Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: COVID-19 has increased the mortality rates among rheumatic patients, mainly those immunocompromised or with underlying comorbidities. During the COVID-19 vaccine development, patients on immunomodulatory drugs such as rituximab (RTX) were excluded from the trials due to their “high risk” categorization.
Aim: Assess the seroconversion rate of RTX-treated rheumatic patients on the COVID-19 vaccine.
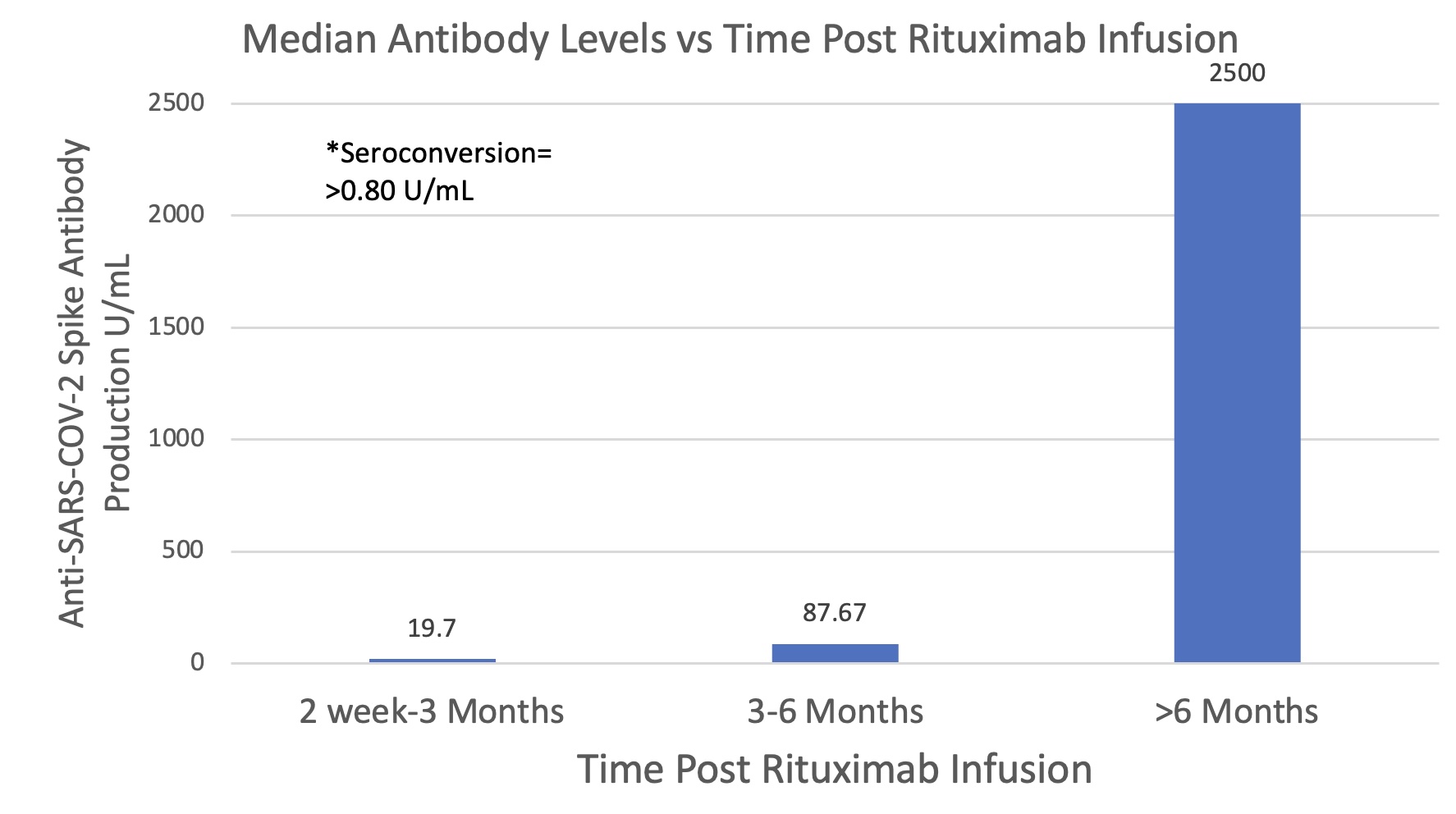
Methods: An observational cohort study on adult patients with various established inflammatory rheumatic diseases at UL Hospitals Group, Limerick receiving ≥2 COVID-19 vaccination and on scheduled RTX infusion (received ≥1 dose). Patients were stratified based on time post-immunization (< 1 month, 1-3 months, 3-6 months, and >6 months post-vaccination). Samples (taken ≥14 days after the latest vaccination) were analyzed using the Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoassay for in vitro qualitative detection of IgG antibodies to SARS-COV-2, and screened for quantitative detection of anti-SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid antigen (for previous COVID-19 infection) and anti-SARS-COV-2 spike protein (for immune response to the vaccine). The control group included patients on anti-TNF and tocilizumab (TOC). Seroconversion in response to the SARs-COV-2 is determined at >0.80 U/mL based on the manufacturer’s guidelines.
