Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes III: Best Day (RA Subpopulations)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: ORAL Surveillance (NCT02092467; a post-authorization safety study of tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily [BID] vs TNF inhibitors [TNFi]) found higher incidence of major adverse cardiovascular (CV) events (MACE) with tofacitinib vs TNFi. A previous analysis of the study indicated that the risk difference was primarily found in patients (pts) with history of atherosclerotic CV disease (ASCVD) and also observed low frequency of baseline statin use. Current management guidelines recommend a high-intensity statin for pts with history of ASCVD or a high 10-year predicted risk of MACE (CV risk), and a moderate-intensity statin for pts with intermediate CV risk.
In this post hoc analysis, we aimed to clarify (1) statin usage by baseline CV risk profile, (2) the impact of statins on lipid levels, and (3) the association between statin use and incident MACE with tofacitinib vs TNFi in ORAL Surveillance.
Methods: Pts with RA aged ≥50 years and ≥1 additional CV risk factor received tofacitinib 5 mg (N=1455) or 10 mg (N=1456) BID, or TNFi (N=1451). Use of statins was assessed at baseline and during the study and classified as high-, moderate-, or low-intensity statin treatment. Low- and high-density lipoproteins (LDL and HDL) were determined in fasting serum. Hazard ratios (HRs; time to first event analysis) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were evaluated based on simple Cox proportional hazard models.
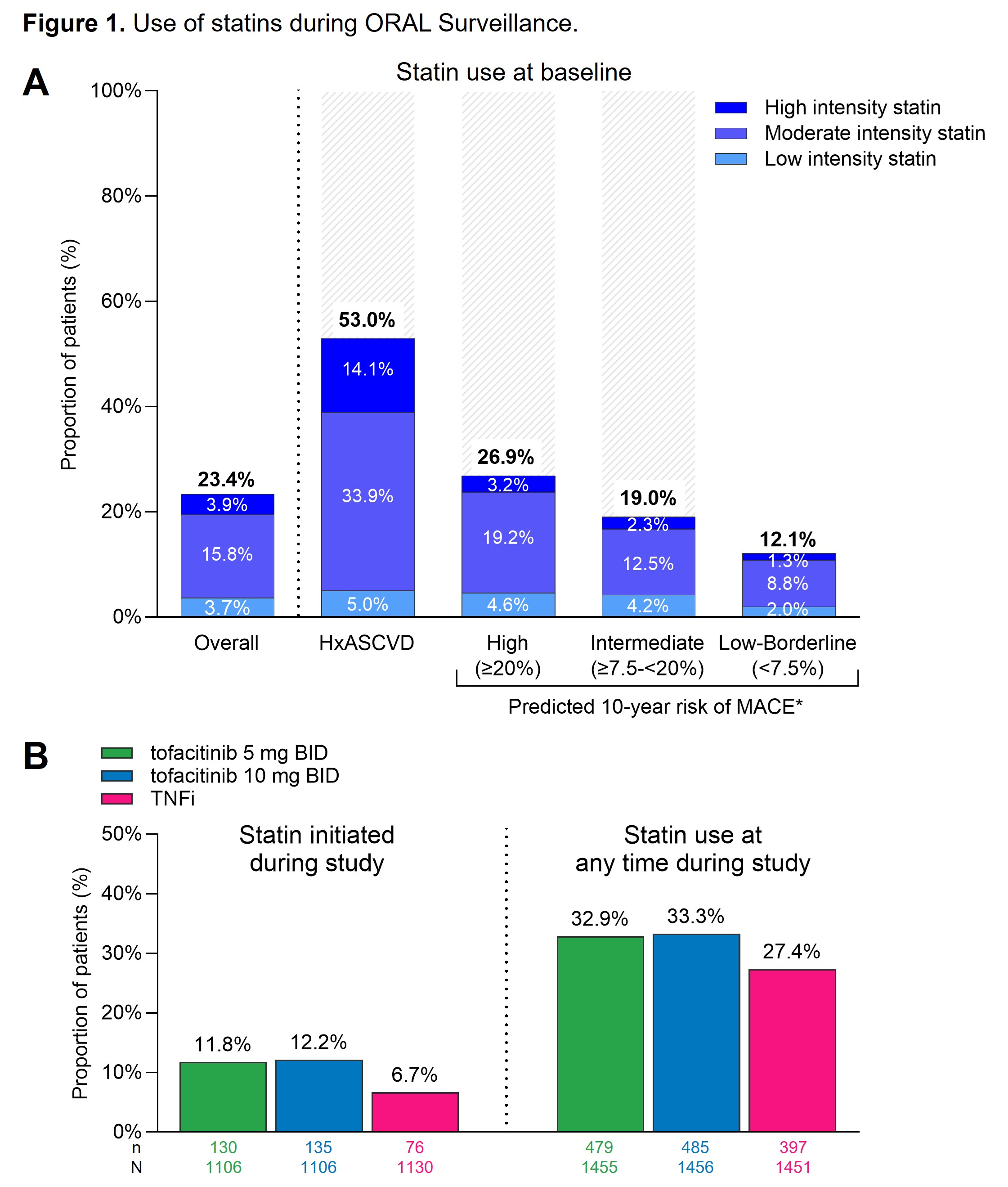
Results: Among pts with history of ASCVD or high CV risk, 53.0% and 26.9%, respectively, used a statin at baseline (Figure 1A). Few of these used a high intensity statin. 19.0% of pts with intermediate CV risk received a statin at baseline, predominantly a moderate-intensity statin (Figure 1A). Baseline statin use was similar in tofacitinib and TNFi treated pts. Initiation of a statin during the study was observed in relatively few pts and more frequently with tofacitinib (11.8% [5 mg BID] and 12.2% [10 mg BID]) than with TNFi (6.7%) (Figure 1B).
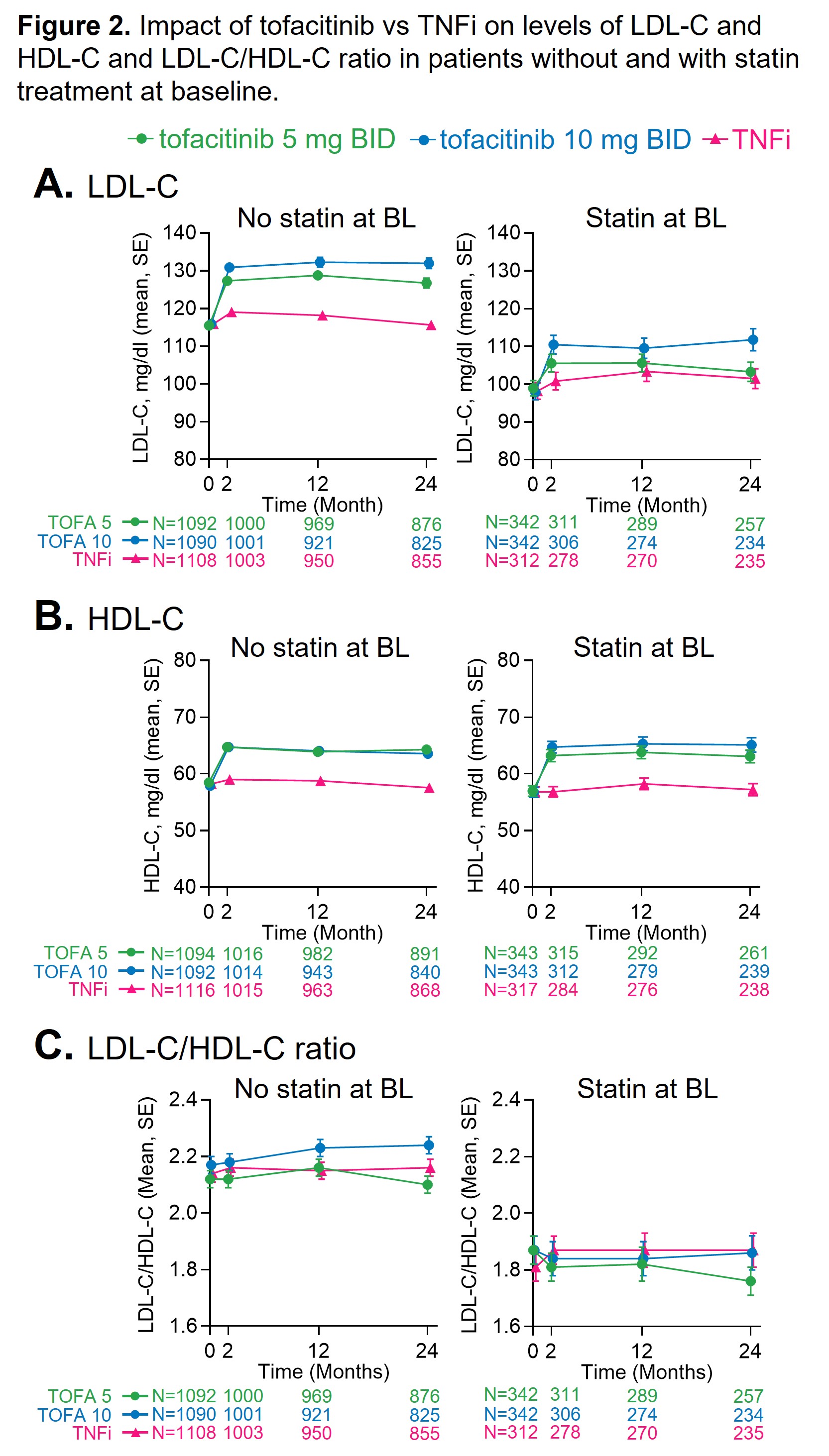
Baseline LDL and the LDL:HDL ratio were lower in pts using a statin (Figure 2). In pts with or without statins, LDL and HDL increased from baseline and to a larger extent with tofacitinib than with TNFi (Figure 2).
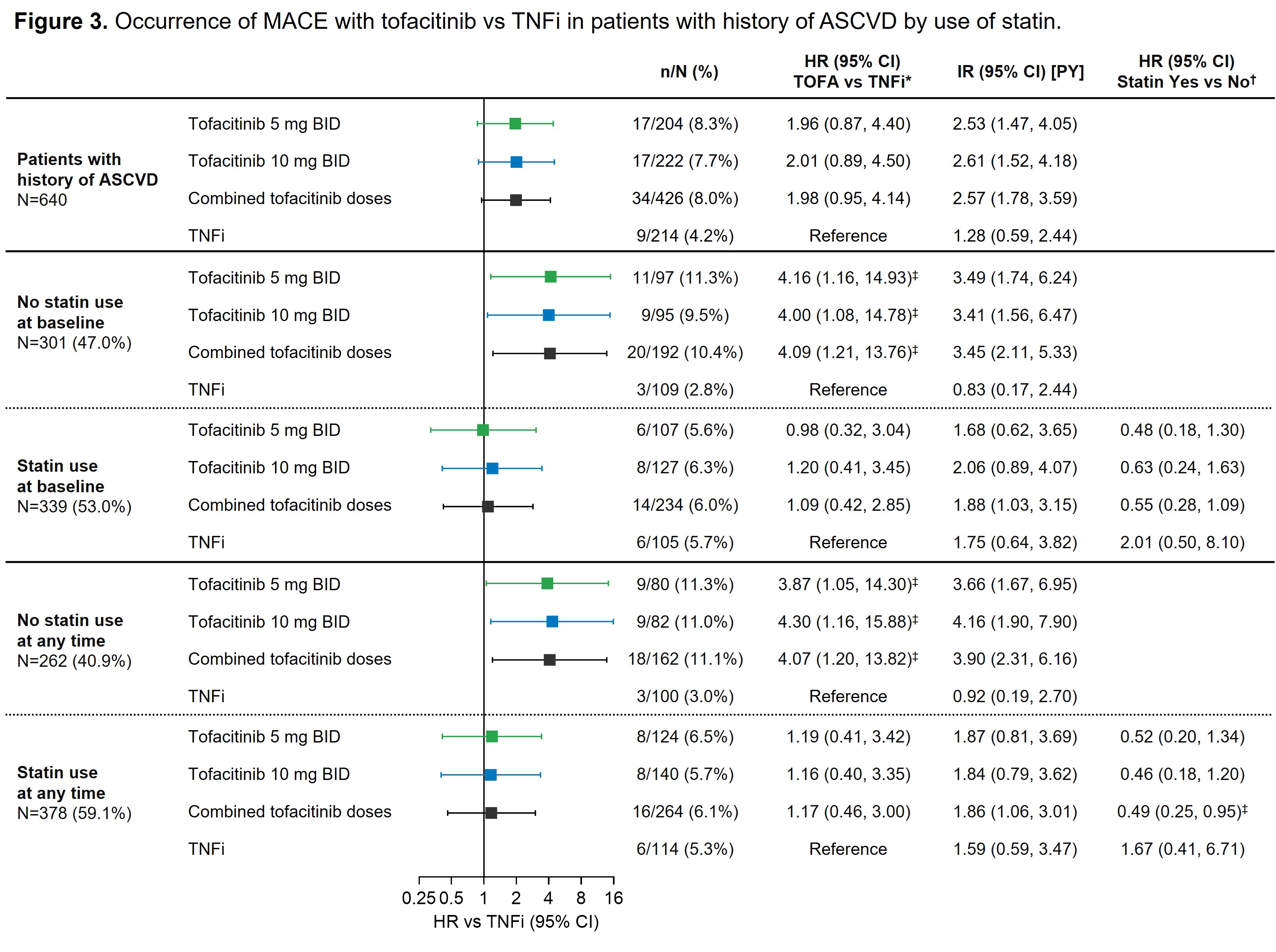
In the overall study population and across treatments, MACE rates were similar in pts with or without baseline statin use (data not shown). Among tofacitinib-treated pts with history of ASCVD, occurrence