Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The clinical manifestations of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) limit physical function and work productivity, posing an economic burden to patients (pts) and society.1 Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A, demonstrated sustained efficacy in controlling disease activity up to Week (Wk) 52 in pts with non-radiographic (nr-) and radiographic (r-)axSpA (i.e., AS)2 in the phase 3 studies BE MOBILE 1 and 2, respectively.3 This analysis assessed the impact of BKZ on work productivity and activity impairment (WPAI) at Wk 16 and Wk 52 in pts across the full disease spectrum of axSpA.
Methods: The parallel BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704) and 2 (NCT03928743) studies comprised a 16-wk double-blind period followed by a 36-wk maintenance period.3 Pts were randomized to subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W) or placebo (PBO). All pts received BKZ 160 mg Q4W from Wk 16. We report mean change from baseline (BL) at Wk 16 and 52 in WPAI Specific Health Problem scores,4 which assess disease impact on pts’ impairment while at paid work (i.e., presenteeism), work time missed (i.e., absenteeism, including sick leave), overall work impairment (composite of presenteeism and absenteeism) and daily activity impairment (outside paid work). Observed case data are reported.
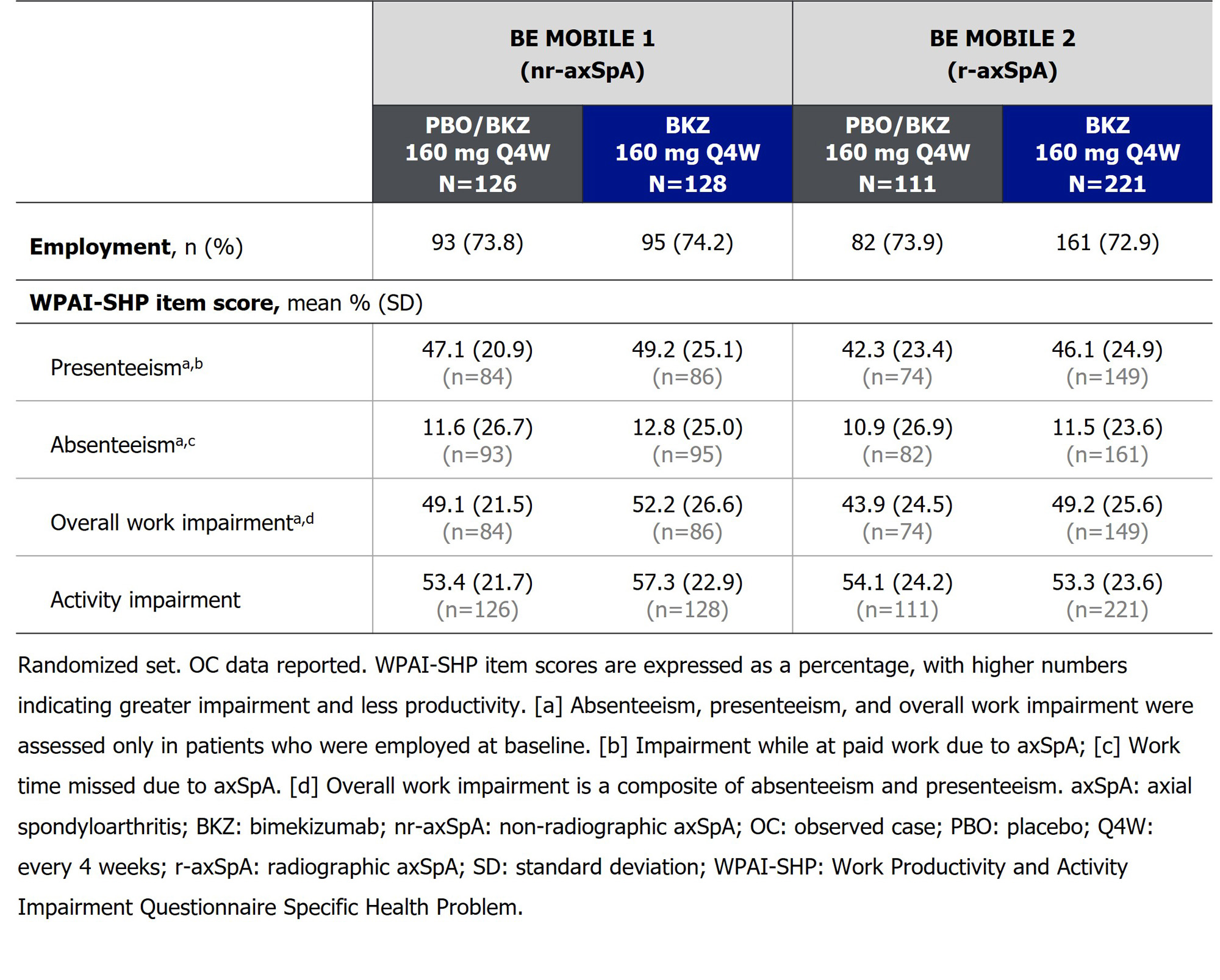
Results: Almost 75% of pts were employed at BL (nr-axSpA BKZ: 95/128 [74.2%], PBO: 93/126 [73.8%]; r-axSpA BKZ: 161/221 [72.9%], PBO: 82/111 [73.9%]). Pts had substantial overall work impairment at BL, with presenteeism contributing most to this (Table).
