Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To study the incidence rate, predictors and outcome of stroke in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) within a defined population in southern Sweden.
Methods: The study included a total of 325 patients diagnosed with AAV within a defined geographical area in Sweden (1997-2016). The diagnosis and classification of AAV was confirmed by case record review using the European Medicines Agency (EMA) algorithm. To identify AAV cases with stroke, two sources were used: (i) The Swedish Stroke Register (Riksstroke): a national stroke register operated since 1994 which includes all cases of stroke diagnosed at stroke-units in Sweden , (ii) The Skåne healthcare register (SHR), an administrative local register of all healthcare services provided to the population in Skåne, was used to identify patients diagnosed at departments not specialized in stroke-care. Diagnosis of stroke for cases identified by the SHR were verified by case record review. From the Riksstroke register we identified 10 controls for each AAV-patient, matched for age, sex and years of stroke diagnosis. Incidence rate of stroke in AAV-patients was calculated per 1000 person-years of follow-up. The person-year was calculated from date of AAV-diagnosis to either date of stroke, death or end of study, December 2018. Using data from the Swedish background population, standardized incidence ratio (SIR) of stroke was estimated. Cox-regression analysis was utilized to investigate predictors of stroke in AAV.
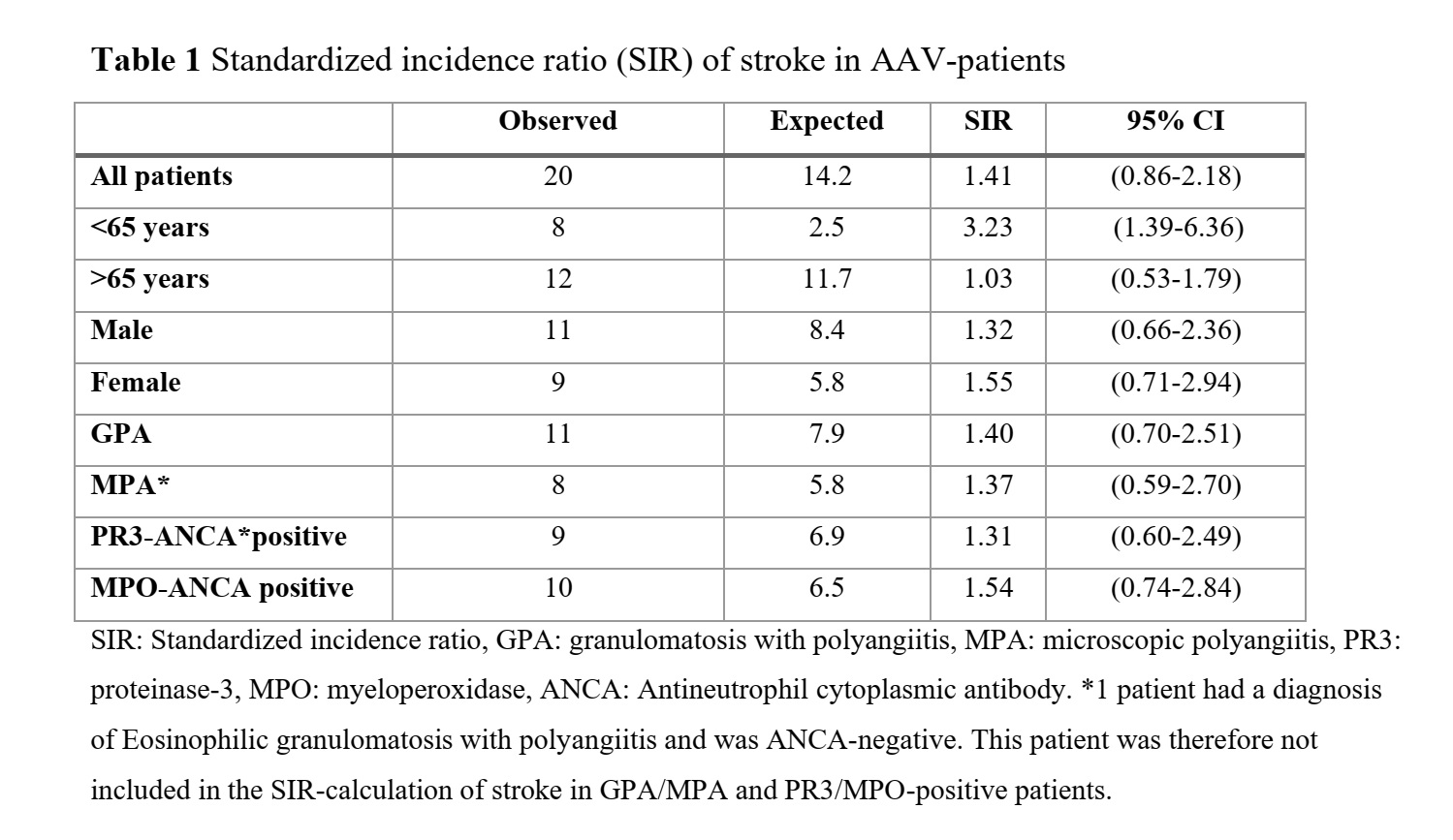
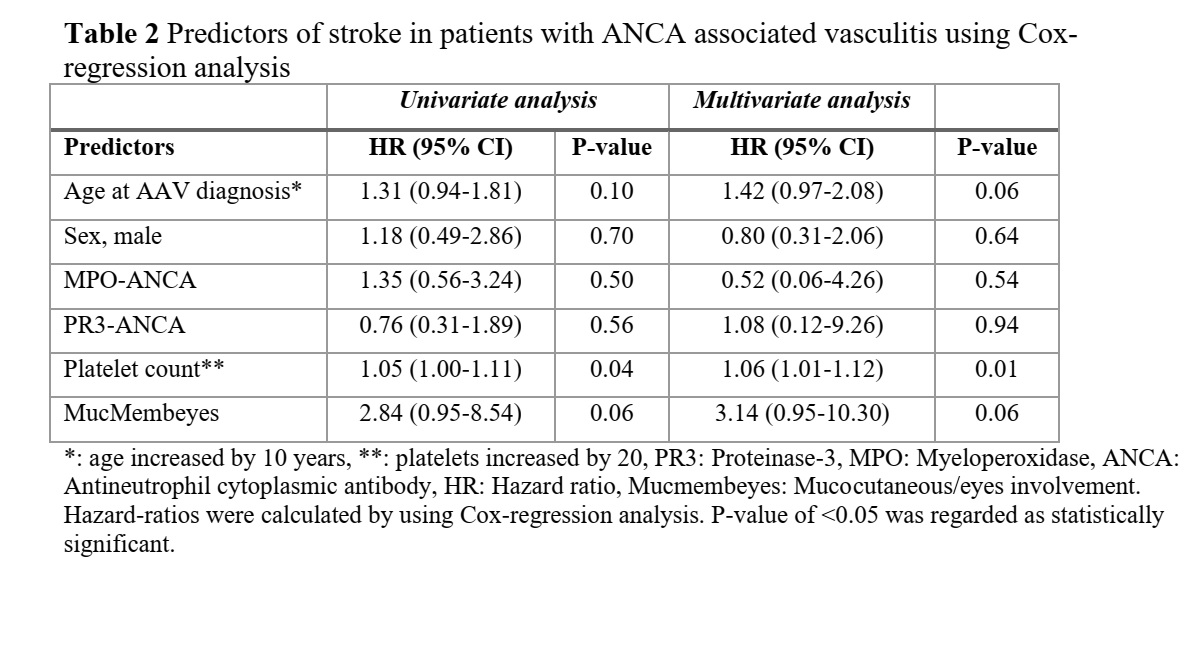
