Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have emerged as a paradigm shift in the treatment of malignancies, but can have significant side effects, termed immune related adverse events (IRAEs), that resemble autoimmune diseases. Inflammatory arthritis (ICI-IA) has significant impact on function, but little is understood about these patterns of arthritis and the specific quality of life impairment.
Methods: We performed a retrospective review of patients at one academic center who experienced ICI-IA and required referral to a rheumatologist in the collaborative Oncology-Rheumatology clinic. All patients were evaluated and completed a Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI). The pattern of ICI-IA was classified by a single rheumatologist based on the arthritis pattern as: inflammatory symmetrical polyarthritis (RA-like, IA), polymyalgia rheumatica-like (PMR), seronegative spondyloarthritis-like (SpA) and exacerbation of osteoarthritis-like (OA). Demographics (gender, age, and race) and malignancy (type, IRAE, type of ICI) data was collected. HAQ-DI, pain and patient global activity (PGA) visual analogue scores were compared based of the type of inflammatory arthritis using average and mean scores.
Results: Our review included 30 patients with ICI-IA: 12 with IA, 4 with PMR, 3 with SpA and 11 with OA. As expected for this age group, a majority, specifically 23, had pre-existent degenerative joint disease (DJD) and 5 had inflammatory arthritis (1 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 2 with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and 2 with gout). Most patients were male (23, 76.6%), and all were Caucasian. The malignancy data and type of ICI are in Table 2. In terms of the patient reported outcomes, the overall HAQ-DI score was 0.57 ± 0.47, indicating that there was little effect of these arthropathies on overall functionality. The pain visual analogue scale had an average score of 41.8 ± 31.4 mm and the Patient Global Assessment had an overall score of 25.6 ± 26.7 mm.
Conclusion: The overall results suggest that the PMR-like pattern of ICI-IA is the most impactful based on the total HAQ scores. In contrast, the pain scores are higher in the SpA group, followed by the IA group. The overall PGA is highest in the IA group, followed by the SpA group. Interestingly, the HAQ scores were lower than the reported average scores of degenerative (0.8) or inflammatory arthritis (1.2). Our sample sizes for the subgroups are currently too small to allow for further statistical analyses of association or subgroup comparisons. Continued patient recruitment and further follow up will allow for understanding of the ICI-IA phenotypes will help understand and improve functionality and quality of life.
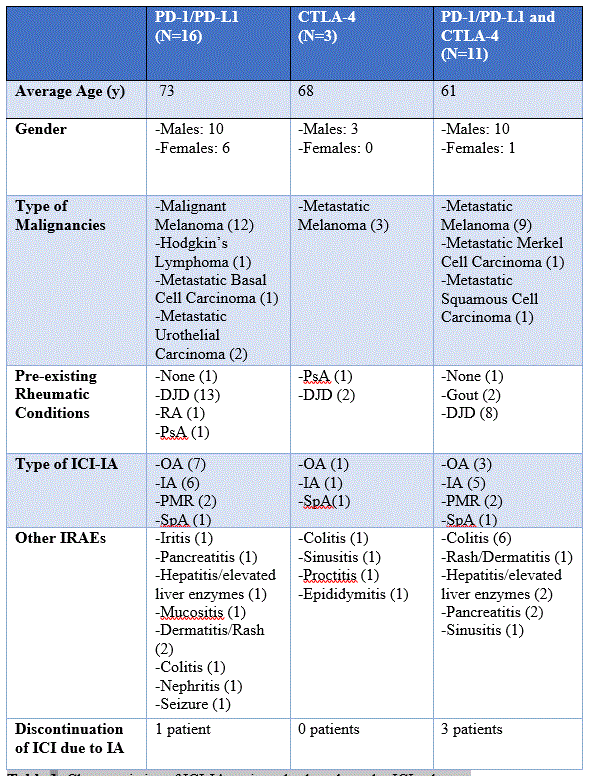 Table 1: Characteristics of ICI-IA patients broken down by ICI subtype.
Table 1: Characteristics of ICI-IA patients broken down by ICI subtype.
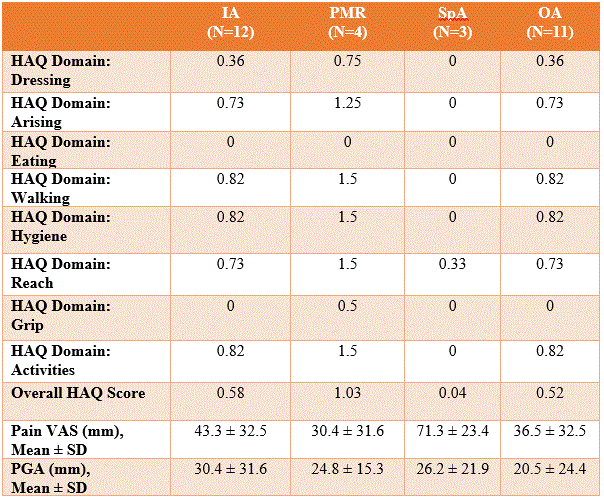 Table 2: The averages of each HAQ-DI domain for each subset of inflammatory arthritis, in addition to the means for pain VAS and PGA
Table 2: The averages of each HAQ-DI domain for each subset of inflammatory arthritis, in addition to the means for pain VAS and PGA
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sarazin J, Impens A, Abdulaziz N, Anderson S, Fecher L, Lao C, Schiopu E. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Inflammatory Arthritis Impact on Function and Patient-Reported Quality of Life Measures Varies Depending on Pattern of Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-induced-inflammatory-arthritis-impact-on-function-and-patient-reported-quality-of-life-measures-varies-depending-on-pattern-of-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-induced-inflammatory-arthritis-impact-on-function-and-patient-reported-quality-of-life-measures-varies-depending-on-pattern-of-arthritis/
