Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interventional musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) procedures, such as ultrasound-guided arthrocentesis and joint injections, are routinely used in rheumatology practice. However, the efficacy and safety of these procedures rely on the competence of the individual physician, and intensive training is essential before independent practice. Assessment tools play a pivotal role in providing structured feedback to the trainees and ensuring end-of-training competence. An international expert panel of radiologists developed the Interventional Ultrasound Skills Evaluation (IUSE) tool to evaluate operator competence in invasive ultrasound procedures relevant for abdominal and thoracal interventions. It is unsuitable for assessing MSUS procedures and therefore, we aimed to develop and establish valid evidence for a modified version of the IUSE assessment tool designed for evaluating trainees in interventional MSUS procedures relevant in rheumatology.
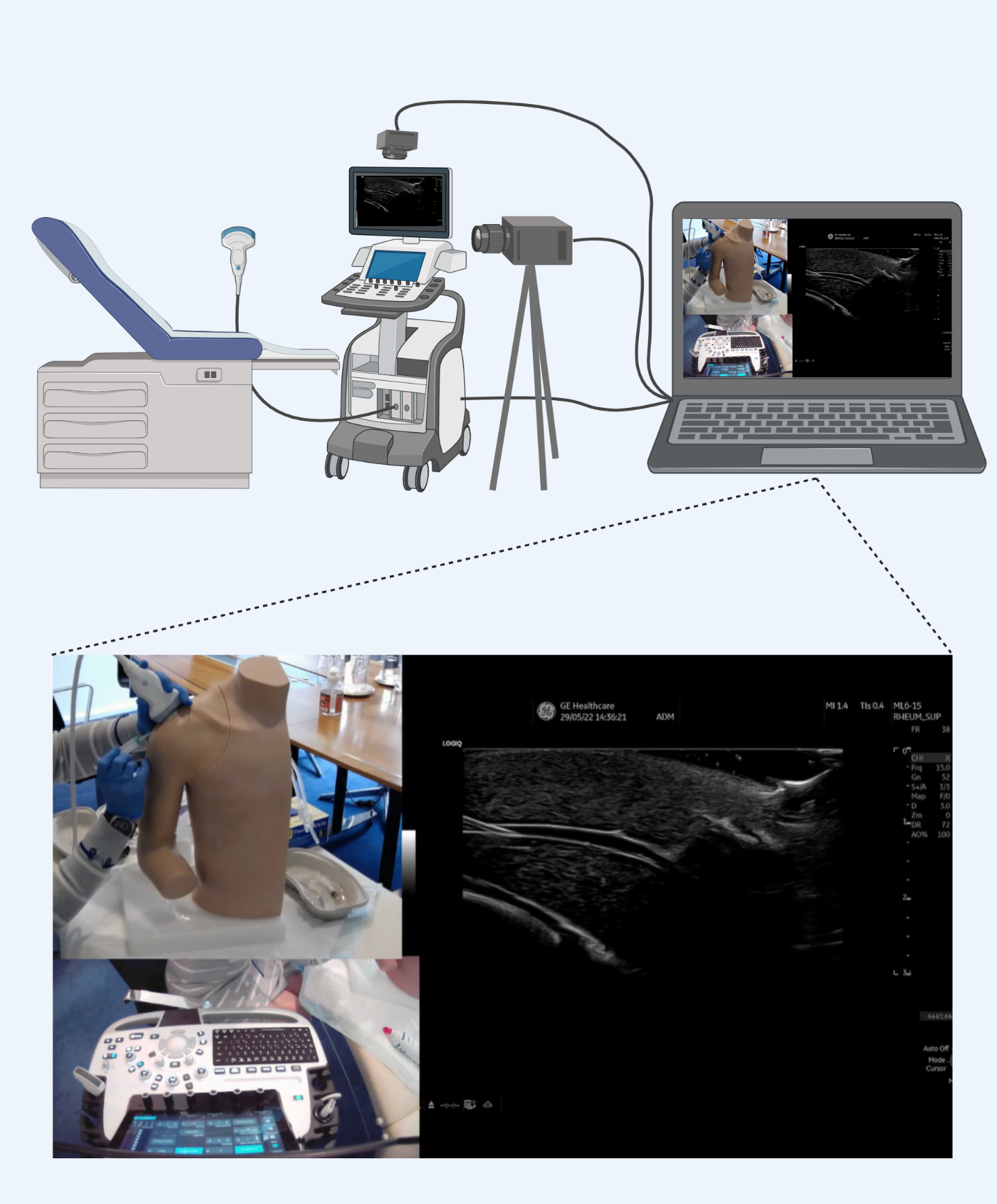
Methods: An expert panel of rheumatologists modified the IUSE tool to reflect the essential steps in interventional MSUS procedures. The modified tool was named the Assessment of Interventional Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Skills (AIMUS) and included 8 items: indications, contraindications, preparation, US equipment, procedural instruments, route, hand-eye coordination and, procedure and outcome. To gather validity evidence for the AIMUS tool, physicians with different levels of interventional MSUS experience were enrolled in the study and instructed to perform two interventional MSUS procedures on simulated patient cases, i.e., subdeltoid bursitis and biceps tenosynovitis. The procedures included both ultrasound-guided aspiration and injection techniques and were performed on a shoulder rubber fantom with ultrasound capabilities, Figure 1. All examinations were video recorded (n=130), anonymized, and subsequently assessed in random order by two blinded raters using the AIMUS tool.