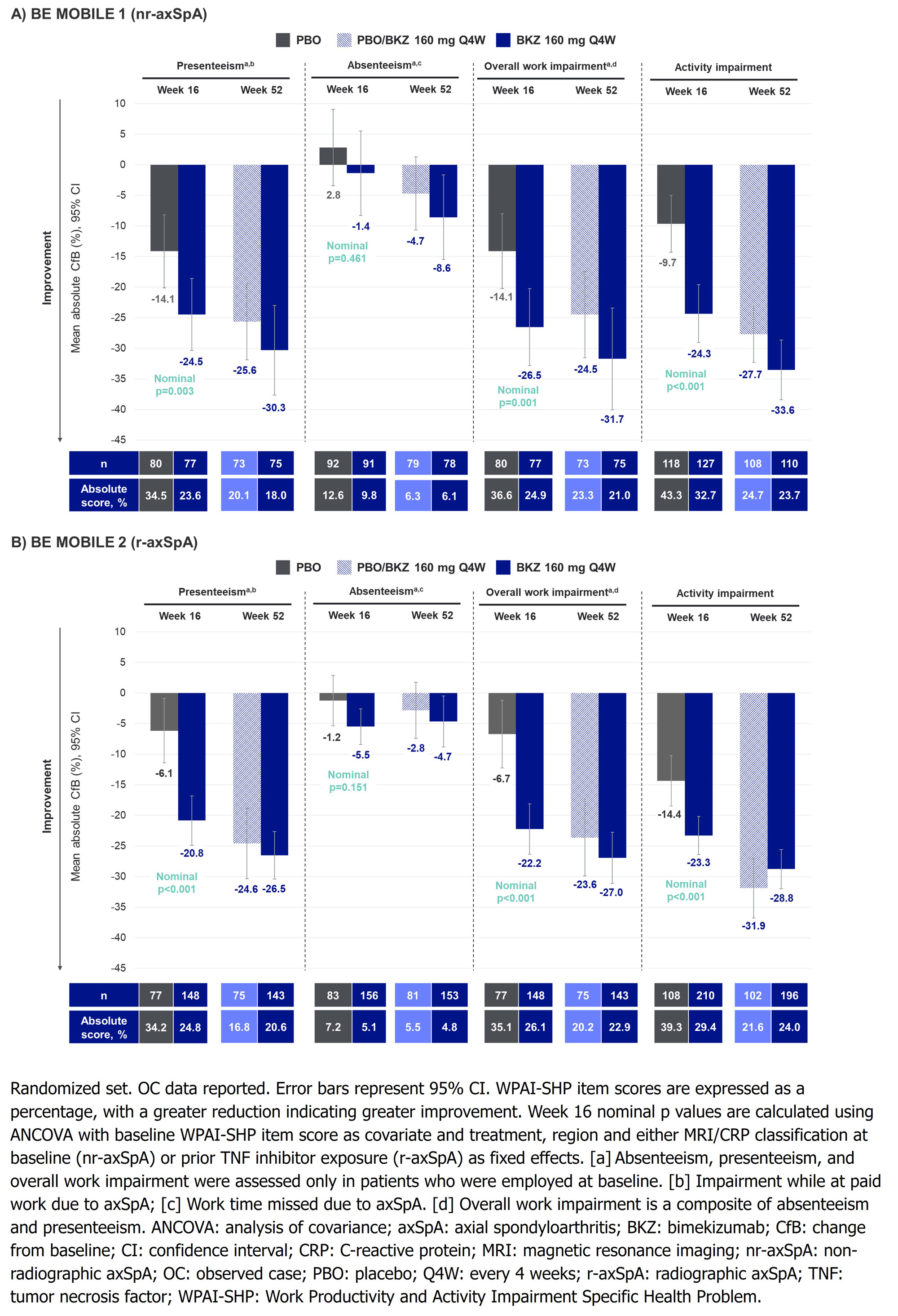
At Wk 16, mean reductions from BL (i.e., absolute improvement) were greater in BKZ- vs PBO-randomized pts for presenteeism (nr-axSpA: –24.5% vs –14.1%, nominal p=0.003; r-axSpA: –20.8% vs –6.1%, nominal p< 0.001), overall work impairment (nr-axSpA: –26.5% vs –14.1%, nominal p=0.001; r-axSpA: –22.2% vs –6.7%, nominal p< 0.001) and activity impairment (nr-axSpA: –24.3% vs –9.7%; r-axSpA: –23.3% vs –14.4%; nominal p< 0.001; Figure). Mean improvements in overall work impairment were sustained or further improved to Wk 52 in BKZ-randomized pts (nr-axSpA: –31.7%; r-axSpA: –27.0%); pts who switched from PBO to BKZ at Wk 16 reached similar levels of improvement to BKZ-randomized pts at Wk 52. Similar trends were seen in presenteeism and activity impairment (Figure).
Mean BL absenteeism scores were low compared with other WPAI items (Table), leaving limited room for improvement. At Wk 16, no clear separation was seen for improvements in absenteeism between BKZ-randomized pts and PBO; this response improved or was sustained in BKZ-randomized pts at Wk 52 (Figure). Absenteeism may also have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Conclusion: BKZ treatment resulted in substantial improvements in overall work and activity impairment at Wk 16, with further improvements at Wk 52 in pts across the full disease spectrum of axSpA.
References:1. Strand V. J Clin Rheumatol 2017;23:383–91; 2. Baraliakos X. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74(suppl 9); 3. Boel A. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:1545–9; 4. Hoepken B. Qual Life Res. 2021;30:945–54.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rudwaleit M, Navarro-Compán V, Deodhar A, Dubreuil M, Mørup M, Taieb V, de la Loge C, Fleurinck C, Massow U, Vaux T, Boonen A. Work Productivity Improved in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Receiving Bimekizumab Treatment over 52 Weeks: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/work-productivity-improved-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-receiving-bimekizumab-treatment-over-52-weeks-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/work-productivity-improved-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-receiving-bimekizumab-treatment-over-52-weeks-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/