Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: PROs, Biomarkers, & Systemic Inflammation (1223–1256)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The latest breakthroughs in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) highlighted the activation of B cells as a trigger of the joint flare initiation and therefore, implicated a central role for B cells in RA pathogenesis. B cell activating factor (BAFF) is essential for B cell activation, differentiation and survival. The main objective of this study was to investigate the role of BAFF in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with TNF inhibitors (TNFi) and its association with treatment response.
Methods: This was a prospective study including 158 patients with RA initiated at the first TNFi and followed-up for 6 months (m). Disease activity was assessed using the Disease Activity Score 28 (DAS28) at baseline and 6m of treatment. Clinical response at 6m of treatment was defined according to the EULAR criteria for good responders. BAFF concentration was measured in serum samples collected at baseline and 6m. Associations between the EULAR response at 6m and clinical/serological variables were evaluated using univariable and multivariable logistic regression models. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to determine the optimal threshold of serum BAFF concentration portending EULAR response at 6m of TNFi treatment, determined as the highest Youden index.
Results: After 6m of TNFi treatment, 38/158 (24%) of patients attained good EULAR response (GR). These patients had lower body mass index (BMI) (p=0.02), lower baseline DAS28 (p=0.02) and lower serum BAFF concentration at baseline and at 6m compared with patients who did not attain GR. To further investigate the role of BAFF, the cohort was stratified by anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) seropositivity. 134 (85%) patients were ACPA positive and 24 (15%) were seronegative. After 6m of TNFi treatment, seropositive patients who attained GR had lower serum BAFF concentration compared with patients who did not attain GR (median [IQR]: 793 [712-956] pg/mL vs. 955 [808-1176] pg/mL; p=0.006) (Fig. 1). However, there were no differences in ACPA negative patients (Table 1). Therefore, the optimal threshold value for serum BAFF concentration associated with GR at 6m of TNFi treatment was evaluated in seropositive patients. Serum BAFF< 968 pg/mL at 6m represented the concentration likely to best discriminate between GR and non-GR at 6m of TNFi treatment (AUC: 0.67; 95% CI: 0.56-0.78; p=0.009; sensitivity: 50%, specificity: 81%; PPV: 89%, NPV: 35%), yielding a positive likelihood ratio of 2.7 (Fig. 2). Then, a logistic regression analysis adjusted by patient characteristics with p-value≤0.1 in univariable analysis (disease duration, BMI and baseline DAS28) was performed. We found that a serum BAFF< 968 pg/mL at 6m was significantly and independently associated with GR attainment in seropositive patients (OR: 5.28; 95% CI: 1.72-16.17; p=0.004).
Conclusion: Our results show that serum BAFF concentrations reflect clinical response to TNFi after 6m of treament, mainly in ACPA positive patients. These results suggest that BAFF may be considered a biomarker of clinical response to TNFi in patients with RA.
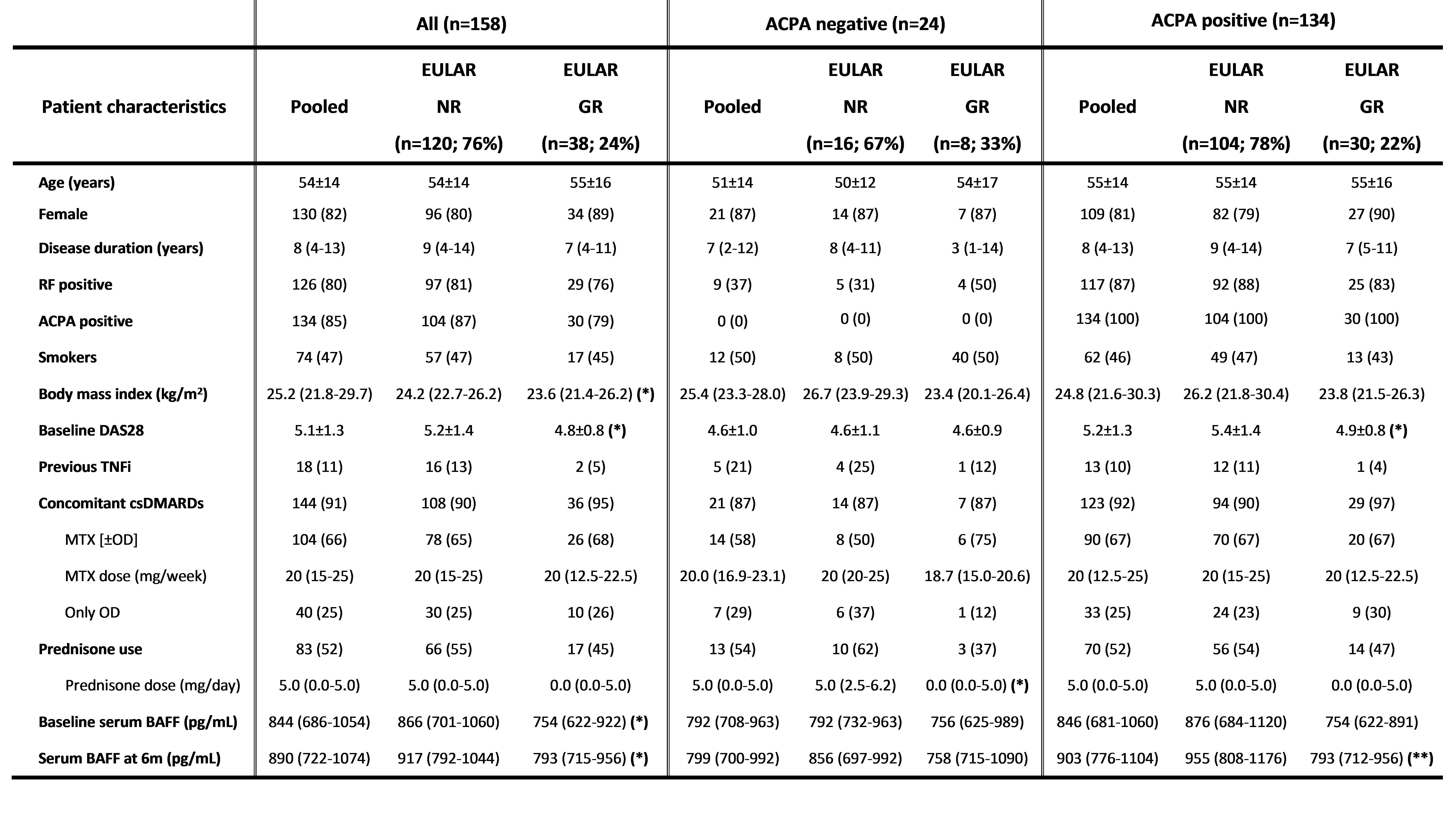 Table 1: Patient characteristics. The table shows mean±SD, median (IQR) or absolute number (percentage) for patients included (n=158). The results are stratified by ACPA positivity. Statistically significant differences between good responders and non-responders are indicated as p < 0.05 (*) or p < 0.01 (**). ACPA, anti-citrullinated peptide antibody; BAFF, B cell activating factor; csDMARDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; DAS28, disease activity score_28; MTX, methotrexate; OD, other csDMARDs; RF, rheumatoid factor; TNFi, tumour necrosis factor inhibitor.
Table 1: Patient characteristics. The table shows mean±SD, median (IQR) or absolute number (percentage) for patients included (n=158). The results are stratified by ACPA positivity. Statistically significant differences between good responders and non-responders are indicated as p < 0.05 (*) or p < 0.01 (**). ACPA, anti-citrullinated peptide antibody; BAFF, B cell activating factor; csDMARDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; DAS28, disease activity score_28; MTX, methotrexate; OD, other csDMARDs; RF, rheumatoid factor; TNFi, tumour necrosis factor inhibitor.
