Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 7, 2017
Title: ARHP Rehabilitation Science
Session Type: ARHP Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Knee osteoarthritis (OA) affects approximately 6% of adults and is a leading cause of disability among U.S. adults. Physical activity (PA) is known to improve the health status of those with knee OA. In 2007-2008, 49% of all employed adults failed to meet U.S. PA recommendations. This pilot study examined the feasibility of a scalable worksite PA program for employees with knee OA symptoms working at a large insurance firm.
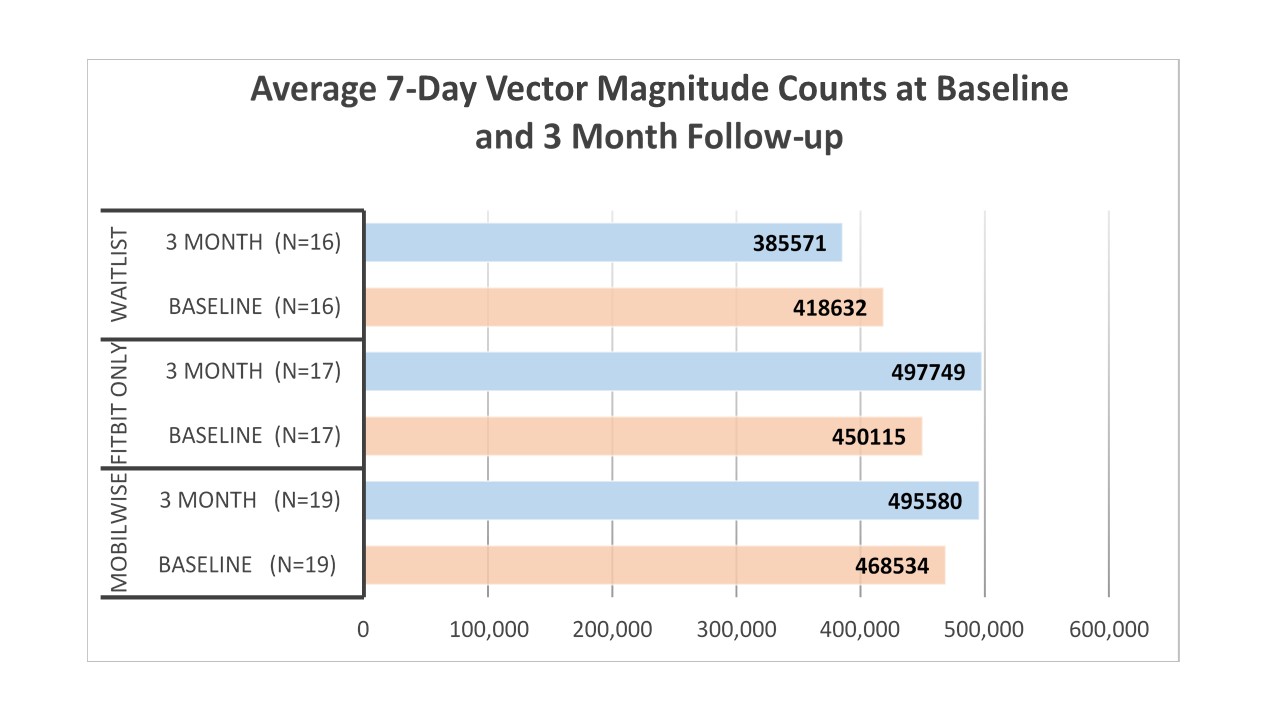
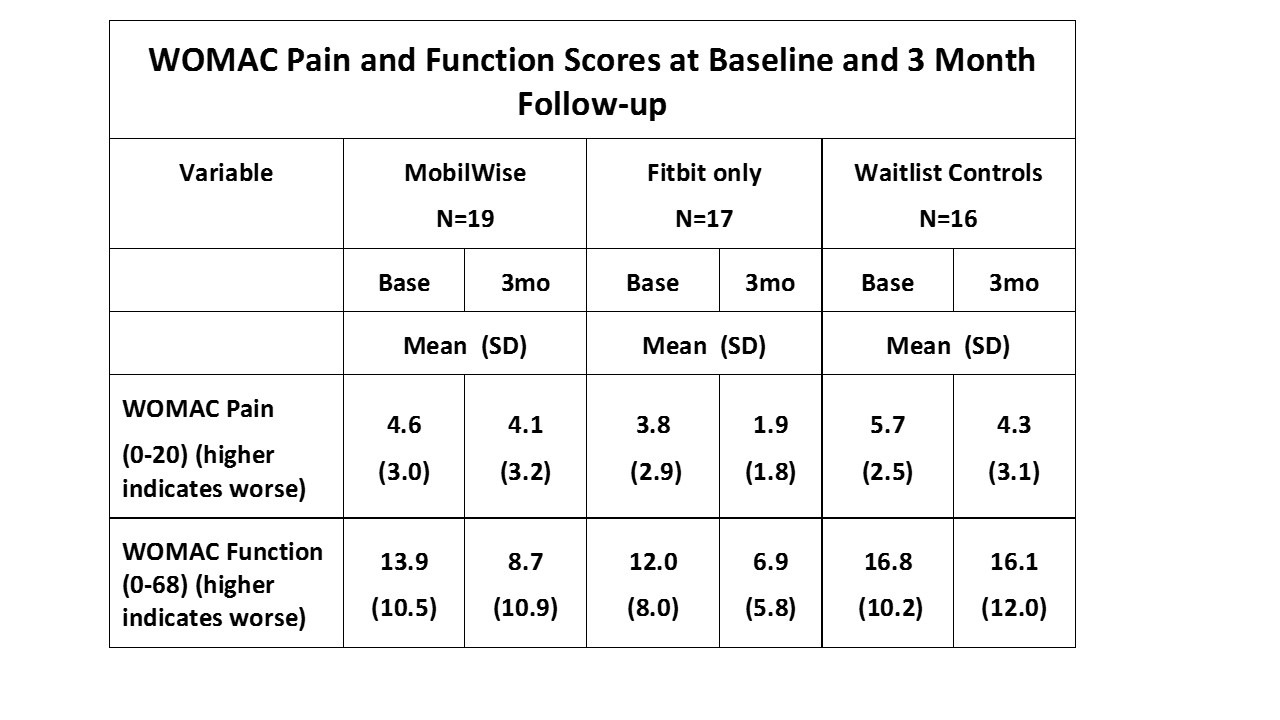
Methods: After exclusion criteria, 61 subjects were randomized to either the MobilWise (MW) lifestyle intervention (n=20), the Fitbit Only (FO) intervention (n= 21), or waitlist control (WC) group (n= 20). Randomization was stratified based on current PA tracker ownership/use and meeting/not meeting PA recommendations of 150 minutes/week of moderate-vigorous PA. MW and FO received an education session including detailed instruction on PA/benefits and the Fitbit Flex monitor. MW group also received weekly individual motivational interviewing-based personalized coaching sessions by phone for 12 weeks. MW and FO groups were asked to synchronize their Fitbit at least twice weekly using the Fitbit App to transfer data to a storage service (Fitabase®), but only MW data were viewed weekly for coaching feedback. WC received the education session and a Fitbit at study’s end. Measures at baseline and 3 month follow-up included demographics, PA assessed by triaxial accelerometer (average 7-day vector magnitude counts), and