Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology – Clinical Poster II: Systemic JIA, Autoinflammatory, & Scleroderma
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile localized scleroderma (jLS) is a chronic inflammatory and fibrosing disease. Treatment is directed towards controlling disease activity to minimize risk for functional impairment and severe damage. To work towards identifying optimal therapy, sensitive disease measures are needed to allow for comparative effectiveness studies.
A prior study identified several lesion features specific to and/or tracking with disease activity. These features were used to generate a new skin activity measure, LS Cutaneous Activity Measure (LSCAM), by LS Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance (CARRA) group. We report its performance in two prospective cohorts.
Methods: The LSCAM was modelled after the modified Localized Scleroderma Scoring Index (mLoSSI). Both measures score and sum disease extension, erythema, and skin thickening across affected sites; mLoSSI weighs extension more. LSCAM also scores violaceous color, tactile warmth, and waxy white/yellow, weighing variables equally. Reliaibity of LSCAM scoring was evaluated in a 1-day meeting where, following a training session, 14 physicians scored 13 jLS patient volunteers twice. Each scorer was given a photo scoring atlas to aid scoring standardization.
Construct validity was determined by comparison to Physician Global Assessment of disease activity (PGA-A) and disease damage (PGA-D) in two cohorts: The patient volunteers as described, and a cohort of jLS patients followed for 12 months on methotrexate treatment (consensus treatment plan (CTP) pilot study). We calculated Kendall’s coefficient of concordance to assess inter-rater reliability, and Spearman’s rho to assess intra-rater reliability and validity. Levels of 0.2 to < 0.4 were considered poor, 0.4 to < 0.6 moderate, 0.6 to 0.8 good, >0.8 excellent.
Results: A moderate to good level of inter-rater reliability of scoring of LSCAM and mLoSSI was found in both rounds at the meeting (Table 1). A good level of intra-rater reliabiilty of scoring was found for LSCAM, mLoSSI, and PGA-A. Among the individual variables, all except waxy white or yellow and tactile warmth had moderate reliability in both rounds (Table 1). Intra-rater was higher than inter-rater reliabiity (Table 1).
Excellent convergent construct validity was found between LSCAM and PGA-A, and good between mLoSSI and PGA-A in the 1-day meeting (Table 2). Good construct validity was found for LSCAM and mLoSSI in the CTP Pilot (Table 2). Divergent construct validity with PGA-D was shown between LSCAM and mLoSSI in the meeting, but not in the CTP Pilot (LSCAM 0.433, mLoSSI 0.350, Table 2). Scores for LSCAM, mLoSSI, and PGA-A decreased over time in the CTP study, with LSCAM appearing to more closely mirror changes in PGA-A score than mLoSSI (Figure 1).
Conclusion: LSCAM is a reliable and valid measure for assessing cutaneous activity in jLS. The level of inter- and intra-rater reliability of LSCAM was similar to greater than mLoSSI. A similar to higher level of convergent construct validity with PGA-A was found for LSCAM compared to mLoSSI, with LSCAM appearing to track better with PGA-A scores in the 12 month study. Our findings suggest the LSCAM will aid monitoring of LS activity, and facilitate conducting comparative treatment studies.
