Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Latinx patients, a heterogenous population with a range of experiences including migration, language, and race, experience a disproportionate burden of adverse outcomes from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and poorer quality of care compared to non-Latinx patients. Disparities could be minimized through improved patient-clinician communication and better coordination of care. We conducted patient focus groups and physician interviews to better understand barriers to communication with Latinx individuals with SLE and RA, and to identify potential opportunities for intervention.
Methods: We developed separate moderator guides a priori for patient focus groups and provider semi-structured interviews to uncover barriers to patient-provider communication, care navigation, and receipt of high-quality care. At an academic medical center, we invited racially diverse Spanish-speaking Latinx patients ≥18 years, receiving rheumatology care for SLE or RA to participate in a 60-minute focus group. We also recruited physicians who routinely care for Latinx patients with SLE and/or RA to participate in 30-minute semi-structured interviews. Focus groups and interviews were transcribed verbatim, entered into DedooseTM and analyzed thematically by two reviewers (MCB, CHF) who then confirmed consensus. Focus group thematic analyses, which were conducted in Spanish, was done by native Spanish speakers (MCB, PW).
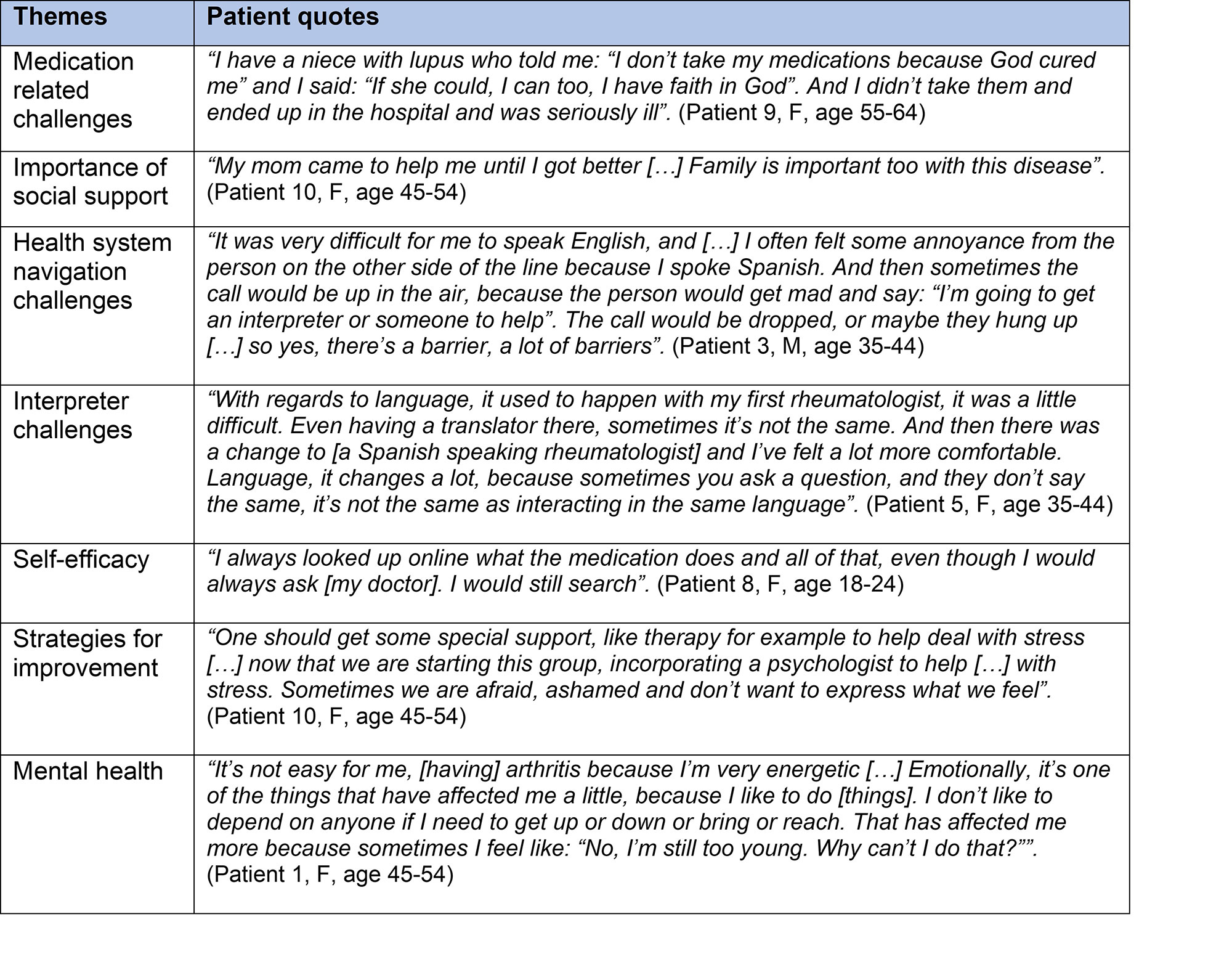
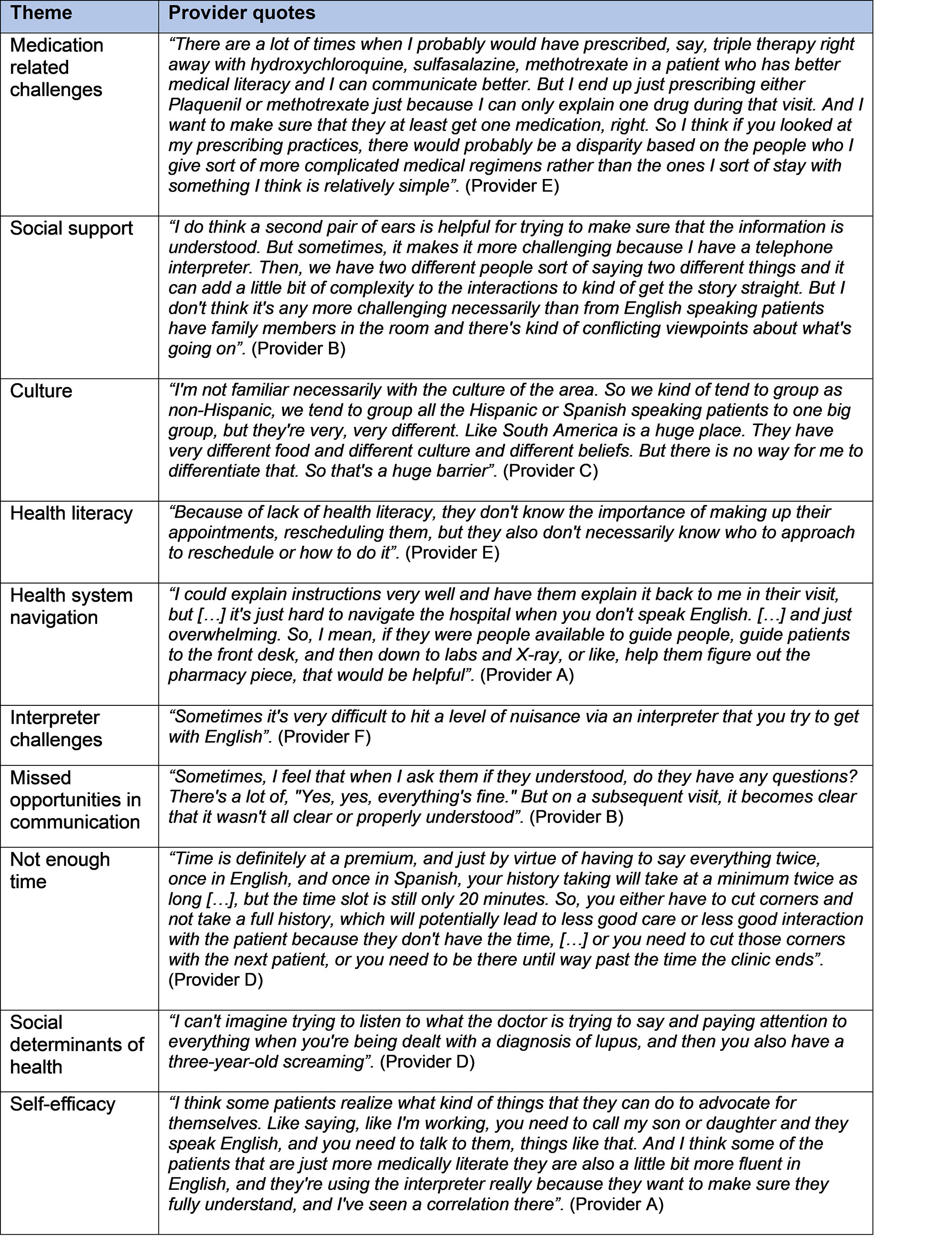
Results: Ten patients with SLE and RA participated in one of two focus groups. Patients all self-identified as Hispanic/Latinx, were 80% female, and aged 18-74 years. Six physicians participated in semi-structured interviews. Half of the providers self-identified as female and none identified as Hispanic/Latinx or spoke