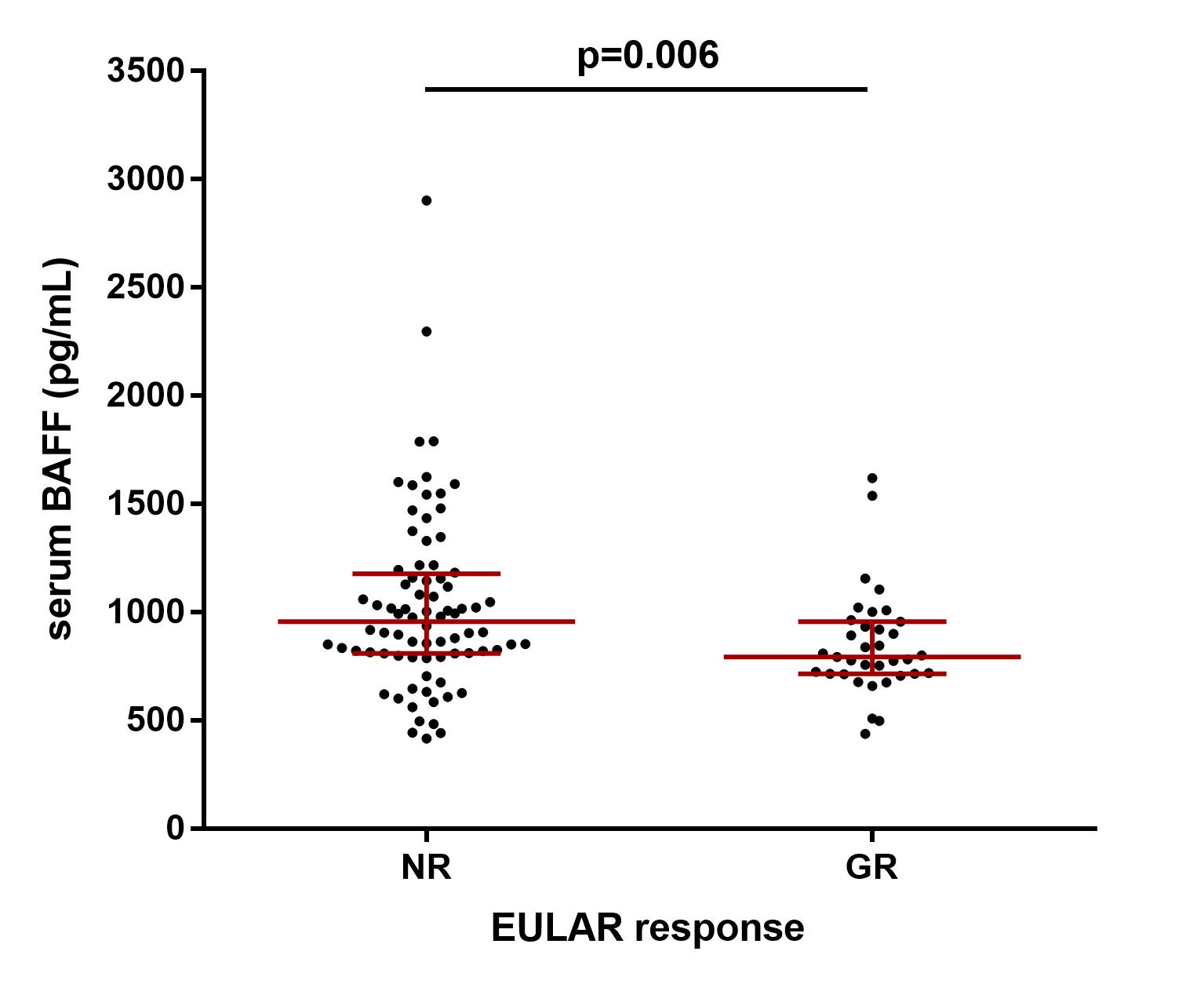 Figure 1. Serum BAFF concentration (median [IQR]) stratified by EULAR response at 6 months of TNFi treatment in seropositive patients.
Figure 1. Serum BAFF concentration (median [IQR]) stratified by EULAR response at 6 months of TNFi treatment in seropositive patients.