 Table 1: Reliability of Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Activity Measure scoring from one day meeting. Thirteen jLS patient volunteers were evaluated two times in a one day meeting by 14 raters: 13 pediatric rheumatologists, 1 pediatric dermatologist. Patients were evaluated in a different random order by each rater in the two rounds. A maximum of two anatomic sites were evaluated per patient, with these sites identified in advance by one of the investigators (K. Torok). PGA-A was scored from 0-100. The average score of each measure and feature is shown; Erythema and skin thickening were scored from 0-3, other variables were scored from 0-1. For inter-rater reliability, Kendall’s coefficient of concordance (W ) were calculated. For Intra-rater reliability, Spearman’s correlation were calculated for each rater. All reliability values shown were found significant, p < 0.0001. LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure = disease extension + erythema + skin thickening + violaceous color + waxy white or yellow + tactile warmth. mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index= 3*disease extension + erythema + skin thickening. PGA-A = Physician global assessment of disease activity
Table 1: Reliability of Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Activity Measure scoring from one day meeting. Thirteen jLS patient volunteers were evaluated two times in a one day meeting by 14 raters: 13 pediatric rheumatologists, 1 pediatric dermatologist. Patients were evaluated in a different random order by each rater in the two rounds. A maximum of two anatomic sites were evaluated per patient, with these sites identified in advance by one of the investigators (K. Torok). PGA-A was scored from 0-100. The average score of each measure and feature is shown; Erythema and skin thickening were scored from 0-3, other variables were scored from 0-1. For inter-rater reliability, Kendall’s coefficient of concordance (W ) were calculated. For Intra-rater reliability, Spearman’s correlation were calculated for each rater. All reliability values shown were found significant, p < 0.0001. LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure = disease extension + erythema + skin thickening + violaceous color + waxy white or yellow + tactile warmth. mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index= 3*disease extension + erythema + skin thickening. PGA-A = Physician global assessment of disease activity