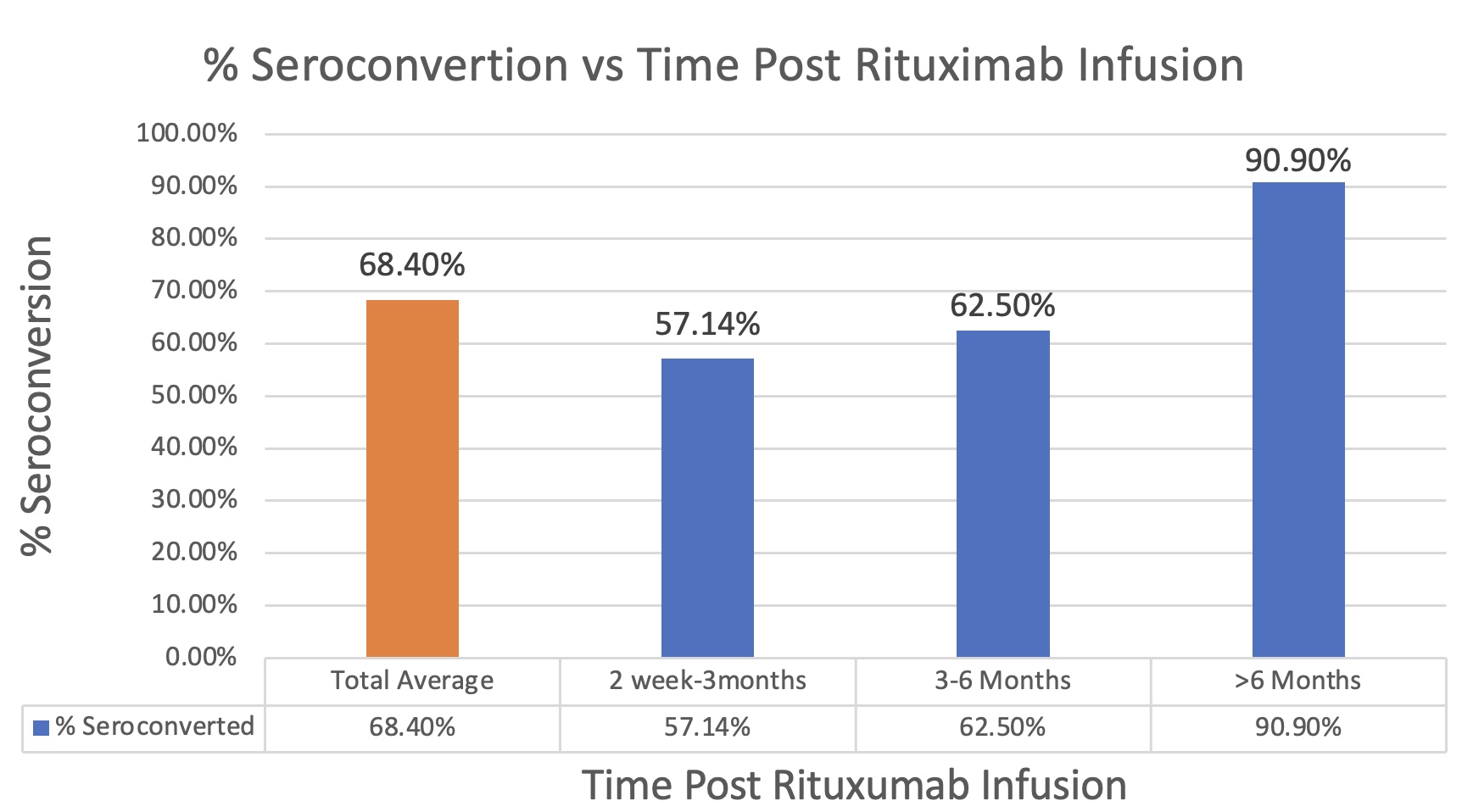
Results: 49 patients were included (38 on RTX, 8 anti-TNFs, 3 TOC). Seroconversion rates were higher in the 1-3-month (75%) and 3-6-month (77%) RTX timelines; however, rates at 1 and 6 months were equal (60%) indicating antibody waning over this time period may not be significant in affecting seroconversion rates (levels remained ≥0.80 U/mL threshold). Whilst average seroconversion for the entire RTX cohort is 68.4%, the highest rates were seen in patients with a 6-month gap (90.9%). The lowest rates were seen in patients receiving immunization in the 2 week-3 months following RTX (57.14%), while the 3-6 months group showed slight improvement (62.5%). The patient population receiving anti-TNFs and TOC showed a 100% seroconversion rate.
Conclusion: Our data shows that a third of RTX patients treated didn’t achieve seroconversion following immunization against SARS-COV-2 while the highest rates were seen in patients who had a 6-month gap. This data suggests benefit for delaying RTX infusion greater than the standard 6-month interval in suitable patients, prior to vaccination, to allow patients to reach adequate seroconversion against COVID-19 before reinitiating treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wilson R, Awan J, Brady M, Hunt C, Adeeb F, fraser a. Seroconversion Rates in Rituximab-Treated Rheumatic Patients Receiving COVID-19 Vaccination [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroconversion-rates-in-rituximab-treated-rheumatic-patients-receiving-covid-19-vaccination/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/seroconversion-rates-in-rituximab-treated-rheumatic-patients-receiving-covid-19-vaccination/