Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: PROs, Biomarkers, Systemic Inflammation & Radiographs
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Novel subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13 SC) was developed to augment the flexibility in the therapeutic use of infliximab and non-inferiority (NI) of CT-P13 SC versus CT-P13 intravenous (IV) was demonstrated for efficacy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)1. CT-P13 SC 120 mg biweekly showed relatively high therapeutic trough levels during the treatment period, which consistently helps in maintaining efficacy over time. Since immunogenicity has clinical importance in patients using anti-TNF alpha agents and there is a general presumption that SC route is more immunogenic than IV route, this needs careful assessment. In this report, immunogenicity assessment of CT-P13 SC with further impact analysis was performed on the pivotal data set1 to determine whether there was any correlation between the magnitude of anti-drug antibody (ADA) positivity and clinical outcomes in RA patients or not.
Methods: The immune response against CT-P13 in human serum was detected using an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) platform with an Affinity Capture Elution (ACE) step. An ADA ECL ACE assay showed the ability to detect ADA at low levels in all samples regardless of residual drug in serum (25 ng/mL ADA in the presence of 80 μg/mL of CT-P13 in RA patient serum). To investigate the impact of ADA titer on PK, efficacy, and safety, key clinical parameters were assessed by visit-based ADA titer quartile. All patients who had ‘Positive’ ADA status result at each visit were included in the analysis and categorized into 4 groups using the 25th, 50th, 75th percentiles of ADA titer result, respectively.
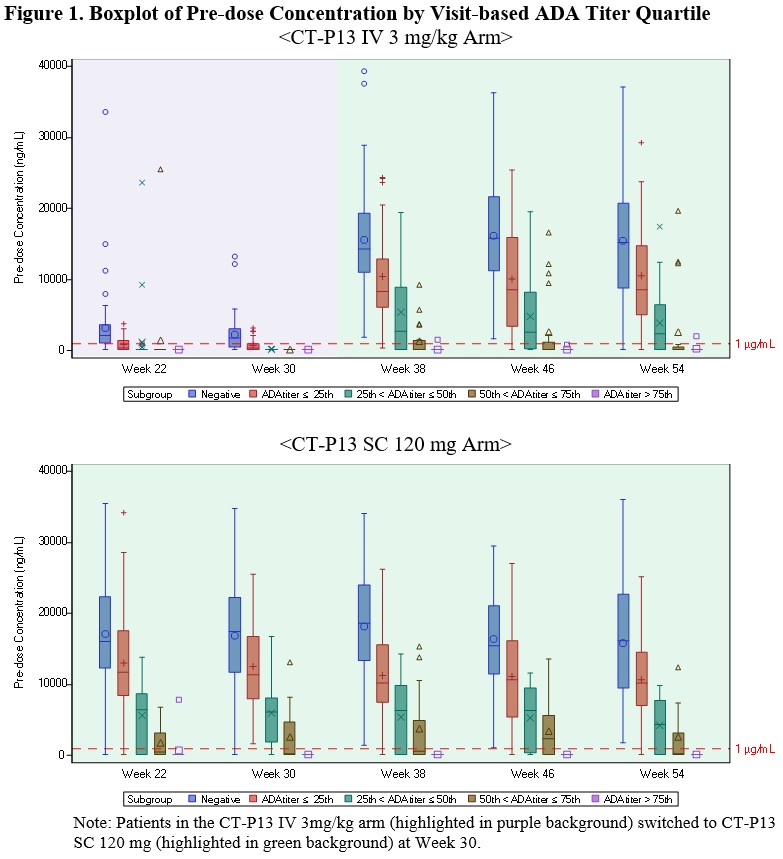
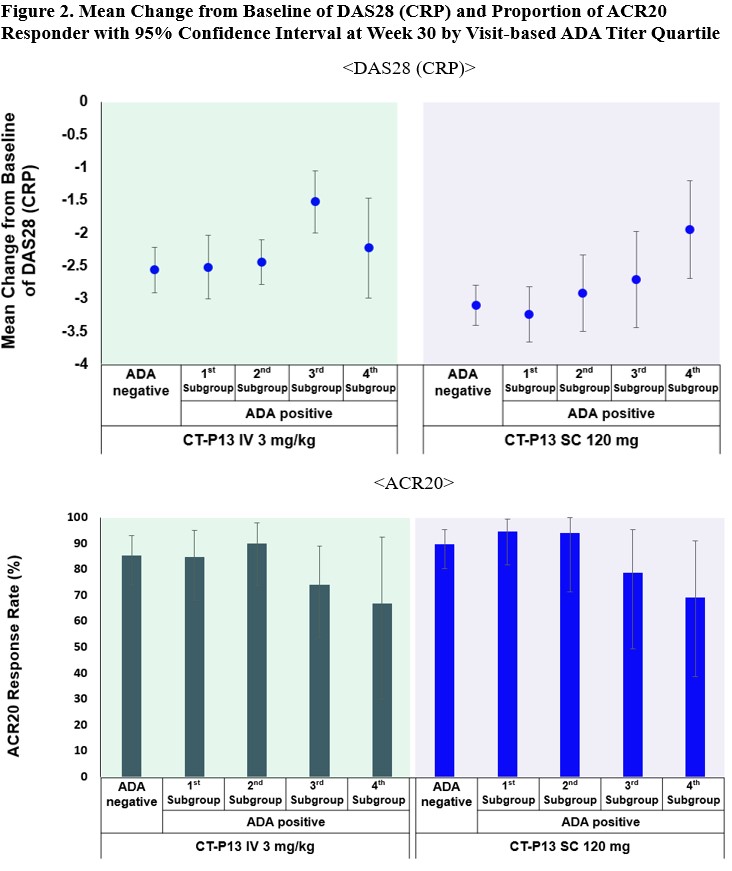
