Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
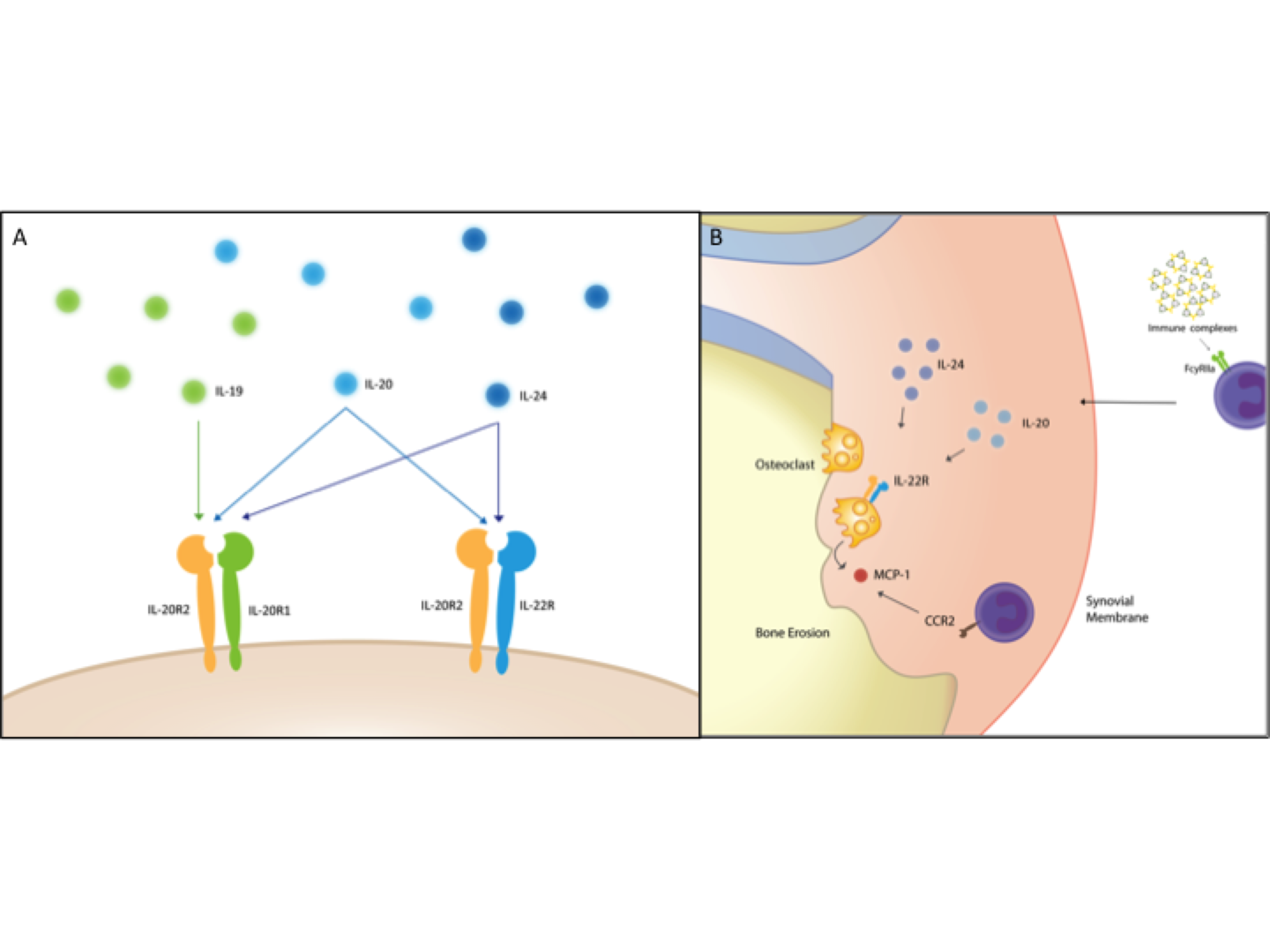
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is often characterized by the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) and bone erosions. Successful treatment can compromise the normal immune response, increasing the risk of infections. The interleukin 20 receptor (IL-20R) axis comprising IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24 (“the IL-20R cytokines”) and their shared receptors activates tissue homeostasis processes but not the immune system (Figure 1A). Consequently, modulation of the IL-20R axis may not lead to immunosuppression, making it an interesting drug target. The objective of this study was to determine the role of the IL-20R axis in early RA with focus on associations of the three cytokines with clinical disease activity and prognosis.
Methods:
The IL-20R cytokines were measured in plasma samples from treatment naive early RA patients during 24 months treatment with methotrexate, adalimumab/placebo and intra-articular glucocorticoid injections (the OPERA trial) (n=152) and healthy controls (n=88). IL-20R1 and IL-22R expression was studied in paired peripheral blood and synovial fluid cells from RA patients (n=15) with at least one swollen joint (for obtaining synovial fluid) with flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Heat aggregated human gamma globulins (HAGGs) and immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen (cFb-ICs) were used to stimulate macrophages. Osteoclasts (OCs) derived from synovial fluid cells were used to assess the effect of the IL-20R cytokines.
Results:
The plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 (but not IL-19) were increased in early RA patients compared with healthy controls (both P<0.002) and decreased after 6 months of treatment (both P<0.0001). The expression of IL-22R (but not IL-20R1) was increased on monocytes from RA synovial fluid compared with monocytes from both RA and healthy control peripheral blood. The plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 were increased in RF and ACPA positive compared with negative early RA patients (all P<0.0001). HAGGs and cFb-ICs stimulated the production of the IL-20R cytokines by myeloid cells. Increased baseline plasma concentrations of IL-20 and IL-24 were associated with Sharp-van der Heijde score progression after 24 months (SpearmanÕs rho=0.19 and 0.26, both P<0.05) in the early RA patients. The IL-22R was expressed by OC precursors and in multinucleated OCs and these cells were activated by IL-20 and IL-24.
Conclusion:
This study suggests that IL-20 and IL-24 link RA-associated autoantibodies with activation of OCs and radiographic progression via the IL-22R1 (Figure 1B). Modulation of this axis holds promise as feasible anti-erosive treatment modalities in seropositive RA.
Figure 1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kragstrup TW, Greisen S, Nielsen MA, Rhodes C, Stengaard-Pedersen K, Lund Hetland M, Hørslev-Petersen K, Junker P, Østergaard M, Hvid M, Vorup-Jensen T, Robinson WH, Sokolove J, Deleuran B. The IL-20 Receptor Axis in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Novel Inflammation-Independent Links Between Autoantibody Positivity and Radiographic Progression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-il-20-receptor-axis-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-novel-inflammation-independent-links-between-autoantibody-positivity-and-radiographic-progression/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-il-20-receptor-axis-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-novel-inflammation-independent-links-between-autoantibody-positivity-and-radiographic-progression/