Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-polygalacturonic acid antibody (PGA-Ab) is a new rheumatoid arthritis (RA)-related autoantibody first identified by our group. The sensitivity and specificity of PGA-Ab is even higher than anti-cyclic peptide containing citrulline (anti-CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF). However, the pathogenesis of PGA-Ab has never been investigated.
Methods: Rabbits were immunized with PGA for PGA-Ab production followed by joint structure analysis by HE staining and micro-CT. Bone resorption index of RA patients were detected to analyze the comparation of PGA-Ab with bone loss. Osteoclasts were induced in vitro from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by M-CSF and RANKL with or without PGA-Ab treatment followed by RNA-Sequence for transcriptome analysis and then confirmed by real time quantitative PCR or western blot. Potential receptors were also identified by immunoprecipitation and protein spectrum sequencing (IP-MS).
Results: After PGA immunization, severe joint inflammation and damage were shown in PGA-Ab positive animals, including increasing synovium thickness, neutrophils and lymphocytes infiltration and reducing bone mineral density of femoral trabecula. Cathepsin k (CSK) and Tartrate Resistant (ACP5) in PGA-Ab positive RA patients were significantly higher than in PGA-Ab negative RA patients. In vitro culture, PGA-Ab treatment increased mature osteoclast numbers, CSK or metalloproteinases (MMPs) releasing and NFAT1c and AP-1 activation. Rho-GTPase signaling pathway-related protein RhoA, RhoD-GTP and ARP2 expression were also increased and PGA-Ab treatment increased wound healing, indicating increased cell migration and motility induced by PGA-Ab. Integrin beta5 (ITGB5) were identified as receptor of PGA-Ab on osteoclasts. Knockdown of ITGB5 eliminated the binding of PGA-Ab with osteoclasts and reduced PGA-Ab-induced osteoclastogenesis significantly.
Conclusion: PGA-Ab is a new RA-related autoantibody, which has pathogenic effect on arthritis bone erosion by inducing osteoclast differentiation through receptor integrin beta 5 via Rho-GTPase signaling pathway.
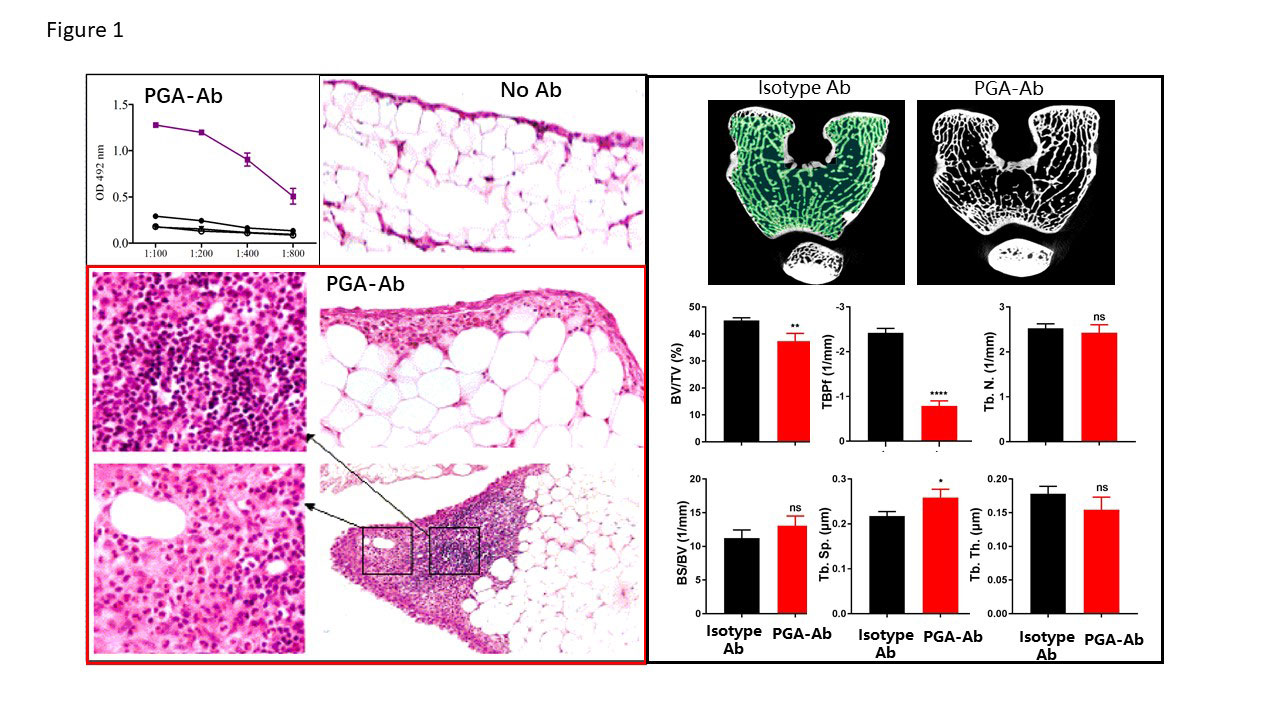
Two month-old female white rabbits -3 per group- were subcutaneous injected with PGA and boosted 2 weeks and 4 weeks later. The mice were bled on 6th week and the sera were assayed for PGA-Abs. Hind knee joints from rabbits without PGA-Ab -B- and with PGA-Ab -C- were fixed with 4% formaldehyde solution and then decalcificated, followed by paraffin section preparation and HE staining. Microscopic observation found obvious inflammatory changes, including synovial hyperplasia, small vessels proliferation and inflammatory cell infiltration, in the joint sections from rabbits with PGA-Ab. -D- Micro-CT images of the distal femur and analysis of BV/TV, bone volume/tissue volume; BMD, bone mineral density; TbTh, trabecular thickness; TbN, trabecular number; Tb.sp, bone separation. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation -n=5 for each group-. *P<0.05 vs. control.