Spanish. Qualitative analyses revealed the following shared themes for patients and providers: health system navigation challenges, issues related to interpreter services, mental health challenges, medication-related challenges, and the importance of social support and self-efficacy in patient care. Patients also cited challenges related to diagnostic delays and provider trust (Table 1). Providers’ described challenges related to social determinants of health and repeatedly noted that additional support staff, interpreters, and Spanish language resources would be beneficial (Table 2). Patients also expressed a desire to connect with other patients like themselves, and a need for better mental health support.
Conclusion: Latinx patients with SLE and RA and interdisciplinary providers caring for them highlighted existing barriers to care, such as health system navigation, interpreter services, mental health, and medication related challenges. Patients emphasized the importance of trust and the need for more support. Insight obtained will allow us to develop a training program for patients to improve self-efficacy and to help overcome some of barriers experienced. Additional health system-based resources for this patient population and the providers caring for them are necessary to reduce disparities in rheumatology care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crespo Bosque M, Weilg Espejo P, Feldman C. Patient and Provider Perspectives on Barriers to Communication and Care of Latinx Patients with Lupus and Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-and-provider-perspectives-on-barriers-to-communication-and-care-of-latinx-patients-with-lupus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-and-provider-perspectives-on-barriers-to-communication-and-care-of-latinx-patients-with-lupus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis/