Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Carriage of HLA-DRB1 shared epitope (SE) alleles and a history of smoking, have been identified as the most prominent risk factors for development of autoantibody positive rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The hallmark autoantibodies, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) can target various antigens, resulting in heterogeneous ACPA profiles among patients. Their exact nature and etiological significance remain unknown. ACPA are multi-reactive and bind citrulline-amino acid motifs where “cit-gly” is a common target. We investigated the co-occurrence of RA-specific autoantibodies, and ACPA-patterns by recognized citrulline (cit)-motifs in relation to HLA-DRB1 and smoking.
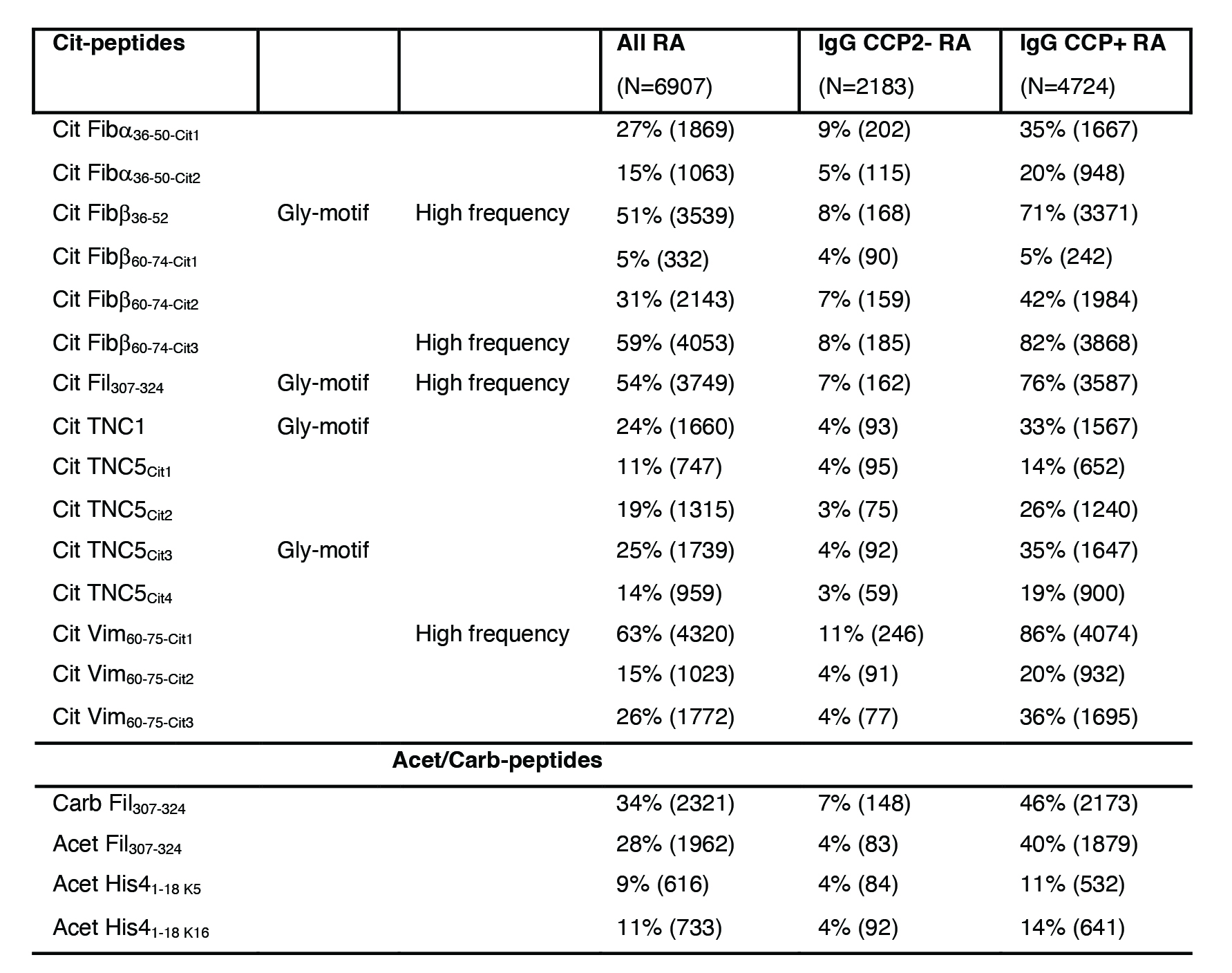
Methods: We measured rheumatoid factor (RF) IgM IgG and IgA, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP2) IgG and IgA, and IgG to 15 anti-cit- peptides elected to cover different cit-motifs and 4 Carb/Acet-peptides, in 6,907 patients from five Scandinavian RA cohorts [1]. Analyses were performed centrally using fluoroenzyme immunoassay and custom-made multiplex solid-phase microarray. Cutoffs was set based on 400 healthy controls and high signals were 3x cutoff. HLA-DRB1 SE alleles were imputed from SNP genotyping data.
