Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S084: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorder – Clinical I: Therapeutics & Outcomes (863–868)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening complication of systemic sclerosis (SSc). Pre-clinical and clinical data have strongly implicated immune dysregulation and B cell activation in the pathogenesis of both SSc and PAH. While standard PAH therapies are approved for SSc-PAH, ongoing immune injury to the pulmonary vasculature is not routinely addressed. Consequently, we sought to determine whether B cell depletion with rituximab (Rx) could be effective in SSc-PAH.
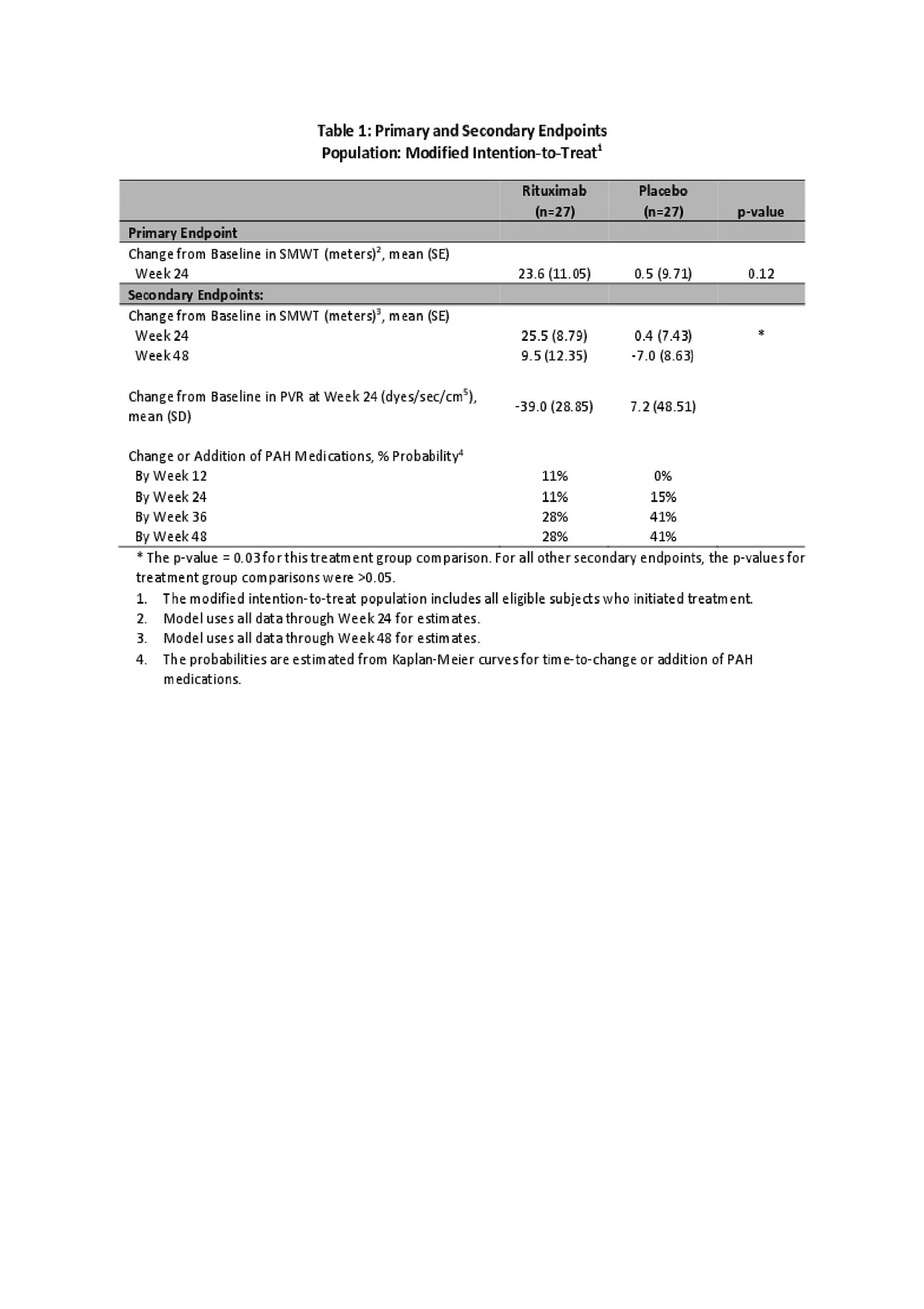
Methods: We conducted a Phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multi-center clinical trial sponsored by the Autoimmunity Centers of Excellence, NIH. SSc-PAH patients on a stable standard PAH therapy without significant interstitial lung or renal disease were eligible. Dosing was two 1000 mg Rx infusions, 14 days apart. In this under-powered proof-of-concept study, multiple endpoints were evaluated to explore the potential for clinical benefit. The primary endpoint was change in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD) at 24 weeks. Key secondary efficacy endpoints included change in 6MWD at other time points, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and time to change or addition of PAH medications, which were expected to remain unchanged until week 24 per protocol. A secondary objective of the study was to evaluate the safety profile of Rx in this population.
Results: Between 2010-2018, 57 participants (29 Rx, 28 placebo (Pc)) were randomized; 91% female, mean age = 58(SD 9.1) years, 90% limited SSc, mean duration of SSc-PAH = 1.8(SD 1.2) years. In the primary longitudinal analysis using data through week 24, 6MWD trended towards improvement after Rx relative to Pc but did not reach statistical significance (23.6±11.1m Rx, 0.5±9.7m Pc, p=0.12, Fig 1). A pre-specified secondary analysis, which included 6MWD data through week 48, demonstrated improvement at week 24 (25.5±8.8m Rx, 0.4±7.4m Pc, p=0.03, Figure 1), that was lost by week 48(9.5±12.4m Rx, -7.0±8.6m Pc, p=0.28). The probability of change or addition of PAH therapies after week 24 was lower in the Rx group (28% Rx, 41% Pc at weeks 38 and 48, Table 1). Changes in PVR at Week 24 were highly variable, but on average Rx fared better (mean(SD): -39 (28.9) Rx, 7.2(48.5) Pc, Table 1). Rx was well-tolerated with no unexpected adverse events or hypersensitivity reactions (Table 2). The number of adverse events, including infections, was similar in both treatment groups. A total of 4 deaths occurred in this at-risk cohort (3 in Rx, 1 in Pc); none of these deaths were directly attributed to Rx.
Conclusion: This is the first controlled trial examining the role of immunotherapy for SSc-PAH. Adjuvant B cell depletion therapy is a potentially effective and safe treatment for SSc-PAH. Our analyses uncovered potential benefits, despite being under-powered, and offer hope that targeted immunotherapy may be a promising approach. These results suggest repeat dosing of Rx after 24 weeks in responsive SSc-PAH patients. These results suggest that B cell-mediated injury contributes to ongoing pulmonary vascular disease in SSc-PAH and warrants further study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nicolls M, Badesch D, Chung L, Domsic R, Medsger T, Pinckney A, Keyes-Elstein L, D'Aveta C, Spychala M, White R, Hassoun P, Torres F, Molitor J, Khanna D, Maeker H, Welch B, Goldmuntz E, Zamanian R, On Behalf of ASC01 Investigators -. Safety and Efficacy of B-cell Depletion with Rituximab for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in a Multi-center NIH Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-b-cell-depletion-with-rituximab-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-a-multi-center-nih-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-b-cell-depletion-with-rituximab-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-sclerosis-associated-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-a-multi-center-nih-clinical-trial/