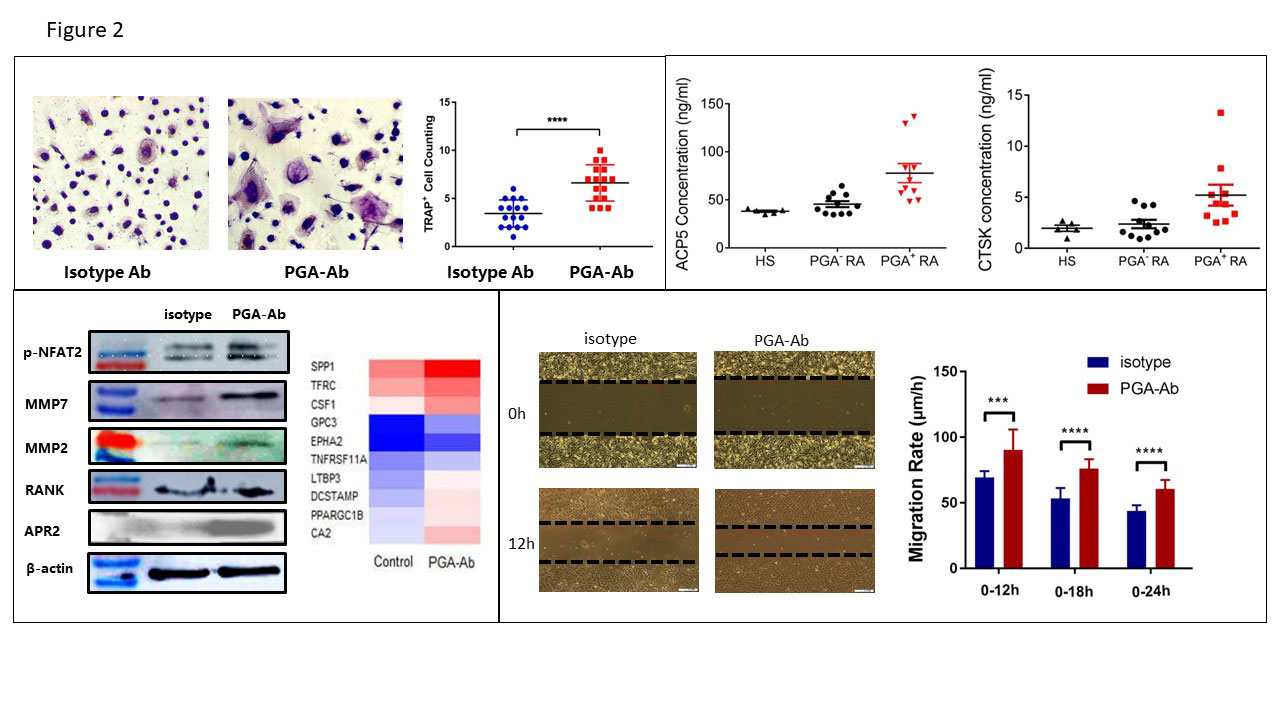
-A- Osteoclasts were induced in vitro from peripheral blood mononuclear cells -PBMC- by M-CSF and RANKL with or without PGA-Ab treatment Representative images of osteoclastic TRAP staining and osteoclast cell number count were shown. -B- Bone turnover biomarker -ACP5 and CTSK- in healthy subjects and RA patients with or with PGA-Ab. -C- Protein extracts were isolated from osteoclasts after treatment with the isotype antibody or PGA-Ab -0.05mg/ml- for 48h and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-NFAT2, beta-actin, and histone-1 antibodies. After treatment with isotype antibody or PGA-Ab for 48h, mRNA extracts were analyzed by RNA-seq for transcriptome analysis and representative heat map of osteoclastgenesis-related gene expression was shown. -D- Cells were treated by isotype antibody or PGA-Ab for 48h followed by migration assay by wound healing.
