Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and kidney biopsy is the gold standard for its diagnosis and treatment1, 2. The development and validation of tools for predicting histological class are important, especially when kidney biopsy is not available or there is a contraindication to the procedure.
Methods: 196 SLE patients who underwent kidney biopsy were included in a retrospective cross-sectional study in the validation cohort. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, accuracy, and positive and negative likelihood ratios were analyzed and compared to 69 LN patients of the development cohort3. Chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests were used for categorical variables and Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney for non-categorical, p< 0.05 was considered significant.
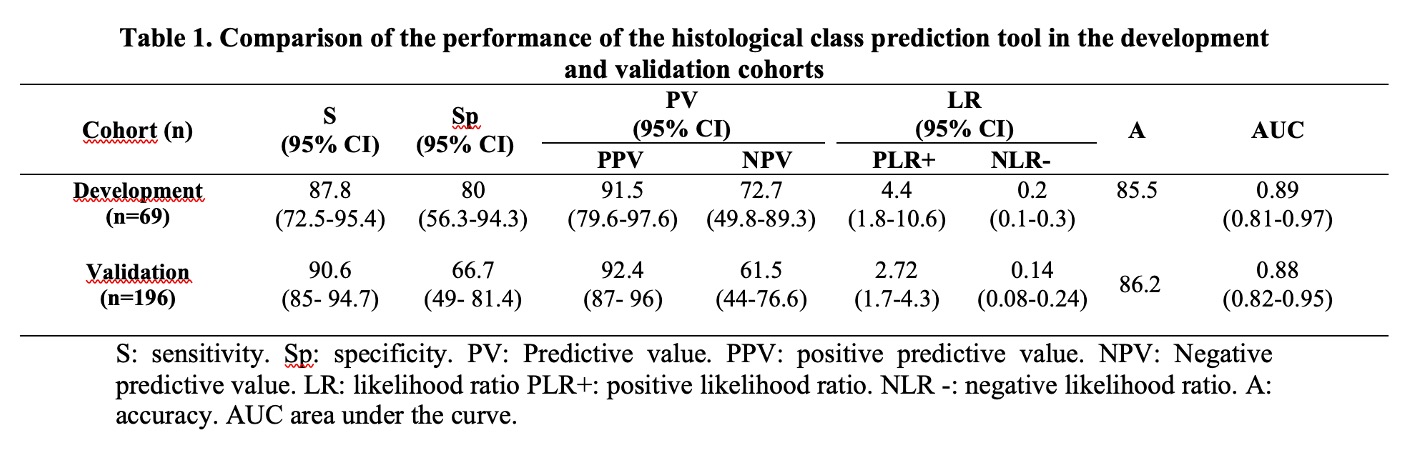
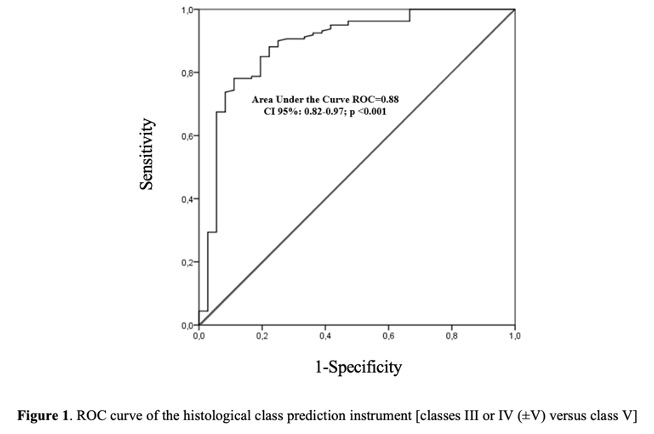
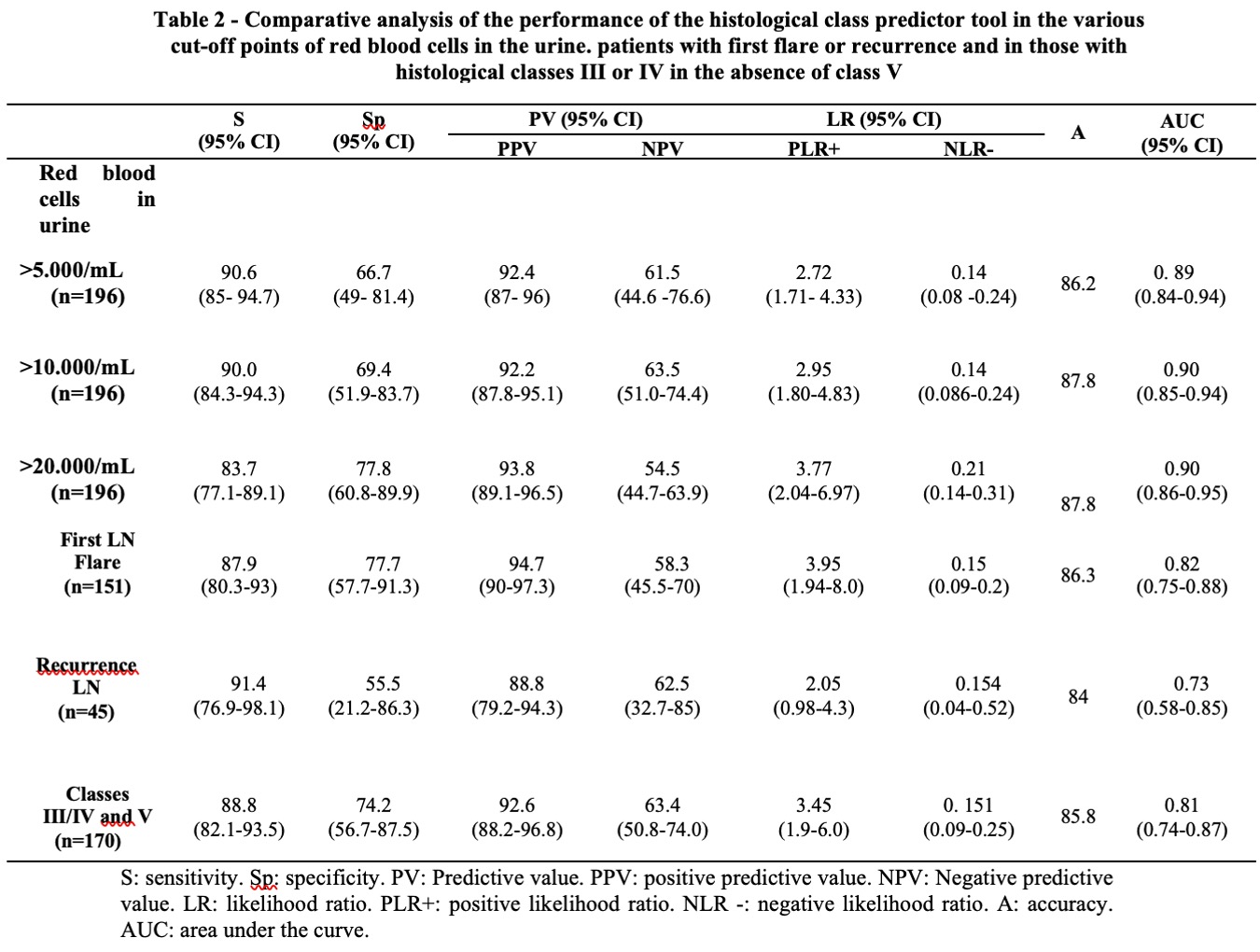
Results: 81.6% of the patients were female, 60.2% were non-Caucasian and the mean age at the time of the biopsy was 31.2±10.4 years. Thirty patients presented class III, 104 class IV, 36 class V and 26 mixed classes (7 class III+V and 19 class IV+V). In the validation cohort, sensitivity was 90.6%, specificity 66.7%, positive predictive value 92.4%, accuracy 86.2% and area under the curve ROC 0.88 in predicting histological class III or IV(±V) versus class V (table 1, figure 1). The presence of red blood cells in urine above 5,000 /mL demonstrated greater sensitivity, while the presence of red blood cells in urine above 20,000 /mL showed greater specificity with similar accuracy (Table 2). Performance of the tool was similar in patients with the first episode of LN and in those who underwent a biopsy during LN recurrence ( >1 flare), with greater specificity in patients in the first episode and in those who did not have mixed classes (Table 2).
