Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: We have previously shown that skin fibroblast activation is related to clinical severity and resolves with improvement in diffuse systemic sclerosis (dcSSc). The immune cells that associate with fibroblast activation are not fully characterized. The purpose of this study was to evaluate associations between immune cells and fibroblasts of varying stages of activation in dcSSc skin.
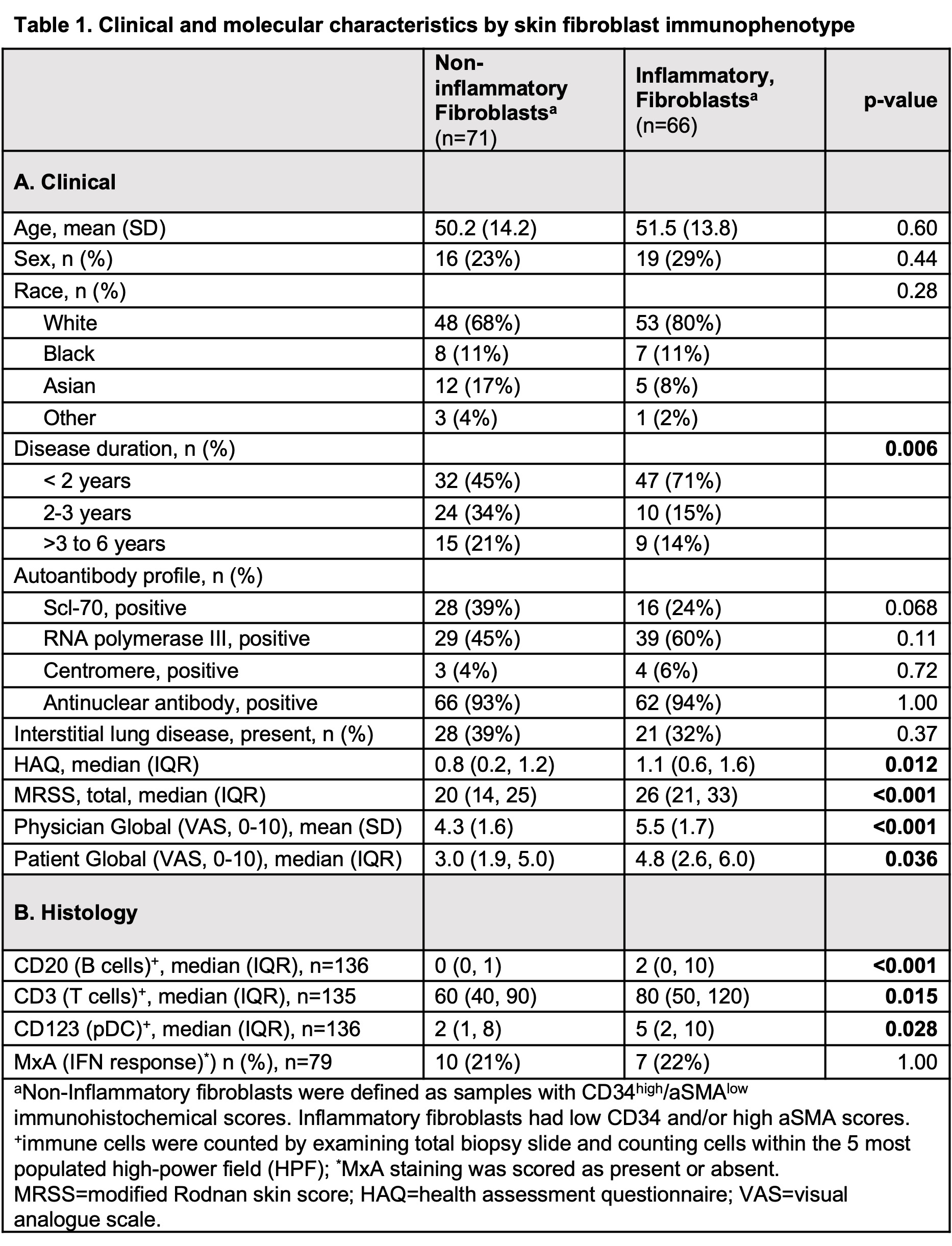
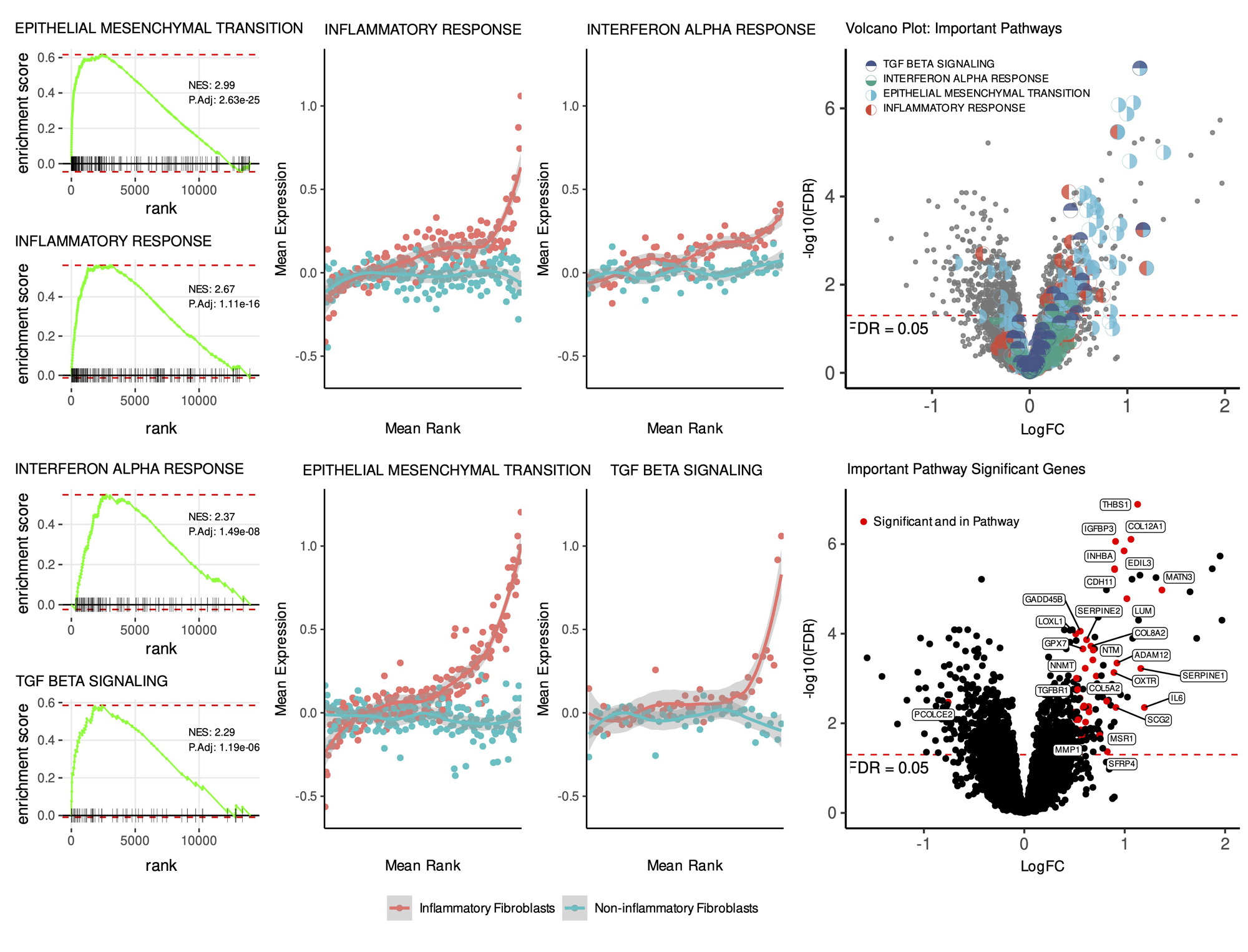
Methods: Histology of 137 forearm skin biopsies from 105 dcSSc patients were scored for fibroblast markers (CD34, alpha smooth muscle actin (aSMA); semiquantitative), and immune cells (B cells (CD20+), T cells (CD3+) and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs; CD123+); count per 5 HPF). 79 samples were also stained for MxA, a type 1 interferon (IFN)-related protein, scored present or absent. Non-inflammatory fibroblast pattern was defined by CD34high/aSMAlow scores. Inflammatory fibroblast pattern was defined as aSMAhigh and/or CD34low scores. Clinical variables and cell counts were compared between fibroblast immunophenotypes using Fisher’s exact, t-test, or Wilcoxon rank-sum. Spearman correlation was used to assess the association between histologic features. Imaging mass cytometry (IMC) was used to visualize immune-stromal cell spatial interactions. Gene expression was analyzed by microarray for all samples. GSEA was performed using hallmark gene sets between fibroblast groups. Average expression of genes in selected pathways were ranked, and a loess curve was fit to each fibroblast group (bands represent 0.99 confidence interval).
