Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) contributes to excess morbidity and mortality in RA patients compared with the general population. In Australia, there is a paucity of published literature on the mortality and morbidity rates in RA patients, despite the significant morbidity and mortality burden on health care costs due to RA. Linked data is the preferred method to estimate morbidity and mortality outcomes as they provide the best case ascertainment. The aim of this study was to describe temporal changes in mortality rates for patients with Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in relation to comorbidity accrual from 1980-2015 in Western Australia (WA).
Methods: Using population-level linked data from WA health administrative datasets (hospital morbidity, emergency department and death data), we followed 17,125 RA patients (ICD-10-AM M05.00–M06.99, ICD-9-CM 714) from 1980- 2015. Comorbidity was ascertained using the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI). Mortality rate ratios (MRR) were calculated per decade between the RA cohort and the WA general population by direct age standardisation method, while temporal trends of comorbidities and in-hospital mortality were estimated per 1000 hospital separations in three consecutive decades.
Results: During 356,069 patient-years, a total of 8955 (52%) deaths occurred in the RA cohort. The leading causes of deaths were cardiovascular diseases 2386 (26.6%), cancer 1511 (16.8%), rheumatic diseases 519 (5.8%), chronic pulmonary disease 491 (5.5%), dementia 269 (3.0%) and diabetes 235 (2.6%). The highest prevalence of comorbidity (688.6 per 1000 separations) was in the period 1991-2000 following a 1.3% average annual increase since 1980. In-hospital mortality rate was also highest (26.7 deaths per 1000 separations) in the same period. After 2001, both RA comorbidity and mortality rates decreased annually by -0.5% and -4.8%, respectively, with annual changes of -4.4% to -2% and from 2011- 2015, respectively. The overall mortality rate in RA patients after age adjustment was 2.5-times (95%CI: 2.52-2.65) higher than the general population between 1980- 2015 and 1.5-times (95%CI: 1.39-1.81) for the period 2011-2015.
Conclusion: The annual comorbidity prevalence and mortality rates in WA have decreased significantly since 2001, reflecting improvements in the management of RA and comorbidity. Nonetheless, the mortality rate in RA patients in WA remains 1.5-times higher than their community counterparts suggesting that there is room to achieve further improvements.
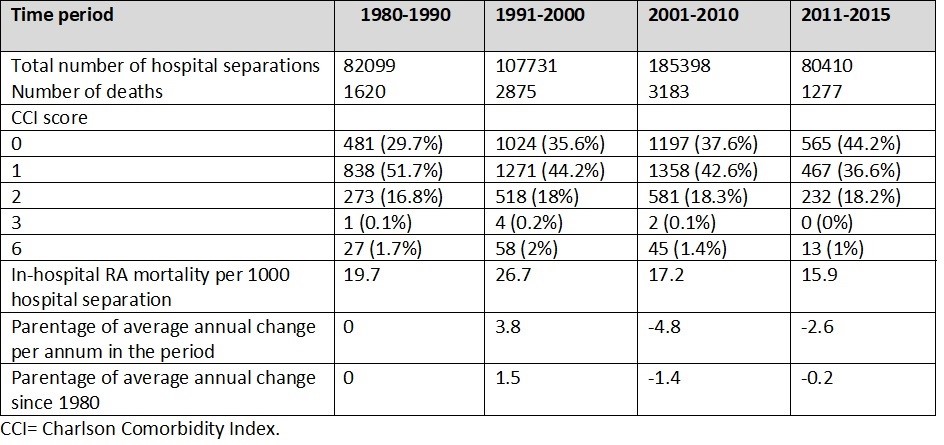 Table 1: Mortality rates observed among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, based on Charlson Comorbidity Index, per 1000 hospital separations, Western Australia hospitals (1980_2015).
Table 1: Mortality rates observed among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, based on Charlson Comorbidity Index, per 1000 hospital separations, Western Australia hospitals (1980_2015).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Almutairi K, Nossent J, Preen D, Keen H, Inderjeeth C. The Influence of Comorbidity on Mortality in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis 1980-2015: A Longitudinal Population-based Study in Western Australia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-influence-of-comorbidity-on-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-1980-2015-a-longitudinal-population-based-study-in-western-australia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-influence-of-comorbidity-on-mortality-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-1980-2015-a-longitudinal-population-based-study-in-western-australia/
