Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: It can be challenging to determine whether rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients who require arthroplasty have ongoing inflammation, in addition to damage in the affected joint on clinical exam. C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), neutrophil-lymphocyte (NLR) and platelet-lymphocyte ratios (PLR) are all blood biomarkers that have been reported to associate with disease activity.
Methods: 239 patients meeting ACR/EULAR 1987 and/or 2010 RA criteria and 162 OA patients were recruited prior to elective total hip, knee, elbow, or shoulder arthroplasty. Disease characteristics and blood samples were collected pre-operatively. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains of the synovium were prepared and scored by a pathologist. Mann-Whitney and Kruskal Wallis tests were used to compare biomarkers among groups. Stata’s backward stepwise regression and multivariable ordered logistic regression was performed to predict synovial lymphocytic inflammation on (1) 239 RA patients, (2) 146 RA patients not on GCs, and (3) 52 RA patients with low disease activity (DAS28-ESR< 3.2).
Results: RA patients (median [IQR] = 159.6 [103.1]) had higher PLR than OA patients (median [IQR] = 138.9[76.5]) (p< 0.001). RA patients (median [IQR] = 2.73 [2.34]) also had a slightly higher NLR compared to OA patients (median [IQR] = 2.45[1.90]) (p=0.052). Additionally, RA patients on glucocorticoids (GCs) had higher NLR (p< 0.001) and PLR (p=0.04) than those not on GCs. In all models predicting SLI in RA, PLR was significantly associated with SLI but not DAS28-ESR or CDAI (Table 1 and Table 2). Patients with DAS28-ESR< 3.2 and high SLI had higher PLR (p=0.01) and CRP (p=0.02) (Figure 1) than those with low SLI. PLR was not associated with SLI in OA patients.
Conclusion: Platelet lymphocyte ratio is associated with synovial lymphocytic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis patients of all disease activity levels. This suggests that inexpensive, routinely performed blood tests may be a useful blood biomarker of RA synovial inflammation, including subclinical synovitis.
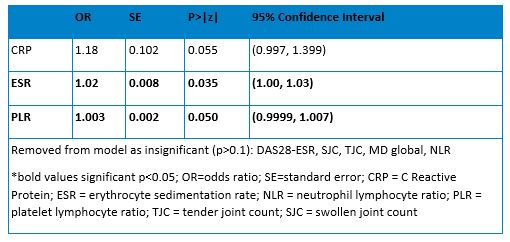 Table 1: Multivariate ordered logistic regression predicting SLI in all RA patients
Table 1: Multivariate ordered logistic regression predicting SLI in all RA patients
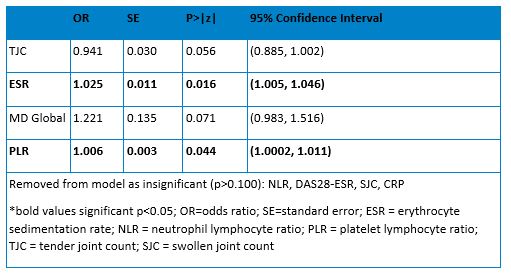 Table 1: Multivariate ordered logistic regression predicting SLI in all RA patients
Table 1: Multivariate ordered logistic regression predicting SLI in all RA patients
 Figure 1: Blood biomarkers by SLI in RA patients with DAS < 3.2 not on GCs
Figure 1: Blood biomarkers by SLI in RA patients with DAS < 3.2 not on GCs
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pearce-Fisher D, Orange D, Mehta B, Jannat-Khah D, Goodman S. Association of Neutrophil Lymphocyte and Platelet Lymphocyte Ratios with Joint Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-neutrophil-lymphocyte-and-platelet-lymphocyte-ratios-with-joint-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-neutrophil-lymphocyte-and-platelet-lymphocyte-ratios-with-joint-inflammation-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