Results: Out of 325 AAV-patients, 20 (6%) suffered a stroke during the follow-up period. The incidence rate of stroke in AAV was 9.7 per 1000 person-years (95% CI 5.5-14.0) and was highest within the first year after AAV-diagnosis, 20.5 per 1000 person-years of follow-up (95% CI 4.1-36.9). Patients diagnosed with AAV at age < 65 years had 3.2-fold increased risk of stroke compared with background population (Table 1). Platelet count at AAV diagnosis was identified as an independent predictor of stroke (Table 2). There were no differences in survival rates or other outcome measures of stroke between AAV patients and their controls. While comparing AAV patients with and without stroke, a higher survival rate in PR3-positive patients compared to MPO-positive patients was observed (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Incidence rate of stroke in AAV is highest during first year after AAV diagnosis and significantly higher than that of the background population among patients younger than 65 years at AAV diagnosis. An elevated platelet count at AAV-diagnosis was able to predict an increased risk of stroke. Prophylactic treatment with antithrombotic and anticoagulant drugs to prevent stroke-occurrence requires further exploration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tabakovic D, Smith R, Jayne D, Mohammad A. Incidence Rate, Predictors and Outcome of Stroke in Patients with ANCA Associated Vasculitis – A Population-based Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-rate-predictors-and-outcome-of-stroke-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-a-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/incidence-rate-predictors-and-outcome-of-stroke-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis-a-population-based-study/