Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 15, 2023
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes IV: Pre-RA & RA Diagnosis
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Non-invasive differentiation of seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from other conditions has been limited in the current practice. We aimed to evaluate the clinical feasibility of a novel blood-based assay to differentiate RA patents from healthy controls and those with other conditions, including osteoarthritis (OA) and inflammatory conditions.
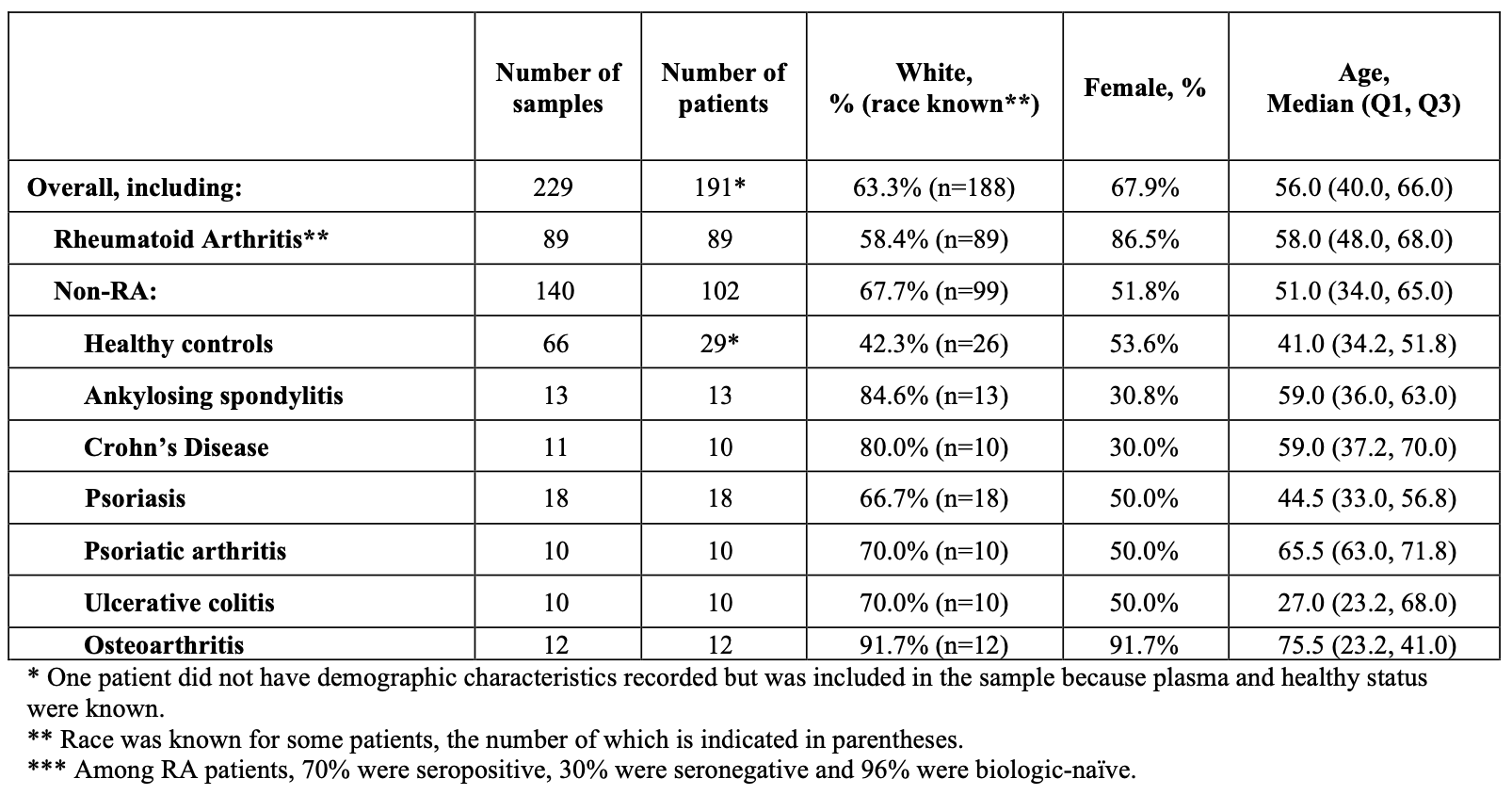
Methods: We acquired plasma samples from 89 individuals meeting 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA (89 samples), 29 healthy controls (66 samples), 12 individuals with osteoarthritis (12 samples) or 61 individuals with an inflammatory condition (62 samples; Table 1). Samples were processed via chromatin enrichment assay that enables access to tissue and disease specific genetic signatures. A machine learning algorithm (involving 5-repeat 10-fold cross-validation training and testing), trained to identify synovial signatures in blood plasma, was used to generate the probabilistic estimates for the presence and absence of RA.
