Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose :
MTP joints are seldom examined in routine clinical visits. As such, it is important to understand how the standard treatment of patients with early RA and their serological RF and ACPA status may affect active inflammation in the MTP joints. This study aimed to characterize 1) 1-year changes in power Doppler (PD) scores of patients with early RA treated as per standard of care, and 2) changes in PD scores based on serological RF and ACPA status.
Methods :
Patients with early RA (ACR criteria) were examined at baseline, 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months and 1 year. At baseline, all patients were DMARD naïve and treated as per standard of care. Except in a few cases, initial treatment involved mainly MTX and occasionally LEF. For the purpose of this study, subgroup analyses were conducted for patients who were characterized as being seronegative for both RF and ACPA (-/-), or seropositive for both RF and ACPA (+/+). At each visit, a rheumatologist imaged the 2nd-5th MTP joints of both feet using US, and graded PD semiquantitatively (score 0-3 per joint, max. score=24/patient). Paired t-tests compared baseline and 1-year PD, and PD between serology groups.
Results :
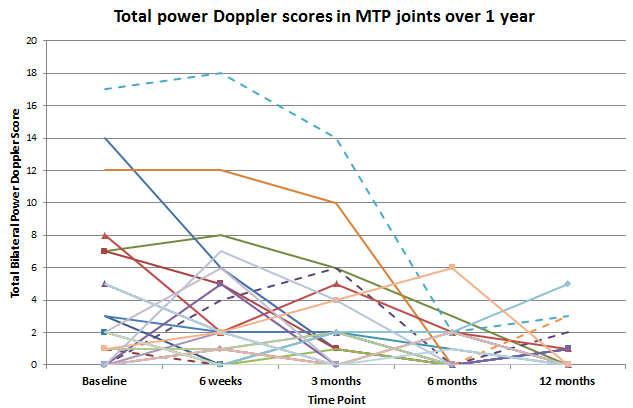
Forty patients were enrolled [mean (SD) age=52.1(10.4) years, n=32 female]. At baseline, PD scores ranged from 0 to 17; at 1-year PD scores ranged from 0 to 5. Mean (SD) PD scores were significantly lower at 1-year [0.5 (1.1)] than baseline [2.3 (4.2)], p<0.05. Changes in the level of active inflammation developed rapidly: within 6 weeks, 8 patients improved (decreased PD≥2) and 5 patients worsened markedly (increased PD≥2). All except 1 of the patients who worsened improved by 3 months (patient stopped medication at 3 months, and improved once restarted). The mean baseline PD (SD) was significantly higher for +/+ patients [n=14, 5.3 (5.8)], than -/- patients [n=20, 0.5 (0.9)], p<0.05. Of all patients who maintained PD=0 at all visits (n=12), 8 were -/- and 3 were +/+. Of 14 patients who had PD≥5 at any visit, 9 were +/+ and 1 was -/-. In 20 patients who either maintained a low PD baseline score (±2 at each visit) or improved, serology was split (n=10 -/-, n=9 +/+). Patients who worsened (increased PD≥2) after baseline (n=6) were split on serology as well (n=2 -/-, n=2 +/+). The two groups of patients followed similar courses of treatment, and their responses were both favourable: 39 patients had inflammation controlled (PD≤3) at 1 year.
Figure 1: PD score at each study visit of patients who showed PD≥1 at any time point (n=28).
Conclusion:
Patients with early RA seropositive for RF and ACPA had, on average, more severe inflammation at baseline. However, serotype did not appear to affect patient response to standard initial treatment. Patients with severe inflammation at baseline and 6 weeks all improved by 3-6 months, and patients with low initial inflammation did not generally worsen, regardless of serology, and without considerable changes to treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beattie KA, Zou H, Ioannidis G, Larche M. Favourable Changes in Power Doppler Scores in the Feet over 1-Year in an Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort: The Role of Rheumatoid Factor and Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibody [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/favourable-changes-in-power-doppler-scores-in-the-feet-over-1-year-in-an-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort-the-role-of-rheumatoid-factor-and-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibody/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/favourable-changes-in-power-doppler-scores-in-the-feet-over-1-year-in-an-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort-the-role-of-rheumatoid-factor-and-anti-citrullinated-protein-antibody/