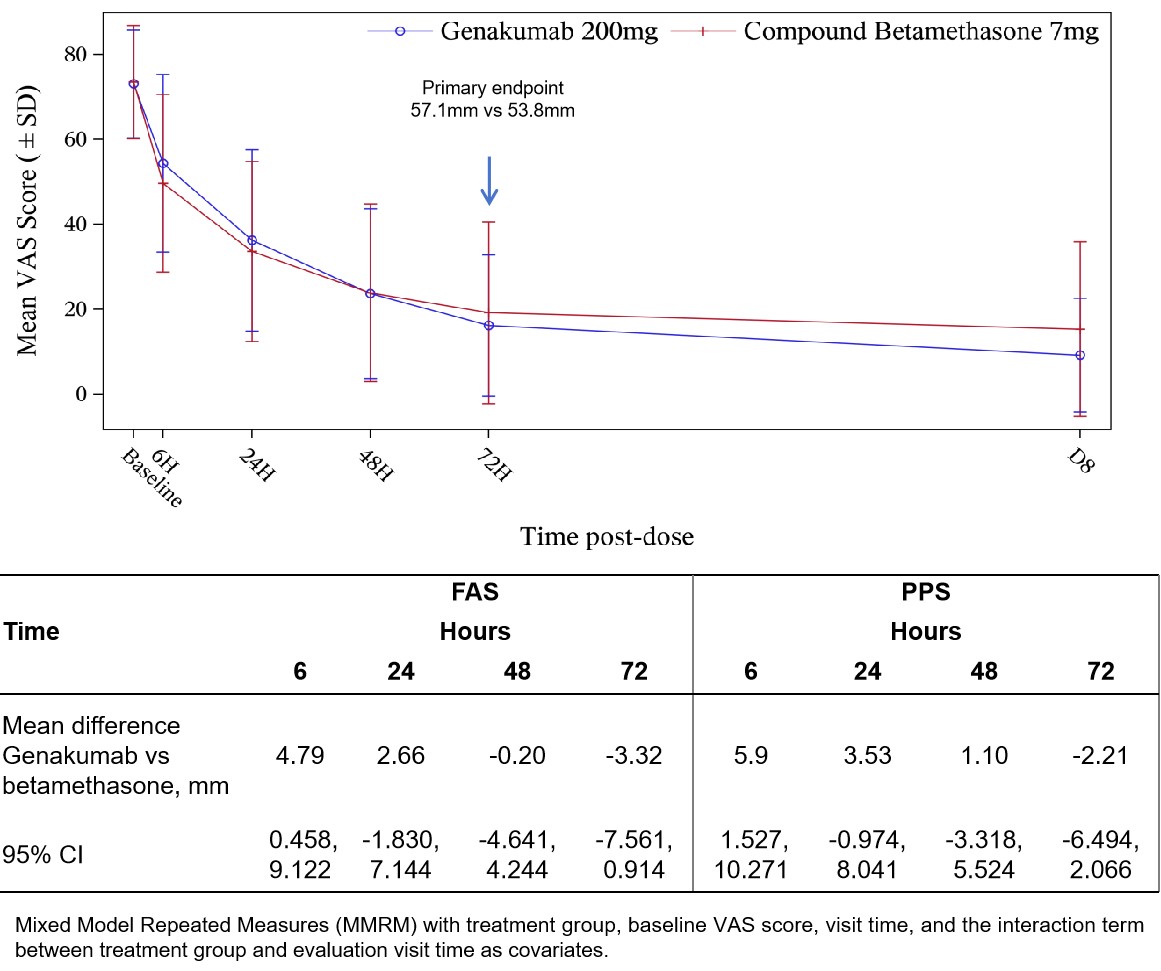
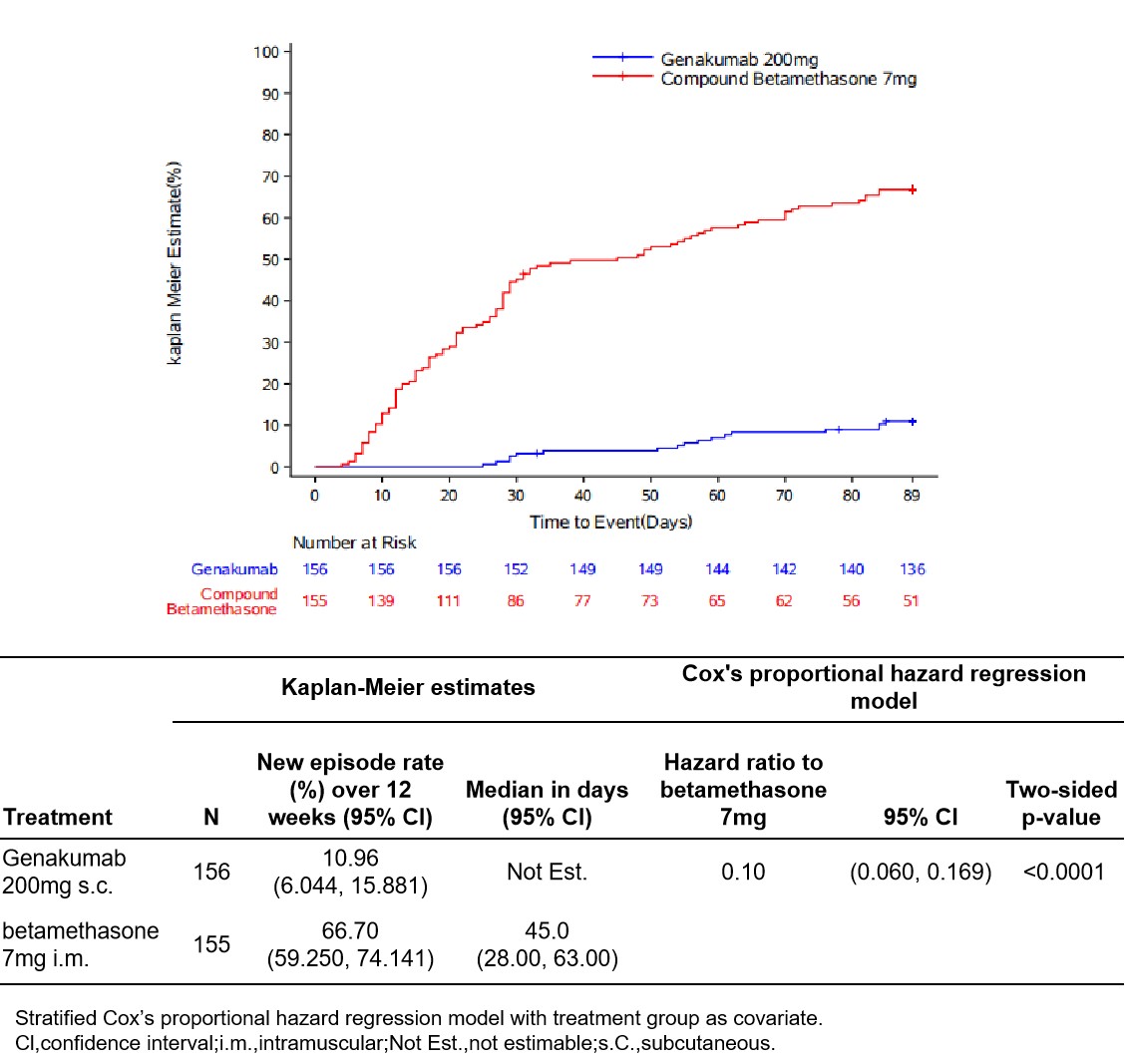
Results: A total of 313 patients were randomized (Genakumab [n=157], Compound betamethasone [n=156]). Median age was 42 (range 35–55) years, 98.7% were men, disease duration 103.89(±76.719)(mean±SD) month, and more than 3 episodes reported during prior year in most patients (3-5/year, 45.7%; 6-12/year, 33.1%; >12/year, 10.6%). Genakumab was non-inferior in change in pain intensity at 72 hours (mean difference; 95% CI) to Compound betamethasone in both the Full Analysis Set (-3.32mm; -7.56, 0.91) and Per Protocol Set (-2.21; -6.49, 2.07)(Figure 2). Genakumab significantly delayed median time to first new episode vs Compound betamethasone (Not estimable vs 45 days) (Figure 3). Genakumab significantly reduced the risk of new episodes by 90% versus Compound betamethasone (HR 0.10; 95% CI:0.060, 0.169; p<0.0001) over the first 12 weeks, and by 87% (HR 0.13; 95% CI: 0.084, 0.208; p<0.0001 ) over 24 weeks.
A total of 159 subjects (51.0%) experienced Treatment-Related Adverse Events (TRAEs), with 79 subjects (50.6%) in Genakumab group, and 80 subjects (51.3%) in Compound betamethasone group. Treatment-Related Serious Adverse Events were reported in 3 patients and all in Compound betamethasone group.
Conclusion: In summary, in adults in whom NSAIDs and/or colchicine are contraindicated, are not tolerated, or do not provide an adequate response,
Genakumab was demonstrated non-inferiority to Compound betamethasone in pain relief of gouty arthritis attacks, and superiority to Compound betamethasone within 12 weeks in delaying new flare which can be maintained until the end of the 24 weeks.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Xue Y, Chu T, Hu J, Gou W, Zhang N, Li J, Yu J, Li S, Li S, Qian L, Duan X, Duan L, Zou H. Efficacy and Safety of Genakumab versus Compound Betamethasone in Gout: The GUARD-1 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-genakumab-versus-compound-betamethasone-in-gout-the-guard-1-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-genakumab-versus-compound-betamethasone-in-gout-the-guard-1-study/