WOMAC pain and function. Feasibility of conducting a larger RCT was assessed by tracking enrollment/retention. Acceptability of MW and FO interventions was assessed by tracking the personal monitor synchronization frequency on Fitabase® and the number of completed coaching encounters.
Results: Participants at baseline were primarily obese (59%), female (73%), Caucasian (44%), with mean age 51 years, BMI 33 kg/m2. Of 10 participants not completing the study, 6 left the company and 4 dropped. Completing participants were not different (BMI and waist circumference) from non-completers.
Feasibility assessment revealed 63% of those screened via web tool signed consents. Proportion of monitored participants who regularly synchronized Fitbits with Fitabase® was 93%. Retention ranged from 80% (WC), 80% (FO) to 95% (MW), with 100% completing MW coaching calls.
Conclusion: MobilWise was moderately successful at improving PA levels and self-reported function in employees with knee OA symptoms, but may not be required to produce change in all those at risk. The Fitbit Only group had equally good/better (improved pain) results at 3 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Semanik P, Lee J, Pellegrini C, Song J, Chang RW. Using Fitbits. Fitabase®, and Remote Coaching to Increase Physical Activity in Employees with Knee Osteoarthritis Symptoms [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-fitbits-fitabase-and-remote-coaching-to-increase-physical-activity-in-employees-with-knee-osteoarthritis-symptoms/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/using-fitbits-fitabase-and-remote-coaching-to-increase-physical-activity-in-employees-with-knee-osteoarthritis-symptoms/