of MACE over follow-up was lower in pts using statins at any time vs those without statin use (HR 0.49 [95% CI 0.25, 0.95]) (Figure 3). This pattern was not observed in TNFi-treated pts with history of ASCVD. Among pts with ASCVD history and no use of statins at any time, occurrence of MACE was higher with tofacitinib vs TNFi (HR 4.07 [95% CI 1.20, 13.82]). In pts with ASCVD history and use of statins at baseline or at any time there did not appear to be a difference in incident MACE with tofacitinib vs TNFi (HR 1.17 [95% CI 0.48, 3.00]) (Figure 3).
Conclusion: This post hoc analysis of ORAL Surveillance emphasizes that there is a gap in the CV preventive care of pts with RA, as evident from inadequate use of statins. Among pts with history of ASCVD, use of statins appears to be critical in mitigating the previously reported MACE risk observed to accompany tofacitinib use vs TNFi.
BID, twice daily; BL, baseline; HxASCVD, history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; n, number of patients with events; N, number of evaluable patients; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
*HR vs TNFi (95% CI) is based on two simple Cox proportional hazard models (one for comparing combined tofacitinib doses vs TNFi, and the other for comparing tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID vs TNFi), with treatment as the only covariate. †HR (95% CI) of statin Yes vs No is based on a Cox model with use of statins as only covariate performed within each treatment group. ‡HR 95% CI excludes 1.
ASCVD, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BID, twice daily; CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; IR, incidence rate; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; n, number of patients with events; N, number of evaluable patients; PY, patient-years; TOFA, tofacitinib; TNFi, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Giles J, Charles-Schoeman c, Buch M, Dougados M, Szekanecz Z, Mikuls T, Ytterberg S, Koch G, Kwok K, Cadatal M, Menon S, Chen Y, Diehl A, Rivas J, Yndestad A, Bhatt D. Use of Statins and Its Association with Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes with Tofacitinib versus TNF Inhibitors in a Risk-Enriched Population of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-statins-and-its-association-with-major-adverse-cardiovascular-outcomes-with-tofacitinib-versus-tnf-inhibitors-in-a-risk-enriched-population-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/use-of-statins-and-its-association-with-major-adverse-cardiovascular-outcomes-with-tofacitinib-versus-tnf-inhibitors-in-a-risk-enriched-population-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/