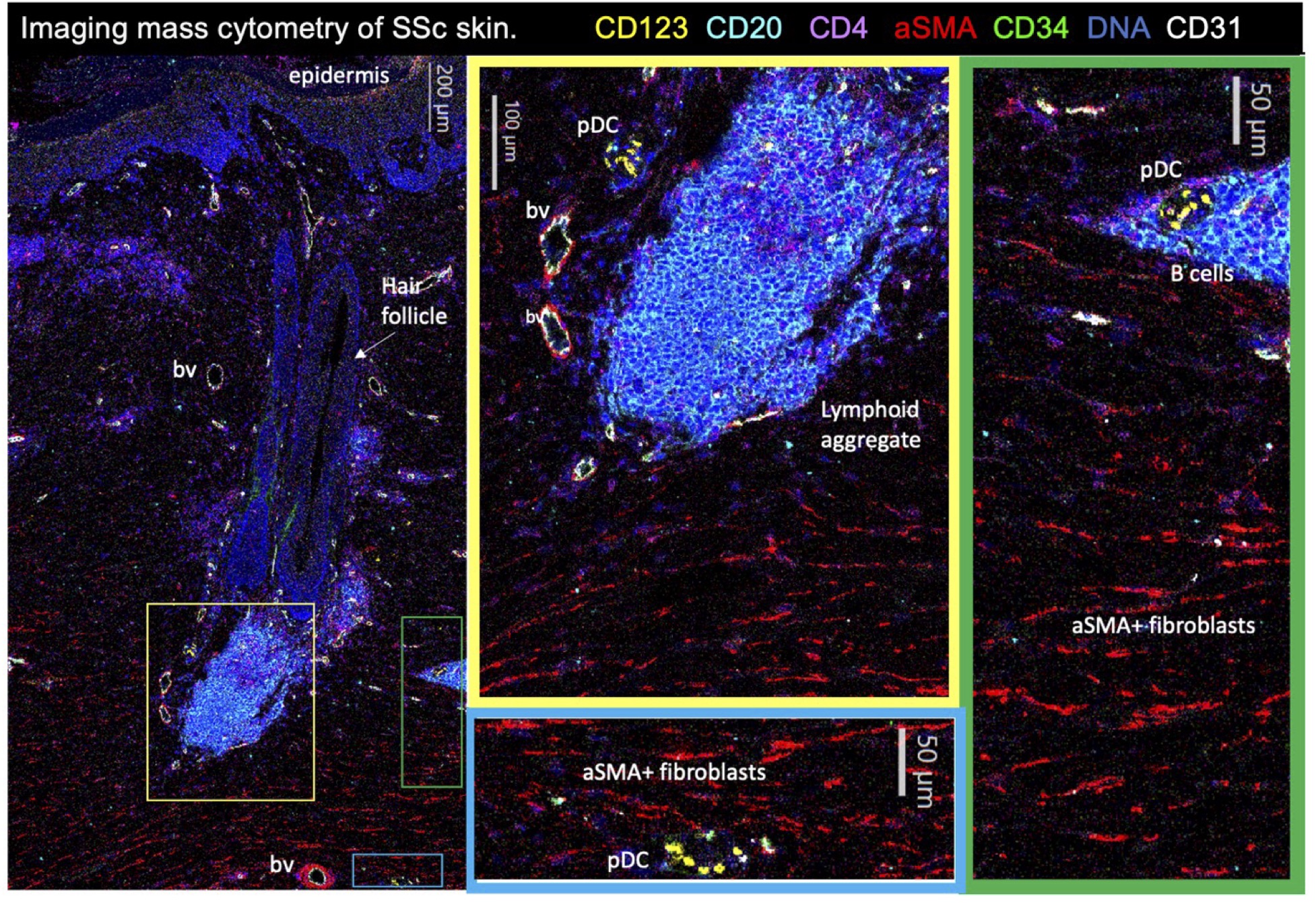
Results: Inflammatory (vs. non-inflammatory) fibroblast samples (66 of 137, 48%) had worse clinical severity (modified Rodnan skin score (p< 0.001), HAQ (p=0.012), Patient Global (p=0.036) and Physician Global (p< 0.001)) (Table 1A) and higher median CD20+ (p< 0.001), CD3+ (p=0.003) and CD123+ cell count (p=0.028) (Table 1B). CD34 (key marker of non-inflammatory fibroblasts) correlated negatively with CD20 (rs=-0.315, p=0.0002), CD123 (rs=-0.281, p=0.0009), and CD3 (rs=-0.236, p=0.0058), while aSMA (key marker of inflammatory fibroblasts) correlated positively with CD20 (rs=0.415, p< 0.00001) and CD3 (rs=0.212, p=0.0135). Samples with detectable MxA protein expression had higher median CD123+ cells (5 vs. 1, p=0.001). IMC in a representative sample revealed infiltrating pDC adjacent to B cells and local interactions between these cells and aSMA+ fibroblasts (Fig. 1). Gene expression analysis demonstrated upregulation of IFN-alpha, TGF-beta, and inflammatory response as well as epithelial-mesenchymal transition among samples with inflammatory vs. non-inflammatory fibroblasts (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: Inflammatory fibroblasts in clinically severe SSc skin are associated with hallmark inflammatory response, IFN-alpha response, and TGF-beta signaling, as well as T cell, B cell, and pDC infiltration. Inflammatory fibroblasts are physically associated with B cells and pDCs in SSc skin. These data are relevant to SSc trials targeting B cell and IFN pathways. To our knowledge, this is the first report using IMC to visualize immune-stromal cell spatial interactions in dcSSc skin. Future work quantifying IMC data will further characterize these associations in a larger sample.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lakin K, Spiera R, Zhang Y, Oliver D, Bloostein A, Ravichandran H, Anandasabapathy N, Barrat F, Gordon J, Orange D. Clinically Severe Systemic Sclerosis Skin Harbors Inflammatory Fibroblasts Associated with Lymphocytes and Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-severe-systemic-sclerosis-skin-harbors-inflammatory-fibroblasts-associated-with-lymphocytes-and-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/clinically-severe-systemic-sclerosis-skin-harbors-inflammatory-fibroblasts-associated-with-lymphocytes-and-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells/