Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a serious and potentially debilitating disease, but low disease activity and even clinical remission can be obtained if an effective therapy can be identified early in the course of the disease. Imaging with Tc99m tilmanocept, a high affinity ligand to CD206 expressed on activated macrophages, offers the potential to meet this need by providing an objective, quantifiable readout of changes in macrophage density in the joints of patients undergoing initiation or change of bDMARD therapy. These macrophage density changes may be observable weeks before disease modification can be detected with standard clinical assessments. This earlier readout would allow for more timely modifications of the treatment strategy and earlier identification of an effective therapy, thus reducing the likelihood of permanent joint damage associated with ineffective therapy and the potential for side effects from exposure to these ineffective therapies.
Methods: An interim analysis of our Phase 2b trial (NCT03938636) was performed using data from 15 subjects with active RA (DAS28 ≥ 3.2; ACR/EULAR 2010 Classification Criteria ≥ 6) set to begin a new or first-time treatment regimen with an anti-TNFα therapy. Hand/wrist planar gamma camera images were obtained at baseline prior to initiation of new treatment, 5 weeks post-therapy initiation, and 12 weeks post-therapy initiation for 11 of the 15 subjects at the time of the analysis. The remaining subjects had completed baseline and 5-week imaging only at the time of this analysis. Images were quantitatively assessed to detect localization within synovial spaces of bilateral hands and wrists by determining average pixel intensity in each region of interest relative to average pixel intensity in an adjacent reference region. Additionally, a panel of established clinical assessments (CDAI, DAS28, HAQ-DI) was performed at each time point in order to compare imaging results with clinical evaluations over the 12-week time course.
Results: In 9 out of 11 subjects with 12-week clinical data available at the time of analysis, Tc99m tilmanocept imaging from baseline to week 5 was predictive of clinical outcome at 12 weeks (Figure 1). Global Tc99m tilmanocept signals declined by an average of 46% from baseline to week 5 in those subjects correctly predicted as responding significantly to anti-TNFα treatment by week 12. In subjects correctly predicted by imaging not to have a significant clinical response by week 12, Tc99m tilmanocept signals increased by an average of 44% from baseline to week 5. Combined data from all 15 subjects demonstrated that baseline global Tc99m tilmanocept uptake values in joints with RA-involved inflammation spanned a range of values of over an order of magnitude. These preliminary results indicate that marked changes in Tc99m tilmanocept global uptake values by week 5 presage clinical efficacy evaluations at week 12 of treatment.
Conclusion: These interim data are supportive of the hypotheses that Tc99m tilmanocept imaging can provide quantifiable imaging assessment of RA-involved joints that enables early prediction of clinical response as well as longitudinal monitoring of clinical status.
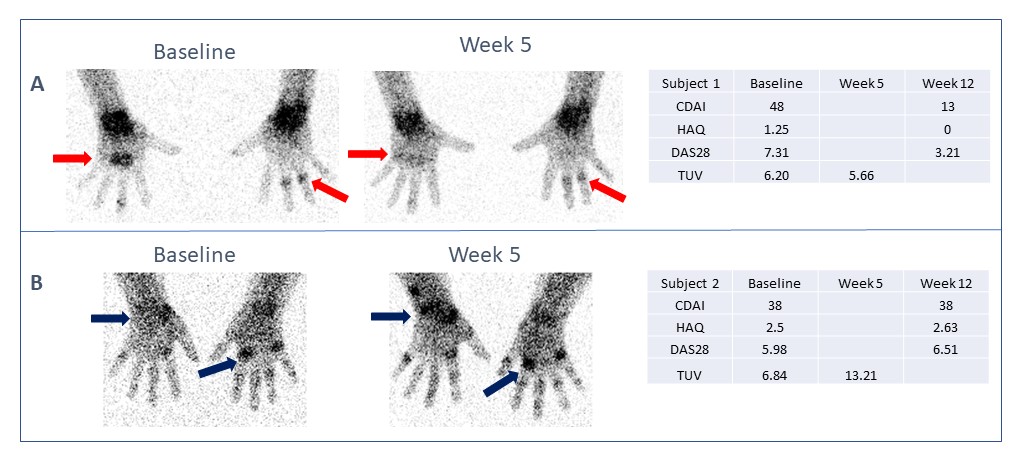 Figure 1: Quantification of Tc99m tilmanocept at Baseline and Week 5 is predictive of clinical efficacy at Week 12. Representative Baseline and Week 5 images and Tc99m tilmanocept quantification (Tilmanocept Uptake Value; TUV) demonstrate changes in localization that are sensitive to and predictive of clinical response at Week 12. Images show decrease in signal localization predictive of clinical response (Panel A) and increase in signal localization predictive of clinical non-response (Panel B) at Week 12.
Figure 1: Quantification of Tc99m tilmanocept at Baseline and Week 5 is predictive of clinical efficacy at Week 12. Representative Baseline and Week 5 images and Tc99m tilmanocept quantification (Tilmanocept Uptake Value; TUV) demonstrate changes in localization that are sensitive to and predictive of clinical response at Week 12. Images show decrease in signal localization predictive of clinical response (Panel A) and increase in signal localization predictive of clinical non-response (Panel B) at Week 12.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leach M, Ralph D, Potter B, Abbruzzese B, Hershey R, Fitzpatrick J, Repp K, Shakhtra H, Palmer M, Korczak N, Villarosa A, Blue M, Jacobs M, Ruis Y, Foley D, Kivitz A, Rosol M. Tc99m Tilmanocept Imaging Is an Early Predictor of Clinical Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Beginning New Anti-TNFα Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tc99m-tilmanocept-imaging-is-an-early-predictor-of-clinical-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-beginning-new-anti-tnf%ce%b1-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tc99m-tilmanocept-imaging-is-an-early-predictor-of-clinical-response-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-beginning-new-anti-tnf%ce%b1-therapy/
