Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and troponin I (TnI) are established cardiac biomarkers that predict cardiovascular events (CVEs) and mortality in apparently healthy individuals and at-risk populations. While patients with psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis, collectively termed psoriatic disease (PsD), have an increased risk of developing CVEs, the use of these cardiac biomarkers to predict CV risk has not been investigated in this population. We aimed to evaluate the association between these cardiac biomarkers and incident CVEs, and assess their predictive value beyond the Framingham Risk Score (FRS).
Methods: A longitudinal cohort study was conducted in patients with PsD without prior history of CVEs. NT-proBNP and TnI concentrations were measured using automated clinical assays in the first available serum sample. The study outcome included any of the following CVEs occurring within the first 10 years of biomarker assessment: angina, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, transient ischemic attack, cerebrovascular accident, revascularization procedures and CV death. Associations with incident CVEs were analyzed separately for each biomarker using Cox proportional hazards regression models first adjusted for age and sex, and subsequently for the FRS. The added value of cardiac biomarkers to improve predictive performance beyond the FRS was assessed using the area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC), net reclassification index (NRI) and integrated discrimination index (IDI).
Results: A total of 1000 patients with PsD were assessed between 2005 and 2019 (mean age 49 ± 12.8 years, 44.6% female) (Table 1). During a mean follow-up of 7.1 years, 72 (7.2%) patients developed incident CVEs. Both TnI (Hazard Ratio (HR) 3.63, 95% Confidence Interval (CI) 1.47, 8.95) and NT-proBNP (HR 1.78; 95% CI 1.16, 2.74) predicted CVEs independently of the FRS (Figure 1). The association was stronger in males than females. Including all cardiac biomarkers and the FRS in a single model, both TnI (HR 3.25, 95% CI 1.34, 7.88) and NT-proBNP (HR 1.68, 95% CI 1.12, 2.54) retained statistical significance. When comparing the predictive performance of the base model (FRS alone, AUC 74.3) to the expanded models, there was no significant improvement in any of the predictive indices with the addition of TnI (AUC 72.3, p = 0.26; NRI 0.10, p = 0.51; IDI 0.008, p = 0.29), NT-proBNP (AUC 74.2, p = 0.98; NRI 0.18, p = 0.13; IDI 0.011, p = 0.24), or both TnI and NT-proBNP (AUC 73.6, p = 0.78; NRI 0.23, p = 0.06; IDI 0.019, p =0.09) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: In patients with PsD, elevated NT-proBNP and TnI predict incident CVEs independent of the FRS. We did not observe a significant improvement in the performance of the predictive model when combining these cardiac biomarkers with the FRS.
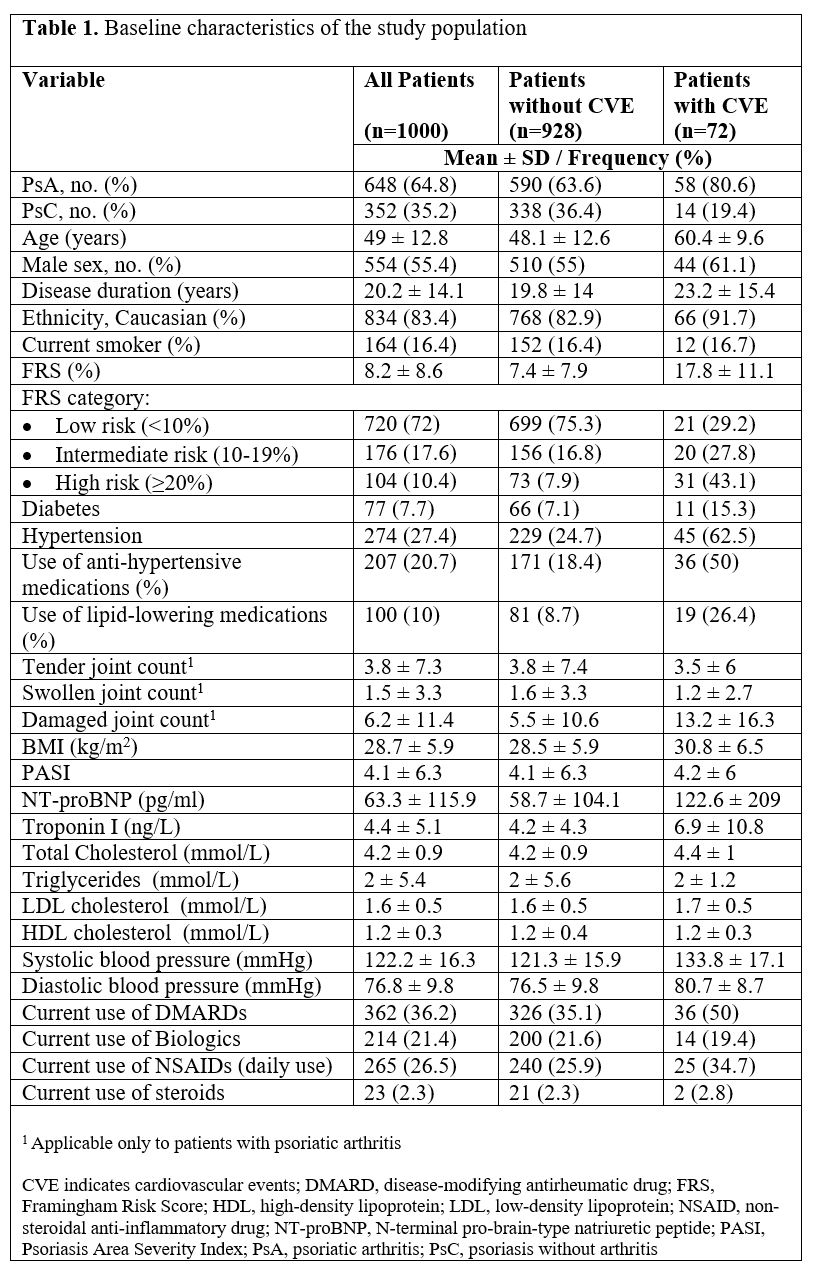 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the study population.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the study population.
 Figure 1. Hazard ratios of cardiac biomarker measures with incident cardiovascular events (n = 1000, 72 events). Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. CI indicates confidence interval; CVEs, cardiovascular events; FRS, Framingham Risk Score; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide; TnI, troponin I.
Figure 1. Hazard ratios of cardiac biomarker measures with incident cardiovascular events (n = 1000, 72 events). Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals. CI indicates confidence interval; CVEs, cardiovascular events; FRS, Framingham Risk Score; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide; TnI, troponin I.
 Figure 2. Comparison of the predictive performance of the base model (Framingham Risk Score alone) and expanded models for prediction of cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic disease. AUC indicates area under the receiver operator characteristic curve; FRS, Framingham Risk Score; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide; TnI, troponin I.
Figure 2. Comparison of the predictive performance of the base model (Framingham Risk Score alone) and expanded models for prediction of cardiovascular events in patients with psoriatic disease. AUC indicates area under the receiver operator characteristic curve; FRS, Framingham Risk Score; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide; TnI, troponin I.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Colaco K, Lee K, Akhtari S, Winer R, Welsh P, Sattar N, McInnes I, Chandran V, Harvey P, Cook R, Gladman D, Piguet V, Eder L. Cardiac Biomarkers Are Associated with the Development of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis and Psoriasis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiac-biomarkers-are-associated-with-the-development-of-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriasis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiac-biomarkers-are-associated-with-the-development-of-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriasis/