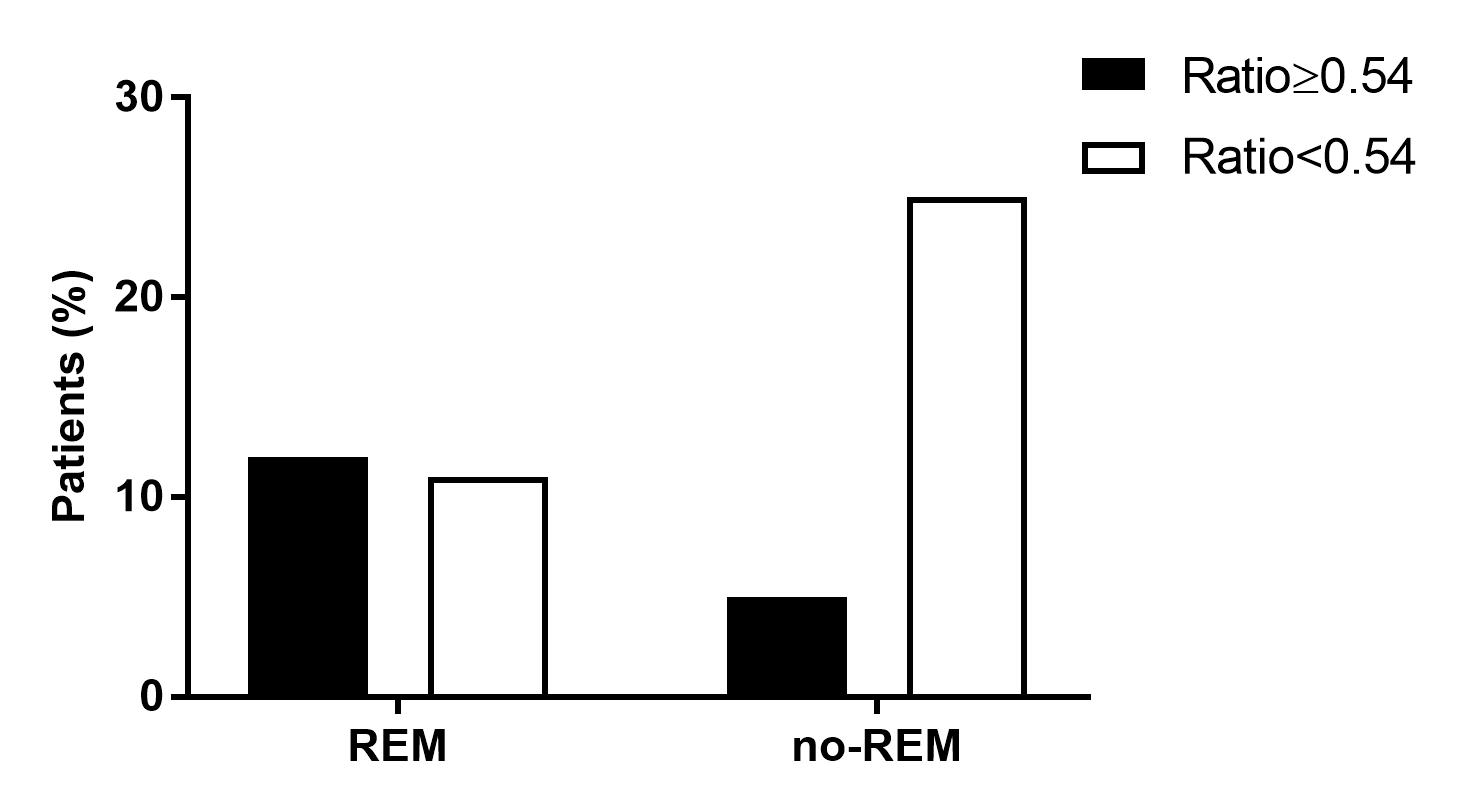 Figure 2. EULAR response at 6 months of TNFi according the serum BAFF concentration threshold.
Figure 2. EULAR response at 6 months of TNFi according the serum BAFF concentration threshold.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hernandez-Breijo B, Parodis I, Plasencia-Rodríguez C, Díaz-Almirón M, Martínez-Feito A, Novella-Navarro M, Pascual-Salcedo D, Balsa A. Serum B Cell Activating Factor Reflects Good EULAR Response to TNF Inhibition in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-b-cell-activating-factor-reflects-good-eular-response-to-tnf-inhibition-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-b-cell-activating-factor-reflects-good-eular-response-to-tnf-inhibition-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
