Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA) have a higher prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), which is the most common cause of death in this group. Disease activity seems to be an independent risk factor for CVD, but there is controversy at the impact on left ventricular systolic function (LVSF). LVSF may be assessed by conventional methods like left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and myocardial shortening or by novel techniques evaluating myocardial strain such as speckle tracking echocardiography (STE).
Methods: Observational, cross-sectional study. RA patients aged 40-75 years that fulfilled the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and matched controls were included. Patients with a poor US window, history of previous CVD (ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular accident or peripheral arterial disease), and pregnancy were excluded. Individuals were evaluated using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography performed and reviewed by 2 certified echocardiographers. LVEF and myocardial strains (circumferential, longitudinal, and radial) were measured; differences were solved by consensus. Descriptive analysis was done with measures of central tendency and dispersion. Student-t and Mann-Whitney U tests were used for comparisons.
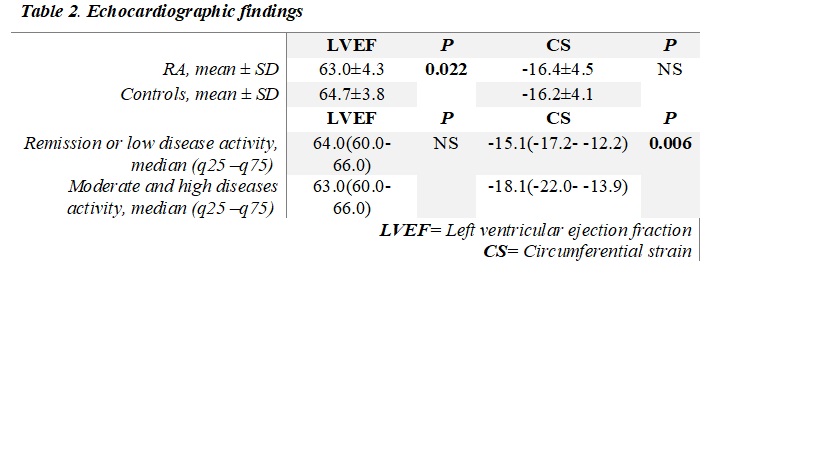
Results: A total of 140 subjects were included. Demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. RA patients were divided into 2 groups, according to disease activity by DAS 28-CRP (remission or low activity and moderate or high activity). Echocardiographic parameters were compared between the RA group and controls also between the 2 groups in which RA patients were divided by disease activity Table 2. The LVEF was lower in RA subjects compared with controls (p= 0.022), however, LVEF was normal ( > 52% in men and >54% in women) in both groups. There was a significant difference in the circumferential strain (CS) between RA patients based on the disease activity by DAS 28-CRP (p= 0.006).
Conclusion: The decrease in circumferential strain depends on disease activity. Myocardial strain by speckle tracking echocardiography may detect early myocardial dysfunction in RA. The rheumatologist needs to establish an appropriate treatment to achieve the disease remission or low disease activity, as there is an impact of the disease activity on the myocardial function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodríguez E, Galarza-Delgado D, Azpiri López J, Colunga Pedraza I, Lugo Pérez S, Zárate Salinas I, Frausto Lerma P, Pérez Villar A, Reyes Soto M, Vera R. Association Between Disease Activity and Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-disease-activity-and-left-ventricular-systolic-function-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-disease-activity-and-left-ventricular-systolic-function-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-case-control-study/