Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The progressive degradation of osteoarthritis (OA) cartilage has been associated with articular innate immune responses (IIR) mediated by the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Additionally, overactivation of anabolic pathways like Wingless-Integrated (Wnt) has been linked to OA pathological process. However, certain anabolic signals can significantly reduce TLR4 activation. Accordingly, we aimed to determine whether the Wnt activation modulates TLR4 activity in human articular cells.
Methods: To do this, we evaluated the effect of diverse Wnt activators, (LiCl [0.1-20mM], Bio [1μM], and Wnt3a [100ng/ml]) and inhibitors (anti-β-catenin XAV-939 and PKF-118310) on TLR4 (LPS 100ng/ml) and IL1R (IL1β 0.1ng/ml) mediated IIRs. In primary human healthy & OA chondrocytes (hOC), osteoblasts (hOB), synoviocytes (hOS), mouse chondrocytes (ATDC5), human osteoblasts SaOs2, and human synoviocytes (SW982), gene expression of 25 inflammatory and catabolic genes were evaluated by RT-PCR in normal or TLR4 defective (siRNA) cells. Proteome and secretoma changes were determined by MALDI/TOFF and validated by ELISA. Cell responses were evaluated by MTT assay, Griess assay, and Green Malachite and CASP1 activity.
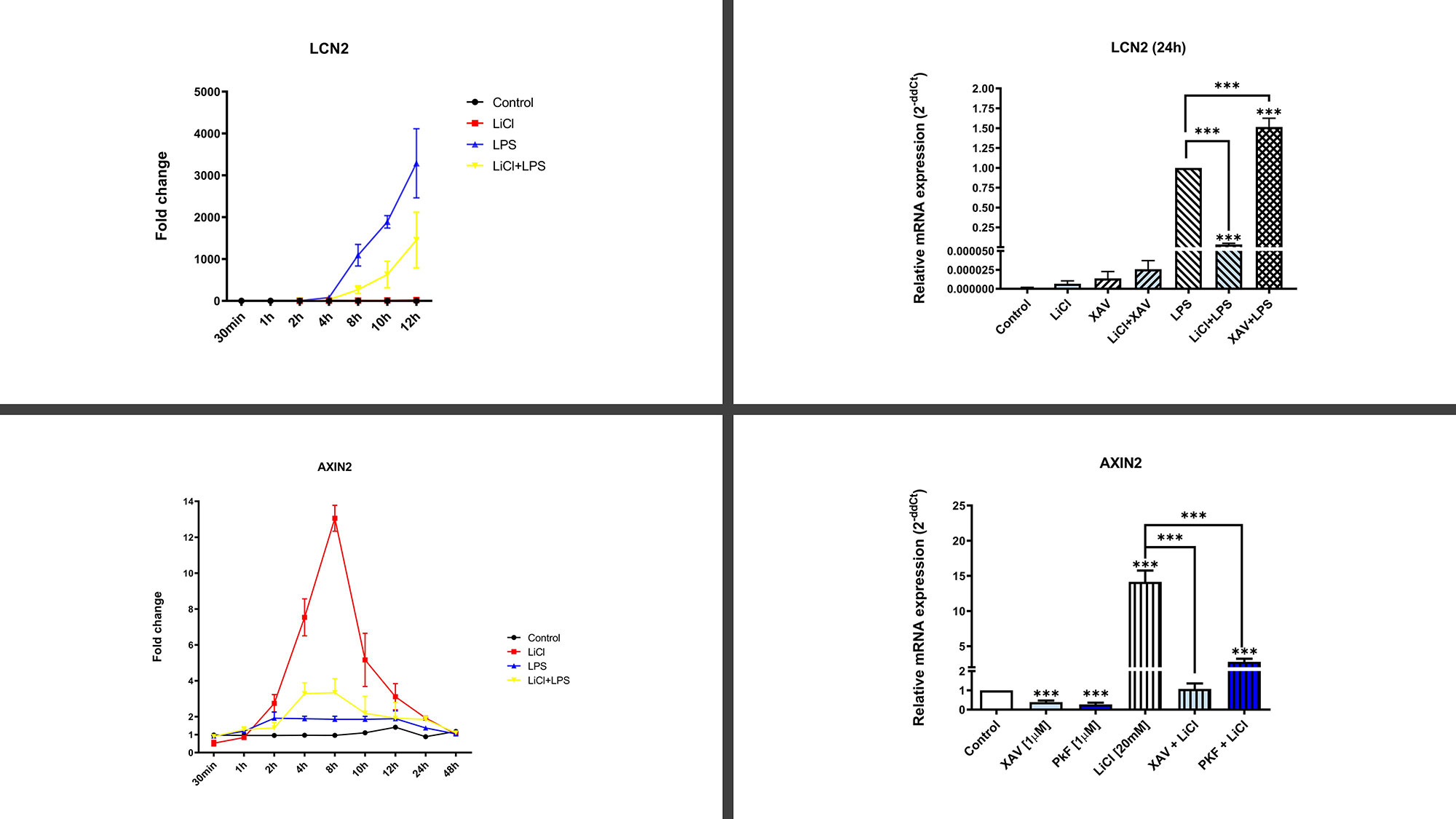
Results: Proteomic results revealed that LiCL activation of Wnt pathway inhibited innate immune responses mediated by receptors TLR4 & IL1R through the inhibition of the signaling pathways NLRP3/IL1, p38/MAPK, NFκB and promoted anabolic effects in articular cells isolated from OA patients. Specifically, LiCl [0.1-20mM] inhibited up to 99% of the gene and protein expression of NOS2, IL6, COX2, MMP9, MMP13, NLRP3, CASP1, IL1β and MAPK14 among other 25 biomarkers (Figure 1). Similar effects of LiCl were obtained with other WNT activators. TLR4 inhibition was validated using the specific TLR4-inhibitor CLI-095 as well as siRNA against TLR4 and NLRP3. Consistent with these data WNT inhibition further increased TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses (Figure 1). Interestingly, we identified that TLR4 and WNT pathway activation were mutually inhibited.
Conclusion: It is known that excessive activation of both TLR4 & WNT is deleterious in the OA context. Our results revealed that WNT activation blocked innate immune responses mediated by TLR4/IL1R in articular OA cells. Conversely, WNT inhibition promoted TLR4-mediated inflammation. Finally, we identified in chondrocytes that WNT and TLR4 were mutually inhibited (Figure 2). All in all, we found a new facet in both signaling pathways and shed some light on the complex OA environment which may prove critical to designing novel therapeutic tools to treat joint inflammatory pathologies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Franco-Trepat E, Alonso Pérez A, Guillán-Fresco M, López Fagúndez M, Pazos-Pérez A, Crespo Golmar A, Piñeiro-Ramil M, Lois Iglesias A, Jorge-Mora A, Gomez R. Wnt Pathway/Innate Immunity Equilibrium in OA Articular Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/wnt-pathway-innate-immunity-equilibrium-in-oa-articular-cells/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/wnt-pathway-innate-immunity-equilibrium-in-oa-articular-cells/