Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) is increasingly being used to assess the activity of axial disease in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). However, five out of six BASDAI questions are not specific to axial disease. The objective of this study was to evaluate the specificity of BASDAI for axial disease in PsA compared to PsA without axial disease by examining differences in baseline scores, change in scores after therapy initiation, and responsiveness between the two groups.
Methods: Participants (pts) were enrolled in the Psoriatic Arthritis Research Consortium (PARC) longitudinal observational study between 2017-Jan 2020. In this study we included PsA pts initiating therapy with a BASDAI score at baseline and follow up. Pts were classified as having axial disease if they a) fulfilled the ASAS axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) classification criteria or b) had imaging (MRI, X-ray, or CT) features of axial disease (sacroiliac joints or spine). We descriptively report scores (BASDAI, individual BASDAI items, patient global, patient pain, and the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data (RAPID3)) at baseline and change in scores following therapy initiation by presence or absence of axial disease.
Results: Among 117 PsA pts who initiated therapy with a BASDAI at baseline and follow up, the mean age was approximately 49 years, 55% were female, and the mean BMI was 29.7 (Table 1). Among these pts, 30 (26%) had imaging evidence of axSpA, 33 (30%) met ASAS classification criteria (7 had missing data for axSpA criteria), and 40 (34%) met one or both of these criteria. The mean baseline BASDAI score at the time of therapy initiation was 5.5 among those with axial disease by either definition and 4.8 among those without axial disease. This was similar when using either ASAS criteria or imaging evidence of axSpA. Item 2 on the BASDAI, which asks about spine pain, was higher in those with axial disease (5.2) compared to those without (4.5). Item 5 (stiffness) was higher in those without axial disease compared to those with axial disease (5.1 vs 3.7). Patient pain, patient global and the RAPID3 were slightly higher in those with axial disease.
The mean change for BASDAI was -0.81 (SD 2.0) among all pts initiating therapy and similar among axial vs peripheral only (-0.75 vs -0.83). Among the subgroup of 95 pts initiating a TNFi or IL17i, mean change in BASDAI was -0.93 (SD 2.0) with similar differences in SRMs compared to the entire group (-0.47 vs -0.41 respectively) thus only the full cohort of therapy initiators is presented. The SRMs for the individual BASDAI items varied from 0.12 (item 6) to 0.41 (item 5) (Table 2). SRMs were similar across axial vs peripheral only disease for BASDAI (-0.37 vs -0.44 respectively) and individual items. The SRMs for the patient global, patient pain, and RAPID3 however were greater among pts with axial disease (Table 2).
Conclusion: While BASDAI was initially developed as an axial disease measure and works well in axSpA, it is a broad measure of disease activity and current symptoms. The BASDAI has similar scores, change in scores, and responsiveness in PsA regardless of the presence of axial disease.
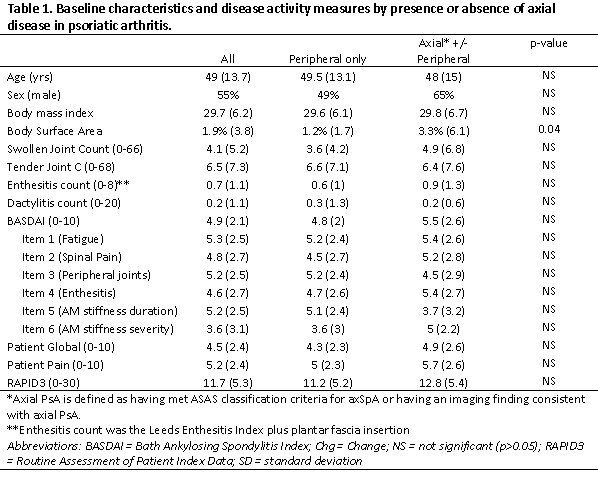 Table 1. Baseline characteristics and disease activity measures by presence or absence of axial disease in psoriatic arthritis.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics and disease activity measures by presence or absence of axial disease in psoriatic arthritis.
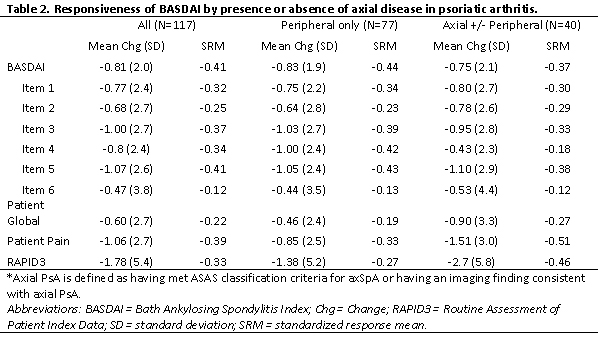 Table 2. Responsiveness of BASDAI by presence or absence of axial disease in psoriatic arthritis.
Table 2. Responsiveness of BASDAI by presence or absence of axial disease in psoriatic arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reddy S, Husni M, Scher J, Craig E, Ogdie A, Walsh J. Use of the BASDAI in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients with and Without Axial Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-the-basdai-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-axial-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-the-basdai-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-with-and-without-axial-disease/
