Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) focuses on achieving remission as a treatment goal. The updated ACR/EULAR remission definition (Boolean criteria 2.0) has raised the threshold for patient global assessment (PtGA) to 2 cm and received endorsement from ACR and EULAR. The revised Boolean 2.0 criteria classify more patients as achieving remission and show increased agreement with index-based criteria in US and European patients. This study aimed to validate the Boolean 2.0 criteria, assess their agreement with index-based remission criteria, and evaluate their predictive value for quality of life (QoL) compared to Boolean 1.0 criteria in Korean patients receiving targeted therapy.
Methods: Data from a multicenter prospective study of Korean patients with RA initiating biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs or Janus kinase inhibitors were analyzed. Remission rates according to Boolean 2.0 and Boolean 1.0 criteria, as well as other index-based remission criteria, were measured at 24 weeks. Agreement between Boolean 2.0 criteria and index-based criteria was analyzed and compared with Boolean 1.0 criteria. Additionally, the likelihood ratio (LR) of Boolean 2.0 criteria in predicting improved QoL (health assessment questionnaire [HAQ] score ≤0.5 or EQ-5D =1) at 48 weeks was estimated and compared to Boolean 1.0 criteria.
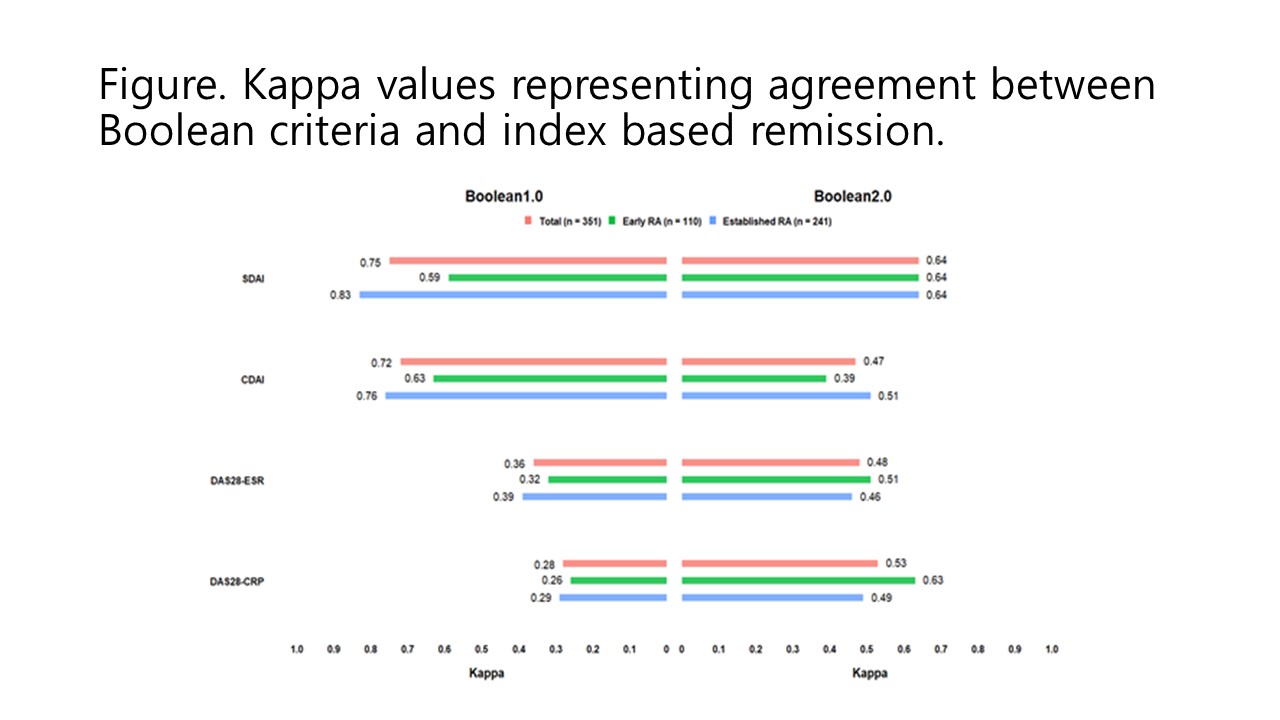
Results: A total of 351 RA patients were included, with a mean age of 53.2 years, and 86.9% were female. Boolean 2.0 criteria showed better agreement than Boolean 1.0 criteria for remission based on DAS28-ESR (kappa 0.48 vs. 0.36) and DAS28-CRP (kappa 0.53 vs. 0.28). However, Boolean 1.0 criteria exhibited higher concordance with SDAI (kappa 0.75) or CDAI (kappa 0.72) than Boolean 2.0 criteria (kappa with SDAI 0.64 and kappa with CDAI 0.47, respectively). Regarding predictive value for better QoL, remission based on Boolean 1.0 criteria showed higher LR compared to remission based on Boolean 2.0 criteria (6.01 vs. 2.49 for HAQ ≤0.5 and 3.53 vs. 2.37 for EQ-5D =1, respectively).
Conclusion: Among Korean patients with RA initiating targeted therapy, the Boolean 2.0 criteria showed enhanced agreement with remission assessments based on DAS28-ESR or DAS28-CRP, while the agreement with remission based on SDAI or CDAI was not improved compared to the Boolean 1.0 criteria. Furthermore, remission defined by the Boolean 1.0 criteria demonstrated a higher predictive value for improved QoL when compared to the Boolean 2.0 criteria.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cho S, Song Y, Han J, Kim H, Nam E, Sung Y. Validation of Boolean 2.0 Criteria for Assessing Remission and Predicting Quality of Life in Korean Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Undergoing Targeted Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-boolean-2-0-criteria-for-assessing-remission-and-predicting-quality-of-life-in-korean-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-undergoing-targeted-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-boolean-2-0-criteria-for-assessing-remission-and-predicting-quality-of-life-in-korean-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-undergoing-targeted-therapy/