Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Dermatomyositis (DM) patients report poor quality of life due to disease activity and persistent itch. Lenabasum is an oral non-immunosuppressive, non-psychoactive cannabinoid type 2 receptor (CB2R) reverse agonist being investigated for use in DM. Our previous studies showed increased IFNγ in DM compared to healthy controls (HC) and a decrease in IFNγ as a result of Lenabasum use. Literature also suggests upregulation of CB2R in the presence of IFNγ. The purpose of our study is to investigate the distribution of CB2R among immune cells in DM blood/skin and the in vitro effects of Lenabasum on these immune cells.
Methods: Image mass cytometry (IMC) was used on 5 HC and 10 DM patients; biopsies were stained with 37 cell markers and 1mmx2mm regions were ablated using the Hyperion Imaging System. Cells were segmented using a nuclear app-based algorithm in Visiopharm. Per cell mean pixel intensity analysis was done with histoCAT. The Phenograph algorithm was used to cluster cells based on expression of cell markers. FC was used on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from 6 HC and 7 DM patients and on eluted skin cells from 9 DM biopsies. Cells (1×106/mL) were stimulated with PMA/Ionomycin/Brefeldin A or Resiquimod/Brefeldin A if they were being stained for T cells or myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC), respectively. For in vitro experiments, samples were treated with Lenabasum (0, 10, or 20μM) for 1 hour before stimulation. Samples were acquired on a BD FACS CANTO and analyzed with FlowJo.
Results: We found that CB2R expression is higher in DM lesional skin compared to HC skin (p< 0.001). CB2R expression is upregulated on pDCs (p< 0.001), mDCs (p< 0.05) and CD4 T cells (p< 0.001) in DM skin compared to HC skin. When evaluating CB2R distribution among lymphocytes, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, NK cells, and endothelial cells, pDCs were found to be major expressors followed by mDCs. FC results from eluted skin cells corroborated these findings, showing a greater percentage of pDCs (48.0% ± 21.4 ) expressing CB2R compared to mDCs (36.4% ± 10.9) and CD4 T cells (26.7% ± 6.9). FC results revealed lower expression of CB2R on DM PBMCs (1.8% ± 0.3) than in cells eluted from DM skin (37.0% ± 7.8) (p< 0.0001). There was no significant difference in CB2R expression in PBMCs between HC and DM CD4 T cells. No difference was noted between HC and DM CD8 T cells as well. Significantly greater CB2R expression was noted in PBMC mDCs (p=0.0167) and pDCs (p=0.0167) in DM compared to HC, but CB2R expression on mDCs and pDCs in the periphery was about 12-fold and 18-fold lower than that of skin cells, respectively. Preliminary in vitro experiments examined Lenabasum’s effects on T cells in the blood. A significant decrease in IFNγ production by lenabasum-treated DM CD8 T cells compared to lenabasum-untreated DM CD8 T cells was noted (p=0.0207). No significant decrease in IFNγ production was observed in DM CD4 T cells or HC CD4 or HC CD8 T cells.
Conclusion: We found that CB2R expression differs between the skin and blood of DM patients, with higher expression occurring in skin. pDCs were found to be major expressors of CB2R in DM skin through IMC and FC, suggesting that these cells may be most affected by Lenabasum in DM.
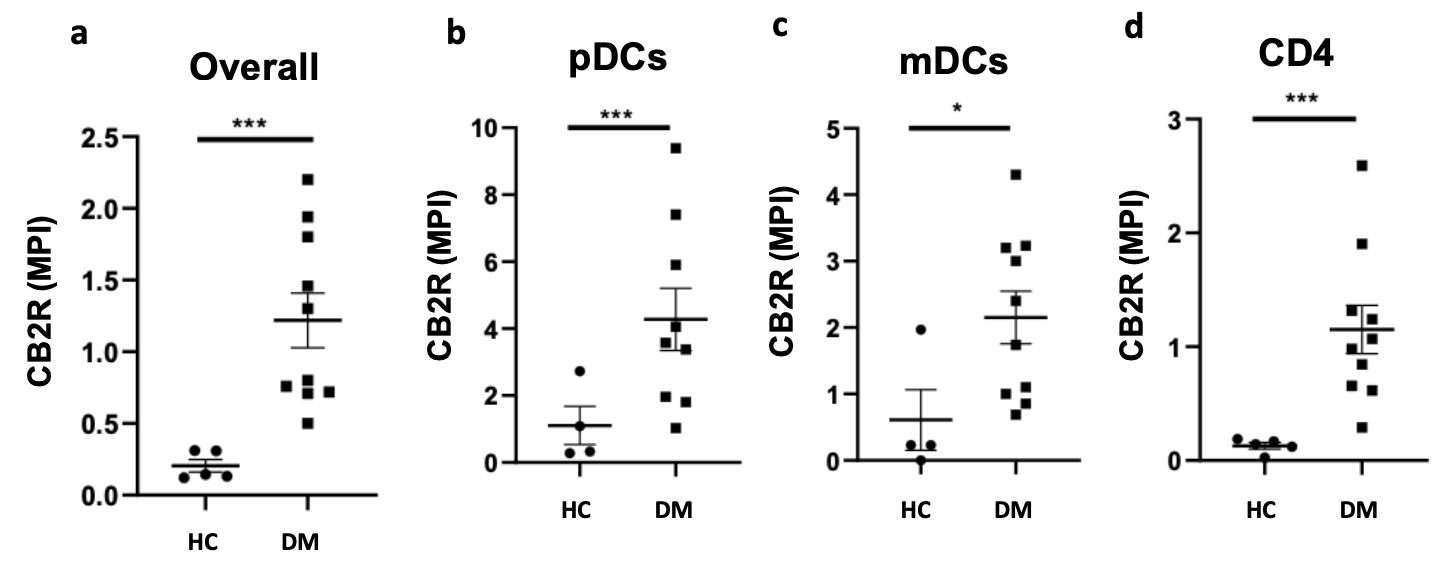 (a) Image mass cytometry findings show that CB2R is significantly upregulated in lesional DM skin compared to HC skin. Mean pixel intensity of CB2R expression is highest on (b) pDCs. CB2R expression in lesional DM skin when compared to HC skin is greater on (b) pDCs, (c) mDCs, and (d) CD4 T cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001
(a) Image mass cytometry findings show that CB2R is significantly upregulated in lesional DM skin compared to HC skin. Mean pixel intensity of CB2R expression is highest on (b) pDCs. CB2R expression in lesional DM skin when compared to HC skin is greater on (b) pDCs, (c) mDCs, and (d) CD4 T cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001
 (a) Flow cytometry results from eluted DM skin cells show highest CB2R expression on pDCs (48.0% ± 21.4), followed by mDCs (36.4% ± 10.9) and CD4 T cells (26.7% ± 6.9). Skin CD8 T cells could not be analyzed because the population was too small. (b) Flow cytometry on HC and DM PBMCs shows significantly higher expression of CB2R in mDCs (p=0.0167) and pDCs (p=0.0167) in DM compared to HC. No significant difference in CB2R expression was noted in CD4 and CD8 T cells from PBMCs (b). Overall, CB2R expression is higher in eluted skin cells compared to PBMCs.
(a) Flow cytometry results from eluted DM skin cells show highest CB2R expression on pDCs (48.0% ± 21.4), followed by mDCs (36.4% ± 10.9) and CD4 T cells (26.7% ± 6.9). Skin CD8 T cells could not be analyzed because the population was too small. (b) Flow cytometry on HC and DM PBMCs shows significantly higher expression of CB2R in mDCs (p=0.0167) and pDCs (p=0.0167) in DM compared to HC. No significant difference in CB2R expression was noted in CD4 and CD8 T cells from PBMCs (b). Overall, CB2R expression is higher in eluted skin cells compared to PBMCs.
