Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex autoimmune disease whose etiology remains largely unknown. Vitamin D has been widely studied due to its association with numerous autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematous, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are associated with levels of 25-hydoxyvitamin D3 (25(OH)D3)(Jiang et al). We hypothesize that a polygenetic risk score (PRS) comprised of alleles from SNPs associated with increasing levels of serum 25(OH)D3 will be inversely associated with the presence of RA autoantibodies (aAbs) among at-risk first-degree relatives (FDRs) of RA subjects.
Methods: The FDR study population was derived from the prospective Study of the Etiologies of Rheumatoid Arthritis (SERA). We tested the following RA-related aAbs; anti-CCP2, anti-CCP3.1, RF-neph, RF IgA, RF IgM, and RF IgG. We selected 189 non-Hispanic white (NHW) FDRs that tested positive for any aAb (aAb+) and compared them to 181 NHW FDRs that tested negative for all autoantibodies (aAb-). FDRs were genotyped using the Illumina MEGAEX BeadChip per Illumina protocols. Five SNPs associated with serum 25(OH)D3 levels were analyzed individually as well as in a PRS: rs4588 (GC), rs12785878 (NADSYN1), rs10741657 (CYP2R1), rs6538691 (AMDHD1), and rs8018720 (SEC23A). A proxy SNP (R2=1.0) was chosen if the GWAS identified SNP was not typed on the MEGAchip. The PRS was calculated by summing the number of copies of the allele associated with increasing serum 25(OH)D3 and ranged from 0 to 10. The PRS was also analyzed as a dichotomous variable (high PRS ≥5 v. low PRS < 5). In a subset of the cohort on whom we had previously measured 25(OH)D3 (N=28), we tested whether the PRS was associated with 25(OH)D3 levels. Logistic regression models were used to test the association between each individual SNP and the PRS variables with the aAb+ outcome. We tested the additive interaction between the SNPs or PRS and vitamin D supplement use.
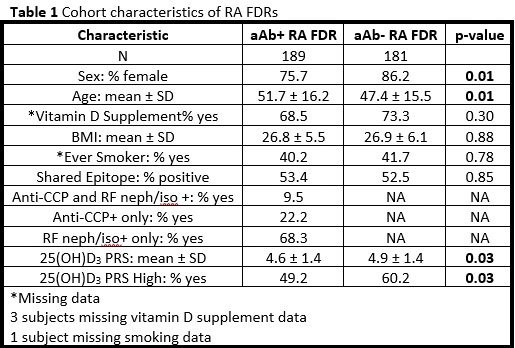
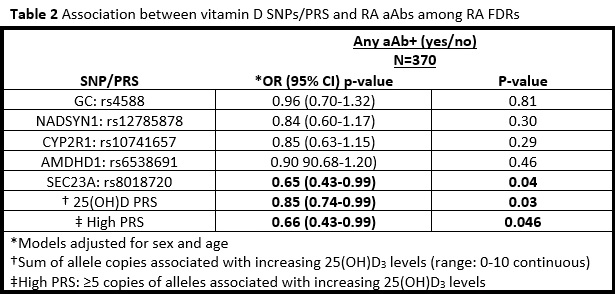
Results: The aAb+ subjects were significantly older and more likely to be male compared to the aAb- subjects (table 1). High PRS was associated with higher levels of 25(OH)D3 compared to low PRS (unadjusted p=0.04 and adjusted for season of blood draw p=0.08, Figure 1). We observed a significant inverse association between the SEC23A SNP rs8018720 and RA aAb+. In addition, both PRS variables were inversely associated with RA aAb+ (Table 2). There was no evidence of an additive interaction between SNPs and vitamin D supplement use.
Conclusion: A higher vitamin D PRS (reflecting higher 25(OH)D3 levels) was inversely associated with RA aAb+. This finding indicates that genes associated with vitamin D regulation may play a protective role in the development of RA aAbs. In particular, the SEC23A SNP may be of interest for future investigation since it was the only vitamin D related SNP individually associated with the aAb+ outcome.
Reference: Jiang X, O’Reilly PF, Aschard H, et al. Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):260. Published 2018 Jan 17. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02662-2
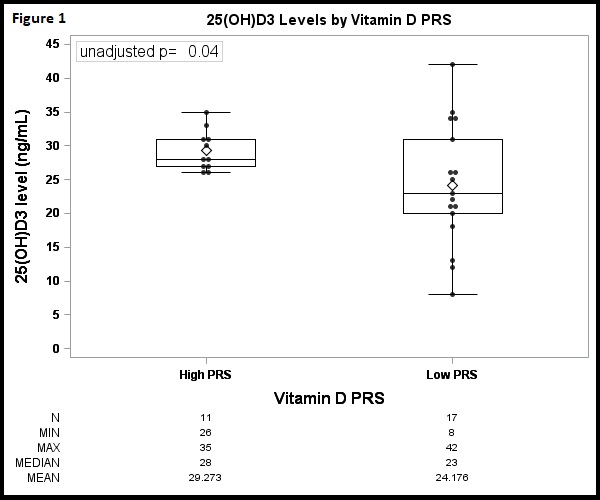 Figure 1: Comparison of mean 25(OH)D3 serum levels by high and low PRS. Subjects with a high vitamin D PRS (≥5 alleles associated with increasing 25(OH)D3 levels) had significantly higher levels of serum 25(OH)D3 (p=0.04).
Figure 1: Comparison of mean 25(OH)D3 serum levels by high and low PRS. Subjects with a high vitamin D PRS (≥5 alleles associated with increasing 25(OH)D3 levels) had significantly higher levels of serum 25(OH)D3 (p=0.04).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bemis E, Young K, Seifert J, Feser M, D. Deane K, Demoruelle M, O'Dell J, Weisman M, Gregersen P, Keating R, Robinson W, Buckner J, Langefeld C, Guthridge J, James J, Holers V, Norris J. Vitamin D Polygenetic Risk Score and the Association with RA Autoantibodies Among First-Degree Relatives of RA Subjects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vitamin-d-polygenetic-risk-score-and-the-association-with-ra-autoantibodies-among-first-degree-relatives-of-ra-subjects/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vitamin-d-polygenetic-risk-score-and-the-association-with-ra-autoantibodies-among-first-degree-relatives-of-ra-subjects/