Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to compare the performance of three validated algorithms for 10-year global cardiovascular risk stratification (GCVR): the European Systemic Coronary Risk (SCORE-2) updated in 2021 [1], the Italian “Progetto Cuore” algorithm (PCA) [2], and the Expanded Risk Score in Rheumatoid Arthritis (ERS-RA) [3] in an Italian RA population.
Methods: RA patients from a multicentre cohort, aged 40-69 years with no previous history of CV disease, were recruited in 2019 and longitudinally followed until 2023 for fatal and non-fatal CV events. Each GCVR was individually calculated at baseline using the electronic formats of the above three algorithms, multiplied by 1.5 when appropriate [4]. All patients were treated according to the “treat to target” strategy [5]. Statistical analysis was performed using STATA v.18 software with proper tests. The expected CV events were adjusted proportionally since the follow-up was less than 10 years. The performance of the algorithms was evaluated by “calibration”, expressed as standardized incidence ratios (SIR) between observed and expected events, and “discrimination”, defined as the ability of the risk function to separate high-risk from low-risk patients and expressed as the area under the receiver operator curve (AUROC), assuming that the expected rates were fixed and observed events followed a Poisson distribution.
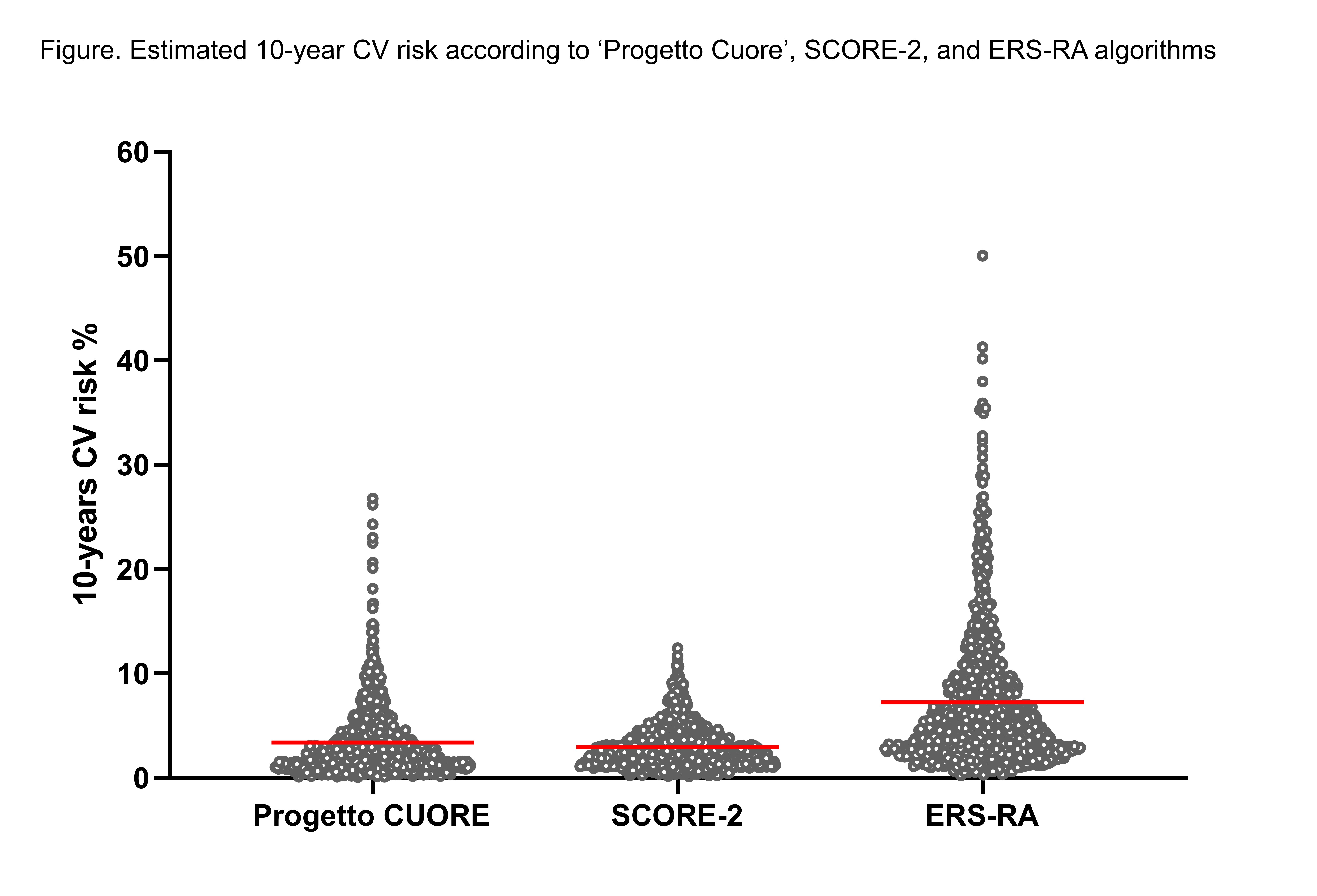
Results: The recruited RA population (n.971; women 79.5%; mean age 57.9±7.4 years; mean disease duration 142±110 months) had a low risk of CV events globally, according to SCORE-2, PCA, and ERS-RA equations estimating a mean 10-year GCVR of 4.3%, 5% and 7.2%, respectively (see Figure). The PCA, SCORE-2, and ERS-RA predicted High CV risk in 1.7%, 2.6%, and 4.0% of patients, respectively. Examining the correlation, we observed that ERS-RA had a Pearson r of 0.79 (95%CI 0.73-0.78; p< 0.0001) compared to PCA and of 0.70 (95%CI 0.67-0.73; p< 0.0001) compared to SCORE-2. The incidence rate of fatal and non-fatal CV events was 0.25/100 patient-years. Overall, the SIR for the SCORE-2 was 0.60 (95%CI 0.32-1.11), for the PGC was 0.52 (95%CI 0.28-0.96), and for the ERS-RA was 0.36 (95%CI 0.19-0.66), indicating an overestimation of the observed CVD risk, with no statistically significant differences among the three algorithms. The discriminatory power, calculated using AUROC, was 0.611 for the PCA, 0.579 for the SCORE-2, and 0.596 for the ERS-RA.
Conclusion: The present study evaluated the prediction of GCVR in an Italian RA population for the first time by comparing three different estimating risk equations. The ERS-RA algorithm did not predict CVD risk more accurately in Italian RA patients than the CVD risk calculators developed for the general population multiplied by 1.5 as recommended by EULAR [4].
References.
1. SCORE-2 Working Group and ESC CV risk collaboration. Eur Heart J 2021;42:2439-5
2. Palmieri L, et al. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2004;40:393-399
3. Solomon DH, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1995-2003.
4. Agca R, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:17-28.
5. Parisi S, et al. Reumatismo. 2019 Sep 23;71(S1):22-49.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cacciapaglia F, Erre G, Piga M, Bartoloni Bocci E, Manfredi A, Favalli E, Chimenti M, Guiducci S, Celletti E, Corrado A, Giollo A, PARISI S, Giovannini I, Gremese E, Spinelli F, Sakellariou G, Viapiana O, Atzeni F. Validation Analysis of the Expanded Risk Score for Rheumatoid Arthritis in a Multicentre Italian Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-analysis-of-the-expanded-risk-score-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-multicentre-italian-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-analysis-of-the-expanded-risk-score-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-multicentre-italian-cohort/