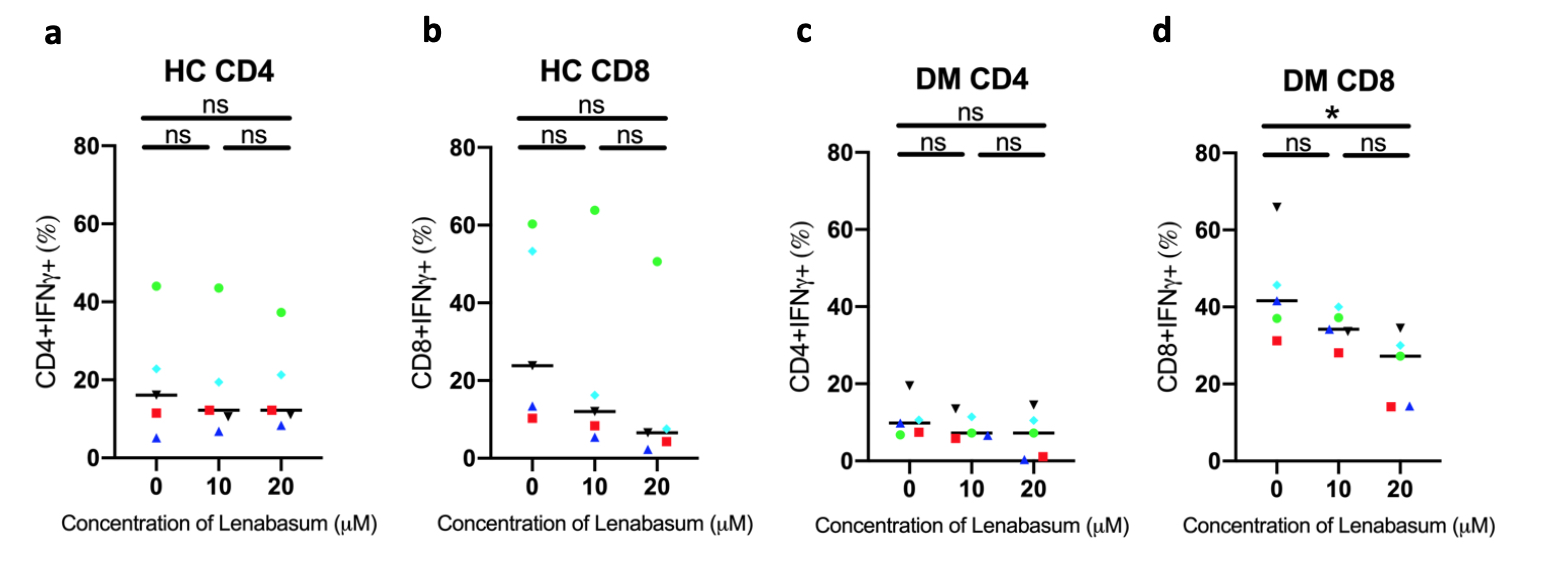 In vitro experiments in stimulated PBMCs treated with Lenabasum show no significant decreases in IFNg production in (a) HC CD4 T cells, (b) HC CD8 T cells, and (c) DM CD4 T cells. There was a significant decrease in IFNg production in (d) DM CD8 T cells treated with 20uM compared to 0uM (p=0.0207).
In vitro experiments in stimulated PBMCs treated with Lenabasum show no significant decreases in IFNg production in (a) HC CD4 T cells, (b) HC CD8 T cells, and (c) DM CD4 T cells. There was a significant decrease in IFNg production in (d) DM CD8 T cells treated with 20uM compared to 0uM (p=0.0207).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maddukuri S, Patel J, Bax C, Wysocka M, Werth V. CB2 Receptor Distribution and Effects of LenabasumTM in Dermatomyositis In Vitro [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cb2-receptor-distribution-and-effects-of-lenabasumtm-in-dermatomyositis-in-vitro/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cb2-receptor-distribution-and-effects-of-lenabasumtm-in-dermatomyositis-in-vitro/