Conclusion: The validation of a tool to predict proliferative histologic class showed similar performance to that found in the development cohort, without difference in accuracy with different cut-off points for red blood cells in urine or number of LN flares. Histologic class prediction tools are useful when kidney biopsy is not available or there is a contraindication to the procedure.
References
1. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Lupus Nephritis Work Group. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the management of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 2024;105(1S):S1-69.
2. Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Andersen J et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2024;83:15-29.
3. Silaide de Araújo Júnior A, Sato EI, Silva de Souza AW et al. Development of an instrument to predict proliferative histological class in lupus nephritis based on clinical and laboratory data. Lupus 2023;32:216-24.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Silaide De Araújo-Júnior A, Sato E, Wagner Silva de Souza A, Jennings F, Mastroianni Kirsztajn G, Sesso R, Reis Neto E. Validation Cohort of a Tool to Predict Proliferative Histological Class in Lupus Nephritis Based on Clinical and Laboratory Data – LUCAS Study (Lupus Nephritis Class Assessment System) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-cohort-of-a-tool-to-predict-proliferative-histological-class-in-lupus-nephritis-based-on-clinical-and-laboratory-data-lucas-study-lupus-nephritis-class-assessment-system/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-cohort-of-a-tool-to-predict-proliferative-histological-class-in-lupus-nephritis-based-on-clinical-and-laboratory-data-lucas-study-lupus-nephritis-class-assessment-system/