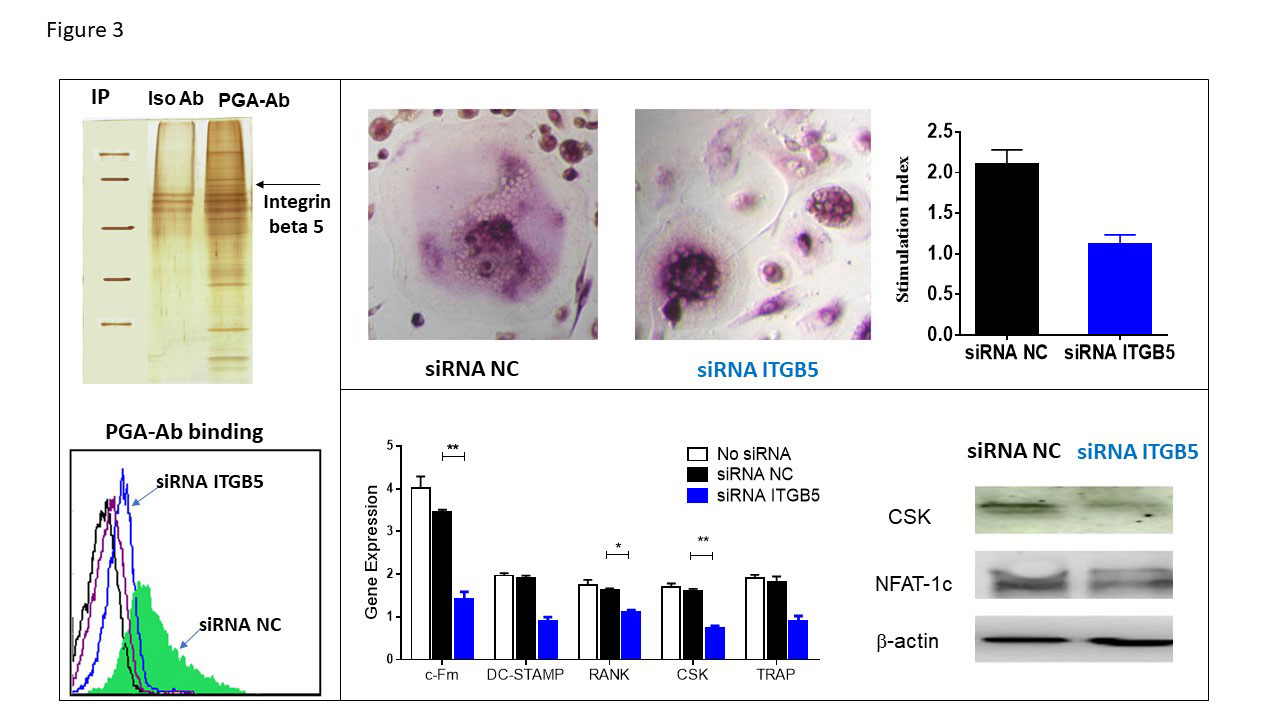
-A- Protein extracts were isolated from osteoclasts followed by incubated with PGA-Ab or isotype Ab for immunoprecipitation. After protein spectrum sequencing for differential bands, integrin beta 5 was identified as PGA-Ab-binding protein. After knock down ITGB5 expression by siRNA, the binding of PGA-Ab and osteoclast were detected by flow cytometry. -B- ITGB5 knock down followed by osteoclastogenesis induced by M-CSF and RANKL. TRAP staining were used for osteoclast cell number count. -C- Gene and protein expression of osteoclasts after ITGB5 silence were detected by real time quantitative PCR and western blot, respectively.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
XIE J, DAI H. Anti-Polygalacturonic Acid Antibody (PGA-Ab) Induced Bone Destruction in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Promoting Osteoclastogenesis via Integrin Beta 5 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-polygalacturonic-acid-antibody-pga-ab-induced-bone-destruction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-promoting-osteoclastogenesis-via-integrin-beta-5/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-polygalacturonic-acid-antibody-pga-ab-induced-bone-destruction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-by-promoting-osteoclastogenesis-via-integrin-beta-5/