Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0252–0282) Miscellaneous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Diseases Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hypocomplementemia (HC) is often observed in IgG4-related diseases (IgG4-RD), but there are also IgG4-RD without HC. This study aimed to clarify the difference of characteristics of IgG4-RD in the presence or absence of HC.
Methods: The data of patients diagnosed with IgG4-RD at our institution were retrospectively analyzed, and these patients were divided into two groups: the HC group, which comprised patients with decreased C3 or C4 level (hypocomplementemia), and nonHC group, which comprised patients with normal C3 and C4 levels. The characteristic, affected organs, blood and imaging findings, and treatment course of the patients in both groups were compared. As additional evaluation of IgG4RD feature using imaging modality, fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET/CT was conducted. The maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion glycation (TLG), which indicate the level of metabolic activity of the tumor, were measured to evaluate disease activity using FDG-PET/CT.
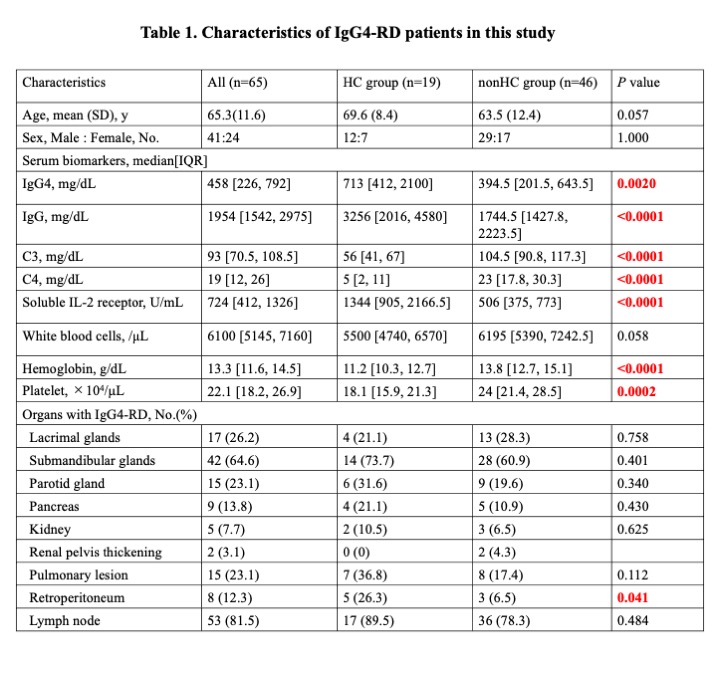
Results: The study enrolled 65 patients. Of these patients, 19 and 46 were included in the HC and nonHC groups, respectively. Table 1 shows the characteristics of patients with IgG4-RD in this study. The HC group had lower hemoglobin levels and platelet counts and higher serum IgG4, IgG, and sIL-2R levels compared than the nonHC group. Moreover, the number of patients requiring treatment was higher in the HC group (17 patients, 89%) than in the nonHC group (28 patients, 61%). Recurrence of IgG4-RD was observed in 3 of the 17 patients in the HC group and 11 of the 28 patients in the nonHC group. Two and three patients in the HC and nonHC groups, respectively, died during the course of this study.
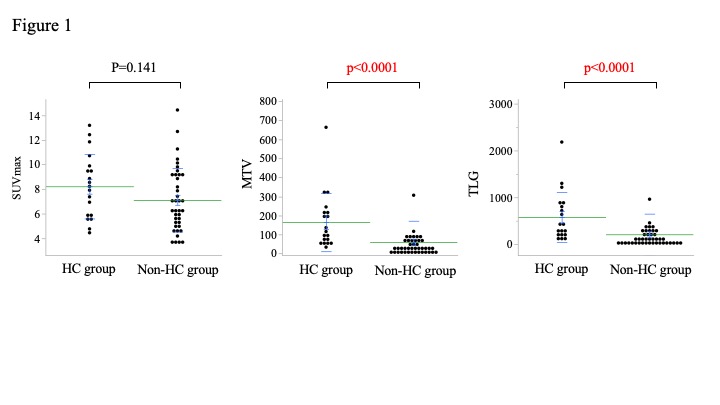
Two of the three index that may reflect IgG4RD activity by analyzed by FDG-PET/CT were significantly higher in the HC group.
Although there was no significant difference in SUVmax between the two groups, the MTV and TLG were significantly higher in the HC group than those of nonHC group (Figure 1).
Conclusion: The HC group had peripheral blood cytopenia and higher IgG4 level than the nonHC group. Moreover, more patients in the HC group required therapeutic intervention and had a poor prognosis. In assessing the activity of patients with IgG4RD using FDG-PET/CT, HC group had higher disease activity compared with nonHC group.
P-values were determined using Mann-Whitney U test or Fisher’s exact test.
Maximum standardized uptake value was not significantly different between the groups; however, metabolic tumor volume and total lesion glycation were significantly higher in the HC group than in the nonHC groups.
The P-value was determined by performing the Mann–Whitney U test.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wakiya R, Ozaki H, Shimada H, Nakashima S, Miyagi T, Ushio Y, Sugihara K, Mizusaki M, Mino R, Chujo K, Kagawa R, Yamaguchi H, Kameda T, Dobashi H. Activity of IgG4-related Disease Differs Depending on the Presence or Absence of Concomitant Hypocomplementemia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/activity-of-igg4-related-disease-differs-depending-on-the-presence-or-absence-of-concomitant-hypocomplementemia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/activity-of-igg4-related-disease-differs-depending-on-the-presence-or-absence-of-concomitant-hypocomplementemia/