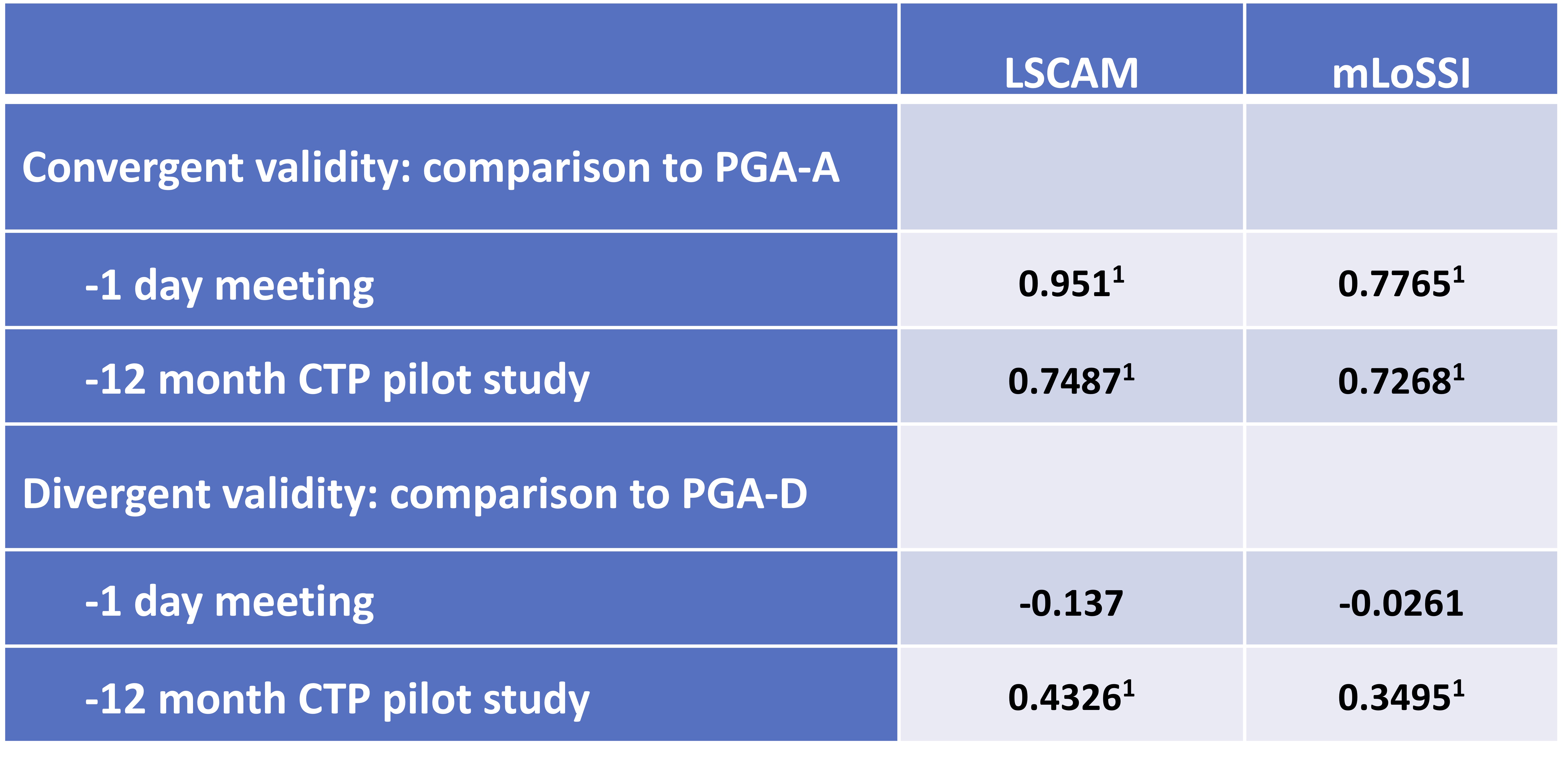 Table 2: Construct validity of Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Activity Measure. LSCAM and mLoSSI scores were analyzed in comparison to PGA-A for convergent validity, and to PGA-D for divergent validity in the two prospective jLS cohorts: 13 patient volunteers in a one day meeting, and 44 jLS patients initiating methotrexate treatment in the jLS CTP pilot study. Spearman’s rho correlation coefficients are shown. 1p < 0.001. CTP: consensus treatment plan; LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure; jLS: juvenile localized scleroderma; mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index; PGA-A = Physician global assessment of disease activity; PGA-D = Physician global assessment of disease damage
Table 2: Construct validity of Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Activity Measure. LSCAM and mLoSSI scores were analyzed in comparison to PGA-A for convergent validity, and to PGA-D for divergent validity in the two prospective jLS cohorts: 13 patient volunteers in a one day meeting, and 44 jLS patients initiating methotrexate treatment in the jLS CTP pilot study. Spearman’s rho correlation coefficients are shown. 1p < 0.001. CTP: consensus treatment plan; LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure; jLS: juvenile localized scleroderma; mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index; PGA-A = Physician global assessment of disease activity; PGA-D = Physician global assessment of disease damage
 Figure 1: Change in scores for Skin Activity measures and PGA-A over 12 months of methotrexate treatment (jLS CTP Pilot study). Fourty-four jLS patients were monitored for 12 months after initiating methotrexate treatment (one of three methotrexate-based consensus treatment plans). The median LSCAM, mLoSSI, and PGA-A scores at each visit is shown. CTP: consensus treatment plan; LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure; mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index; PGA-A: physician global assessment of disease activity.
Figure 1: Change in scores for Skin Activity measures and PGA-A over 12 months of methotrexate treatment (jLS CTP Pilot study). Fourty-four jLS patients were monitored for 12 months after initiating methotrexate treatment (one of three methotrexate-based consensus treatment plans). The median LSCAM, mLoSSI, and PGA-A scores at each visit is shown. CTP: consensus treatment plan; LSCAM: Localized scleroderma cutaneous activity measure; mLoSSI: modified localized scleroderma severity index; PGA-A: physician global assessment of disease activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li S, Becker M, Hong S, Ferguson P, Nyrienda T, Andrews T, Stewart K, Rabinovich C, Fuhlbrigge R, Mason T, Pope E, Ibarra M, Dedeoglu F, Higgins G, Laxer R, Punaro M, Torok K, Investigators C. Reliability and Validity of a New Skin Activity Measure for Localized Scleroderma [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validity-of-a-new-skin-activity-measure-for-localized-scleroderma-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reliability-and-validity-of-a-new-skin-activity-measure-for-localized-scleroderma-2/
