Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The degree of protein citrullination and degradation by matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) play a central role in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Autoantibodies are known to target citrullinated proteins such as vimentin. Elevated levels of vimentin MMP-generated fragments are found in blood and studies have shown that blood markers such as VICM are associated with disease activity and response to treatment such anti-GM-CSF. Tocilizumab (TOCI) is a MAb targeting the IL-6 receptor. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between blood levels of MMP-degraded and citrullinated Vimentin, as compared to levels of non-citrullinated vimentin (VIM), and contrast that to the standard anti-CCP biomarker in patients treated with tocilizumab (TOCI).
Methods: VIM, VICM and Anti-CCP were quantified in serum samples from baseline and week 8 of 257 RA patients treated with either TOCI (8 mg/kg), MTX (7.5-20 mg/kg) monotherapy and compared to a reference cohort of 64 healthy donors. Biomarkers were correlated to disease activity measures and the change in levels from baseline to 8 weeks were compared between treatment arms. Predictive response analyses were conducted. Marker data was LN-transformed and corrected for age, race, gender, BMI and disease duration.
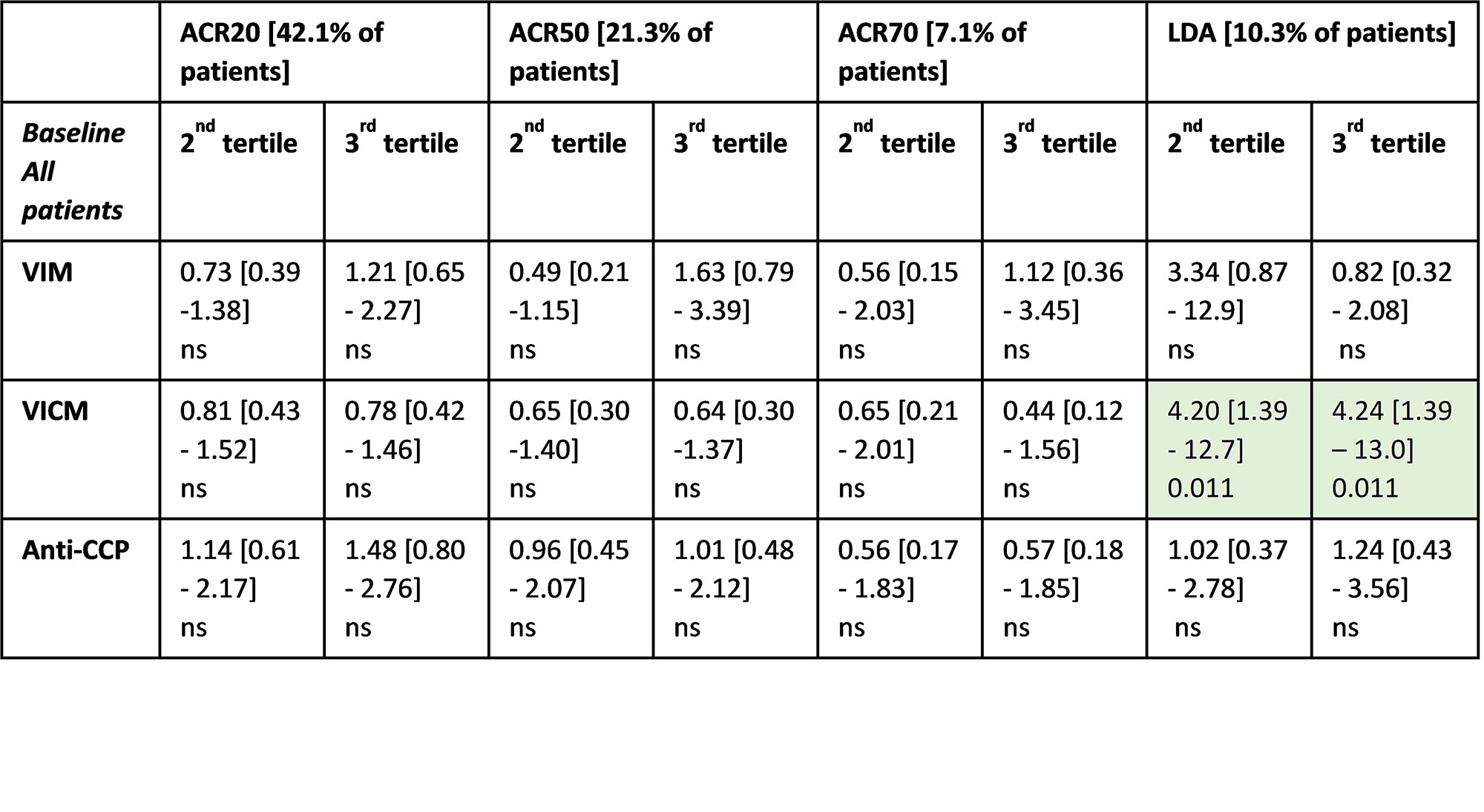
Results: All measured biomarkers were significantly elevated in RA serum compared with the reference cohort: VIM, 2.2 vs 1.0 ng/mL (p< 0.05); VICM, 11.4 vs 0.4 ng/ml (p< 0.0001); Anti-CCP, 165.7 vs 4.0 RU/mL (p< 0.001). VICM but none of the other markers correlated with CRP and ESR. The level of VICM was significantly decreased in response to TOCI (2.9-fold, p< 0.0001) and to MTX (1.5-fold, p< 0.05) compared to placebo. A 1.9-fold difference was observed for VIM between MTX and TOCI (p< 0.0001). There was a 1.8- and 1.6-fold difference between TOCI, and MTX and PBO, respectively. No significant change was observed for anti-CCP. High baseline level of VICM was predictive for low disease activity (LDA) response at week 8 as the only of the three markers (table).
Conclusion: The VICM fragment is a double posttranslational epitope: it is both citrullinated and released from vimentin by the action of MMPs. It can differentiate between RA and healthy donors to the same level as anti-CCP but can also be modulated by TOCI and act as a pharmacodynamic marker, because its release is dependent on MMP activity, which is partly regulated by IL-6.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Drobinski P, Nissen N, Karsdal m, Willumsen N, Bay-Jensen A. In Contrast to Anti-CCP, Then MMP Degraded and Citrullinated Vimentin (VICM) Is Both a Diagnostic and Treatment Response Biomarker [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-contrast-to-anti-ccp-then-mmp-degraded-and-citrullinated-vimentin-vicm-is-both-a-diagnostic-and-treatment-response-biomarker/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-contrast-to-anti-ccp-then-mmp-degraded-and-citrullinated-vimentin-vicm-is-both-a-diagnostic-and-treatment-response-biomarker/