Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster (0623–0659)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Measuring disease activity in patients with inflammatory arthritis is important for providing optimal treat-to-target care. The COVID-19 pandemic has widened disparities in care among racial minorities. The purpose of this study is to understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the resultant transition to telehealth on disease activity measurement to assess disparities in care.
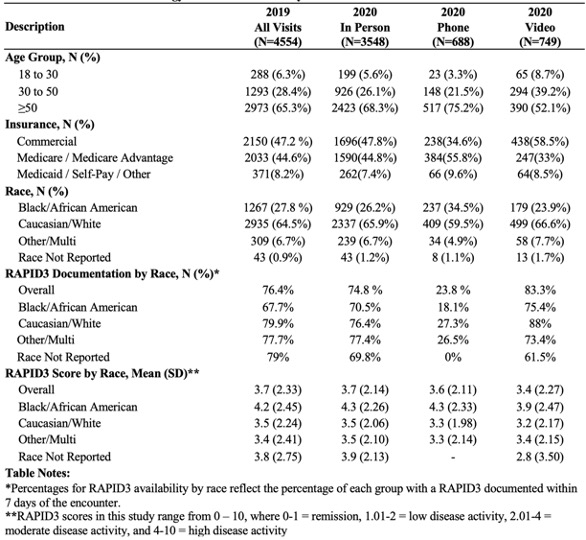
Methods: This study assessed outpatient encounters at a single academic rheumatology practice between July 1st and October 31st in 2019 and 2020. Patients were included if they had a visit diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis (RA, JIA, PsA, AS, ReA, IBD-associated arthropathy) or SLE. All visits in 2019 were done in-person. Visits in 2020 were stratified by encounter type (in-person, phone telehealth, and video telehealth). Patient reported disease activity was measured by RAPID3 (scale 0-10) either at clinic intake (in-person) or through the patient online EMR portal (phone, video, in-person). Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the proportion of visits with a RAPID3 documented and average RAPID3 scores, stratified by race and visit modality. Modified Poisson regression was used to assess the association between RAPID3 documentation and year seen, age, race, insurance, and encounter type in unadjusted and adjusted models. We also calculated unadjusted year-over-year changes in RAPID3 documentation from 2019 to 2020 for each of these groups.
Results: There were 4554 visits during the study period in 2019 (all in-person) and 4985 in 2020 (3548 in-person, 699 phone, and 749 video; Table 1). In 2020, the proportion of visits completed by telehealth (phone or video) was similar among Black (31%) and white (28%) patients. However, telehealth encounters among Black patients were mostly by phone (60% of telehealth visits) whereas phone visits were the minority among white patients (45% of telehealth visits). In both 2019 and 2020 the RAPID3 was less likely to be completed by Black patients, though their RAPID3 score was higher, suggesting more rheumatic symptoms.
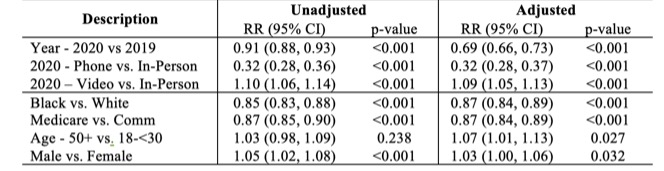
Encounters in 2020 were less likely to have a RAPID3 documented versus 2019 (adjusted risk ratio, aRR 0.69, p< 0.001, Table 2), driven by the absence of RAPID3 documentation among phone visits (phone vs. in-person: aRR 0.32, p< 0.001). The RAPID3 score is collected by electronic survey or during in-person check-in and our clinic did not have a systemic method to collect RAPID3 scores for phone visit patients. Over the entire study period, Black patients were significantly less likely to have a RAPID3 documented than White patients (aRR 0.87, p< 0.001, Table 2).
Conclusion: As telehealth use accelerated in 2020 in this academic clinic, the collection of patient-reported measure of disease activity remained stable for in-person and video visits, but decreased for patient visits completed by phone. The high use of phone visits among Black patient exacerbated the pre-existing disparity in RAPID3 collection between Black and White patients. These data necessitate a change in RAPID3 collection procedures to reduce systematic disparities in care for patients with inflammatory arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Apte P, Overton R, Henao R, Economou-Zavlanos N, Doss J, Clowse M, Leverenz D. Impact of COVID-19 and Telehealth on RAPID3 Screening in an Academic Rheumatology Practice: Identifying Disparities in Care [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-covid-19-and-telehealth-on-rapid3-screening-in-an-academic-rheumatology-practice-identifying-disparities-in-care/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/impact-of-covid-19-and-telehealth-on-rapid3-screening-in-an-academic-rheumatology-practice-identifying-disparities-in-care/