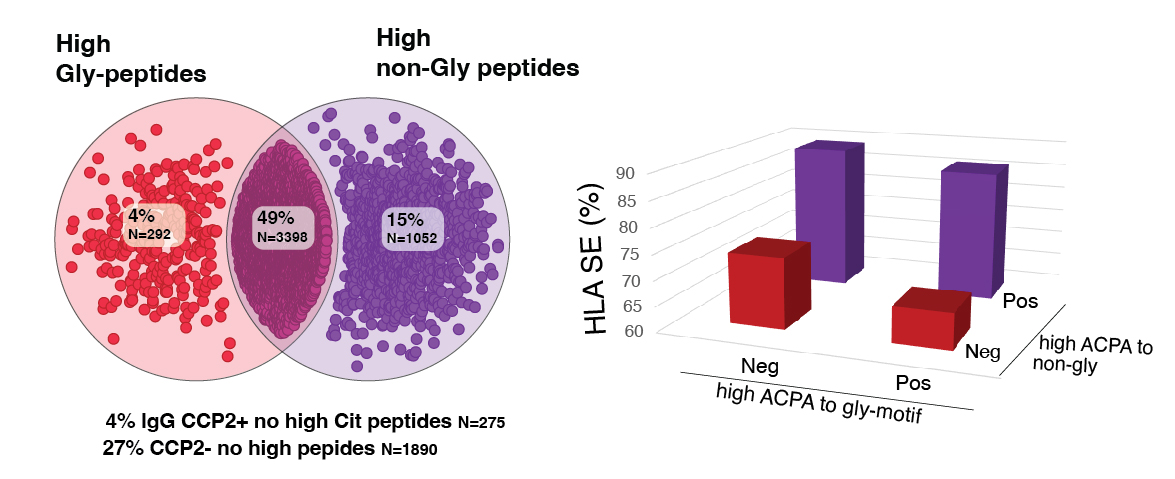
Results: Compared to using only CCP2-IgG and/or RF-IgM, seropositivity increased from 76% to 84% when all autoantibody tests were included. Single-cit peptides derived from four multi-cit peptides (Cit Fiba36-50, Cit Fibb60-74, Cit TNC5, Cit Vim60-75) showed differential binding patterns, supporting recognition of cit-motifs rather than long peptides. Four cit-peptides (Cit Fibb36-52, Cit Fibb60-74-Cit3, Cit Fil307-324, Cit Vim60-75-Cit1) (table 1) captured 97% of IgG anti-CCP2+ patients. Different ACPA overlapped, but when dichotomizing patients based on high reactivity ( >3x cutoff) to peptide cit-motifs, non-glycine but not glycine-motif ACPA associated with HLA-SE alleles (figure 1). In IgG anti-CCP2+ patients, 90% of those with only high non-glycine ACPA were HLA-SE allele carriers, compared to 67% in the group with glycine-motif only ACPA, yielding an odds ratio (OR) of 4.5 (95% CI: 1.9-11, Fisher’s exact test). Smoking status did not correlate with fine-specificity subsets or IgG anti-Carb/Acet but independently associated with IgA/IgM RF and IgA/IgG anti-CCP2 double positivity.
Conclusion: While glycine-motifs are commonly citrullinated and prevalent ACPA-targets, our data in this large cohort of routine care treated patients with RA reveals that HLA-SE alleles are primarily associated with ACPA to non-glycine cit-motif, providing new insight in ACPA epitope spreading. The association between IgA and smoking supports a chronic mucosal response. Our results advance our understanding of citrulline responses in relation to key environmental and genetic RA risk factors.
Reference:
1. Westerlind et al RMD Open 2023 Sep;9(3):e003027
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mathsson-Alm L, Westerlind H, Gehring I, Hansson M, Ghasemzadeh N, Rojas-Restrepo J, Saevarsdottir S, Sexton J, Lillegraven S, Haavardsholm E, Hetland M, Hammer H, Kvien T, Glintborg B, Padyukov L, Askling J, Grönwall C. Refined Autoantibody Profiles in RA Reveal That Primarily ACPAs Binding Non-glycine Citrulline Motifs Are Associated with Shared Epitope Alleles [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/refined-autoantibody-profiles-in-ra-reveal-that-primarily-acpas-binding-non-glycine-citrulline-motifs-are-associated-with-shared-epitope-alleles/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/refined-autoantibody-profiles-in-ra-reveal-that-primarily-acpas-binding-non-glycine-citrulline-motifs-are-associated-with-shared-epitope-alleles/