Results: The 4 subgroups categorized by quartiles at each visit from week 22 to week 54 were: 1st (ADA titer ≤ 3), 2nd (3 < ADA titer ≤ 9), 3rd (9 < ADA titer ≤ 27) and 4th (27 < ADA titer). There was a trend for pre-dose concentration to decrease as ADA titer increases for both CT-P13 SC and CT-P13 IV arms as expected (Figure 1). Patients in the 1st and 2nd subgroup maintained a sufficient therapeutic drug concentration level. Figure 2 shows the correlation between ADA titer and efficacy outcomes where the change from baseline of DAS28 (CRP) and the proportion of patients achieving ACR20 were lower in the 3rd and 4th subgroup than 1st and 2nd subgroup. The ADA impact was especially apparent in the 4th subgroup where the mean pre-dose concentration of the patients was below the therapeutic drug concentration level (1 μg/mL), which led to worse efficacy outcomes in both IV and SC arms than other subgroups. Nevertheless, no impact of ADA on the safety profile in both arms was observed. A neutralizing antibody (NAb) method with enhanced drug tolerance but limited performance was also developed and clinical consequences of NAb titer in terms of PK, efficacy, and safety were not different from the results with ADA.
Conclusion: The analysis of both ADA positivity and titer is clinically meaningful in the prediction of PK profile and clinical response. CT-P13 SC administration did not result in a greater incidence of ADA compared to the CT-P13 IV and there were no clinical differences depending on the formulation.
References:
1. Westhovens R, et al. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019;78:1158-1159.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Westhovens R, Yoo D, Wiland P, Zawadzki M, Ivanova D, Berrocal Kasay A, Chalouhi E, Balázs E, Lee S, Kim S, Suh J, Hwang C, Choi D. Utility of Measuring the Immunogenicity to CT-P13 for Subcutaneous Use in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: 1-Year Results from a Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Pivotal Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-measuring-the-immunogenicity-to-ct-p13-for-subcutaneous-use-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-1-year-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-controlled-pivotal-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/utility-of-measuring-the-immunogenicity-to-ct-p13-for-subcutaneous-use-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-1-year-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-controlled-pivotal-trial/