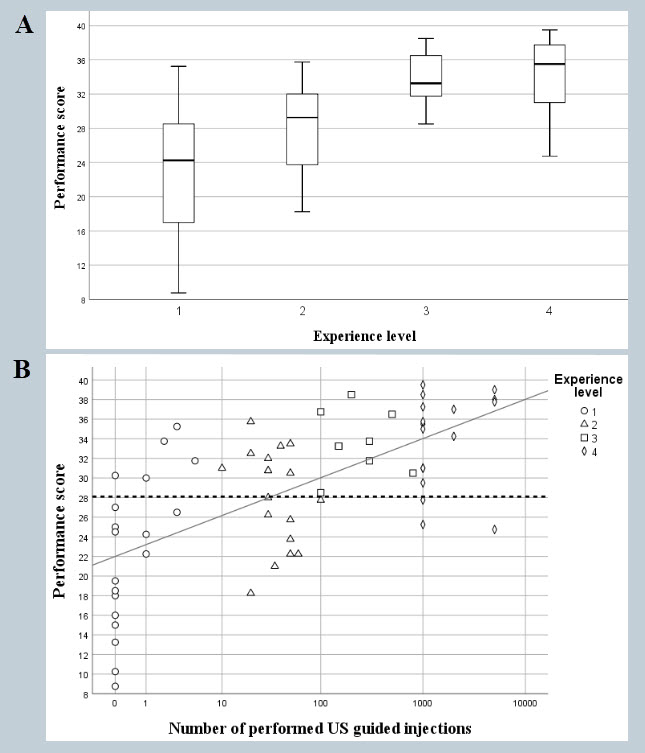
Results: Sixty-five physicians from 21 different countries attending the EULAR 2022 conference were included and categorized into four groups based on their experience with interventional MSUS, determined by the number of procedures performed: 19 novices (0-10), 18 intermediate (10-100), 9 experienced (100-1000), and 17 experts ( >1000). Two participants were excluded from the analysis due to a lack of data on their experience. The internal consistency of the AIMUS tool was excellent, with a Cronbach alpha of 0.9. The inter-case reliability was good with a Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.7 and the inter-rater reliability was moderate to good (PCC 0.6). The ability to discriminate between different levels of experience was highly significant (p< 0.001), with a linear correlation between the performance scores and the participant experience levels, Figure 2.
Conclusion: We have developed and established solid validity evidence for the AIMUS tool for evaluating trainees’ interventional MSUS skills. The AIMUS tool can be used in daily clinical practice and implemented in training curricula for establishing competency-based training for interventional MSUS procedures in the future.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Carstensen S, Terslev L, Just S, Østergaard M, Pfeiffer-Jensen M, Konge L. A New Tool Assessing Trainees’ Interventional Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Skills [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-tool-assessing-trainees-interventional-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-skills/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-tool-assessing-trainees-interventional-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-skills/