Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) severely impacts patients’ (pts) physical function and health-related quality of life (HRQoL).1
Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A. BKZ reduced disease activity in pts with active non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS; i.e. radiographic axSpA) in the phase 3 studies BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704) and BE MOBILE 2 (NCT03928743), respectively; all primary and ranked secondary endpoints at Week (Wk) 16 were met, including change from baseline (CfB) in physical function (BASFI) and HRQoL (ASQoL and Short-Form 36-Item Health Survey [SF-36] Physical Component Summary [PCS]).2,3 Here, we assess the impact of BKZ on physical function and HRQoL in pts with active nr-axSpA and AS to Wk 24 in both studies.
Methods: BE MOBILE 1 and 2 were conducted in parallel and had similar designs, with a 16-wk double-blind period followed by a 36-wk maintenance period. Pts were randomized to BKZ 160 mg Q4W or placebo (PBO); all pts received BKZ 160 mg Q4W from Wk 16 onward.2,3 We report proportion of pts achieving low BASFI score (≤0/1/2/3/4) and clinically relevant thresholds in HRQoL (ASQoL: ≥4-point reduction from baseline [BL];4 SF-36: ≥5-point increase from BL5) at Wk 16 using non-responder imputation, and CfB in BASFI, ASQoL, and SF-36 to Wk 24 using multiple imputation.
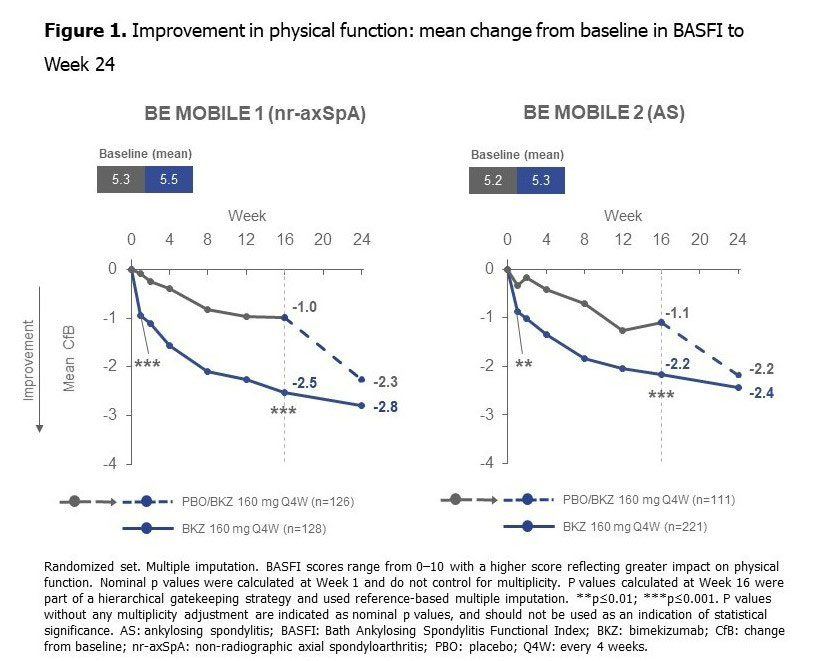
Results: 254 nr-axSpA (BKZ: 128; PBO: 126) and 332 AS pts (BKZ: 221; PBO: 111) were randomized. At BL, mean BASFI, ASQoL, and SF-36 PCS scores indicated impaired physical function and HRQoL (Figure 1, 2). BL mean SF-36 Mental Component Summary scores indicated non-impaired mental function (nr-axSpA: BKZ: 51.3, PBO: 51.9; AS: BKZ: 50.9, PBO: 51.9) which persisted to Wk 24.
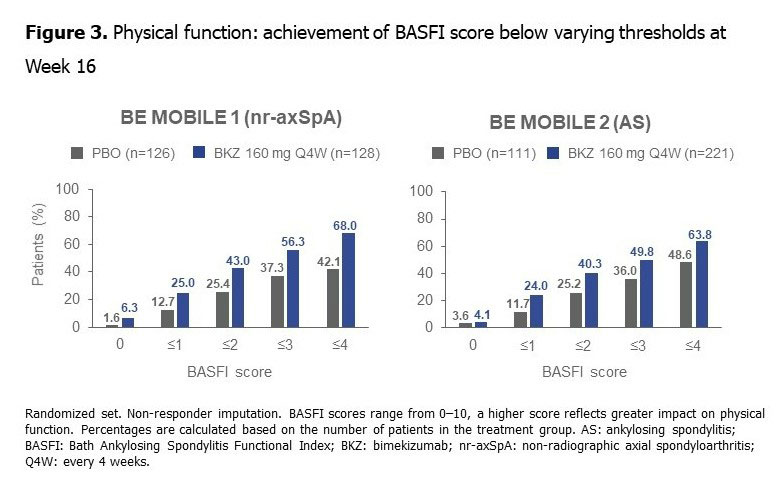
A greater proportion of pts treated with BKZ vs PBO achieved lower BASFI scores at Wk 16, indicating less physical function impairment (Figure 3). Pts treated with BKZ also achieved improvement in mean BASFI scores to Wk 24, with separation from PBO observed by the first post-BL assessment at Wk 1. For pts who switched from PBO to BKZ at Wk 16, Wk 24 responses approached those seen in BKZ-randomized pts (Figure 1).
Similarly, at Wk 16 a higher proportion of pts treated with BKZ vs PBO achieved the thresholds for clinically relevant improvements from BL ASQoL (nr-axSpA: 58.6% vs 33.3%; AS: 57.5% vs 45.0%), and SF-36 PCS (nr-axSpA: 64.8% vs 41.3%; AS: 63.8% vs 49.5%). Pts treated with BKZ also achieved improvements in mean ASQoL and SF-36 PCS scores to Wk 24, with separation from PBO at first post-BL assessment. For pts who switched from PBO to BKZ at Wk 16, Wk 24 responses approached those seen in BKZ-randomized pts (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Treatment with BKZ resulted in meaningful improvements in physical function and HRQoL, with separation from PBO at first post-BL assessment, and a greater proportion of BKZ vs PBO treated pts met clinically relevant thresholds of improvements at Wk 16. Pts with nr-axSpA and AS had consistent responses.
References: 1. Strand V. J Clin Rheumatol 2017;23(7):383–91; 2. Deodhar A. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:772–3; 3. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:12–3 4. Hoepken B. Qual Life Res. 2021;30(3):945–54; 5. Reveille JD. Value Health 2020;23(10):1281–5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dubreuil M, Gaffney K, Gensler L, Kay J, Navarro-Compán V, de la Loge C, Ellis A, Fleurinck C, Oortgiesen M, Taieb V, Deodhar A. Bimekizumab Improves Physical Function and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-improves-physical-function-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-improves-physical-function-and-health-related-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/