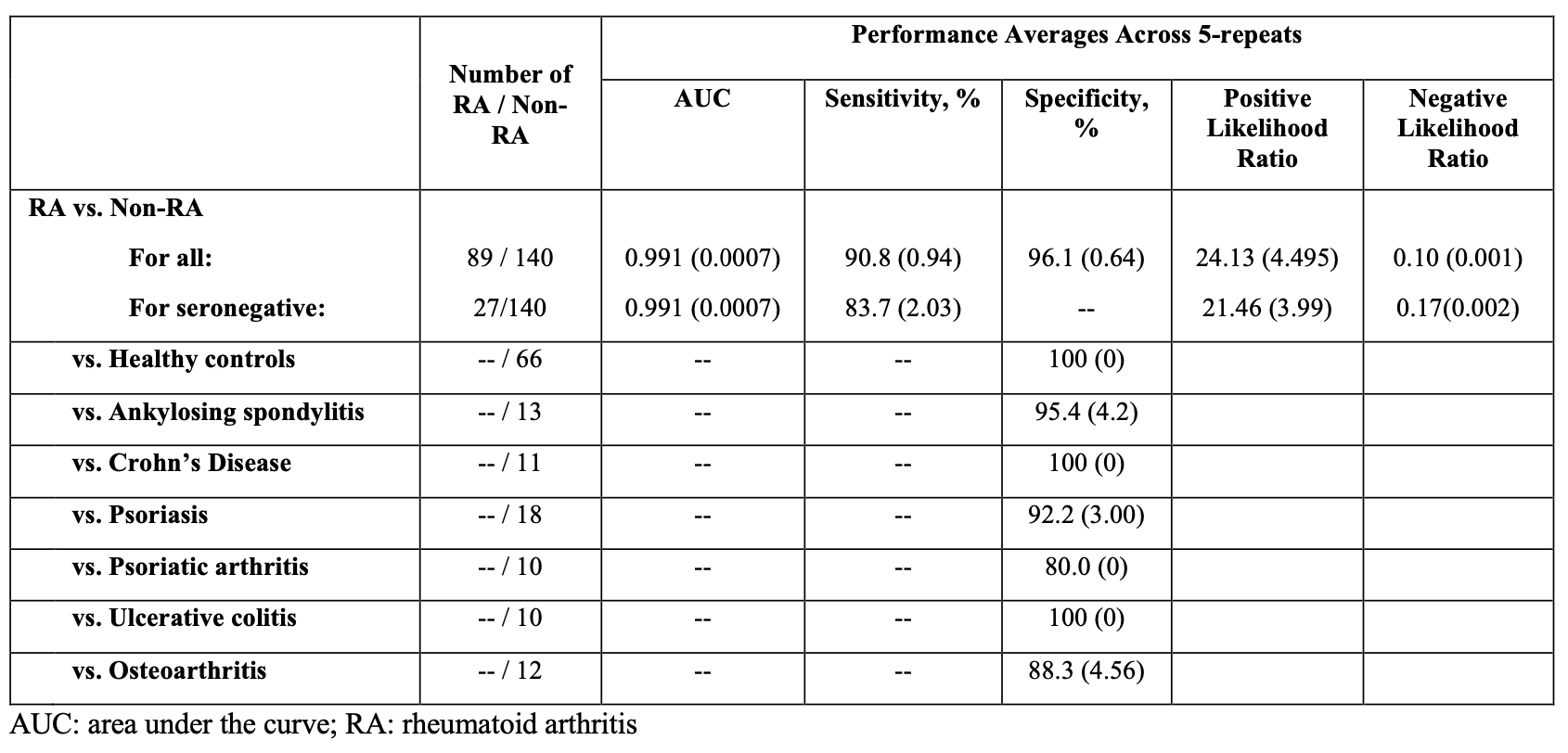
For RA vs non-RA, we report the area under the curve (AUC), mean (standard deviation; SD) sensitivity, overall specificity, positive likelihood ratio and negative likelihood ratio. For comparator conditions, we report specificity alone.
Results: Table 1 describes the study sample. RA subjects were 70% seropositive, 30% seronegative, 96% biologic-naïve (Table 1).The test distinguished RA from non-RA with the following overall accuracy: AUC 0.991 (0.0007), sensitivity 90.8% (0.94%), and overall specificity 96.1% (0.64%), positive likelihood ratio 24.13 (4.495) and negative likelihood ratio 0.10 (0.001). For seronegative RA, the results included sensitivity 83.7% (2.03%), positive likelihood ratio 21.46 (3.99), and negative likelihood ratio 0.17 (0.002). In comparator groups, specificity was 80.0% (0 %) for psoriatic arthritis, 88.3% (4.56%) for osteoarthritis, 92.2% (3.04%) for psoriasis, 95.4% (4.21%) for ankylosing spondylitis, and 100% (0%) for healthy controls, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis (Table 2).
Conclusion: A novel non-invasive assay differentiated individuals with RA from healthy controls and those with other inflammatory conditions without RA with high sensitivity and overall specificity. In comparator cohorts, the assay demonstrated high specificity for all groups, including healthy controls, osteoarthritis, and other inflammatory conditions. The sensitivity was maintained in seronegative individuals. Further research is needed to confirm these results in an independent study.
Note: Both Dr. Shadick and Dr. Weinblatt are last authors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Taylor P, Antonova J, Geis J, Dilger K, Chernoff D, Abdueva D, Shadick N, Weinblatt M. A Novel Blood-Based Assay Differentiates Seropositive and Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis from Healthy Individuals and Those with Other Inflammatory Diseases or Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-blood-based-assay-differentiates-seropositive-and-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-healthy-individuals-and-those-with-other-inflammatory-diseases-or-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-blood-based-assay-differentiates-seropositive-and-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-healthy-individuals-and-those-with-other-inflammatory-diseases-or-osteoarthritis/