Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1517–1552) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: BMS-986353 (CC-97540; CD19 NEX-T) is a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy that expresses the same CAR as lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel); it is manufactured via the NEX-T™ process to reduce manufacturing time and optimize phenotypic attributes. In Breakfree-1 trial (NCT05869955), BMS-986353 showed promising initial safety and efficacy in pts with severe refractory SLE.1 Here, we report updated data on BMS-986353 in the SLE cohort.
Methods: This phase 1, multicenter trial assesses safety and efficacy of BMS-986353 in pts with severe, treatment-resistant autoimmune diseases. Inclusion criteria required active disease (BILAG A score) and an inadequate response to ≥ 2 immunosuppressants and steroids. After lymphodepletion, a single BMS-986353 infusion was administered at 2 dose levels (DLs) to optimize risk–benefit in SLE: DL1, 10×106; DL2, 25×106 CAR+ T cells. All pts were weaned off lupus-directed therapies by day 29 post-infusion. Primary endpoint was safety.
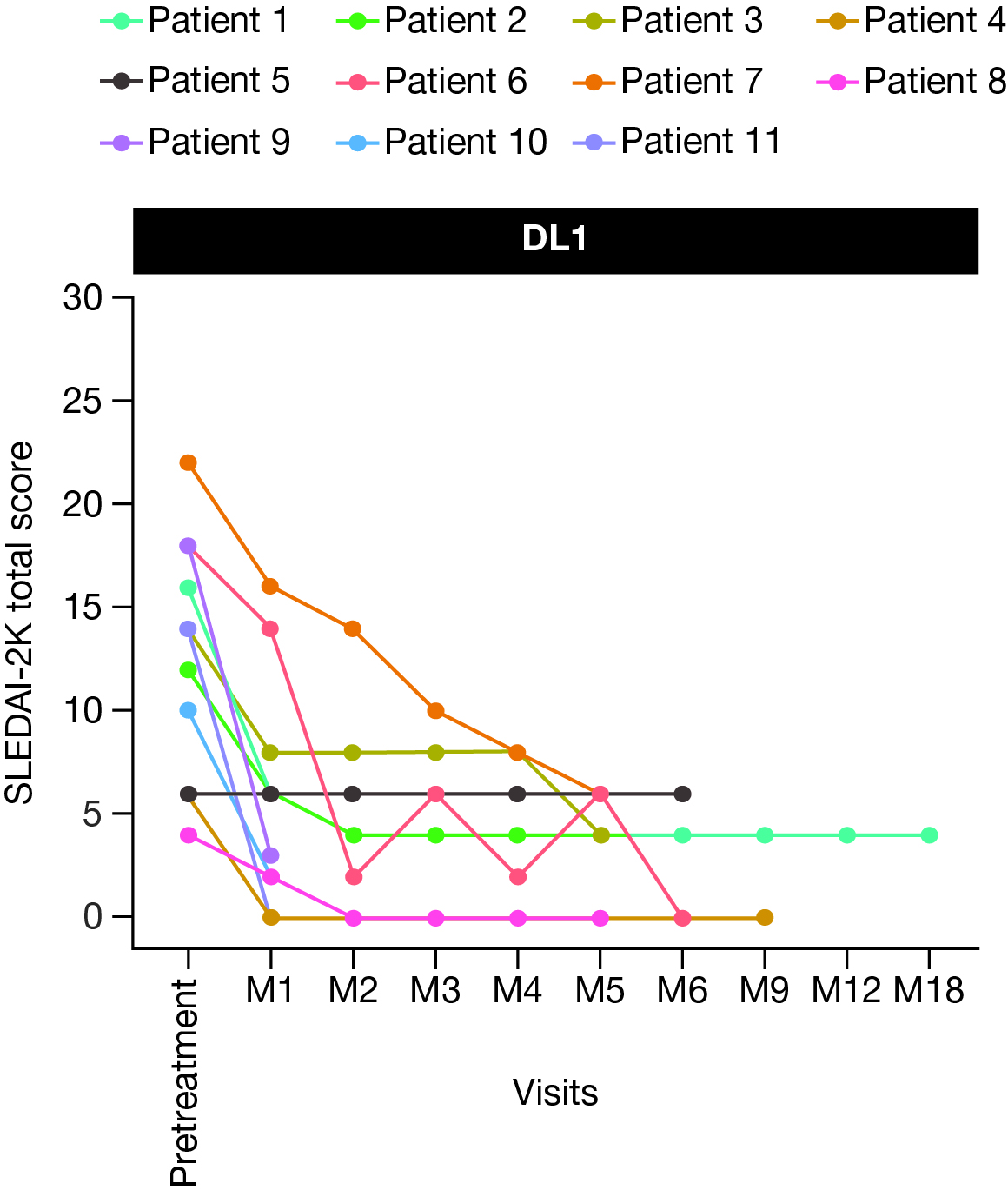
Results: As of March 17, 2025, 26 pts with SLE were enrolled; 19 were treated with BMS-986353 (DL1, n=13; DL2, n=6), with 17 (DL1, n=11) evaluable for efficacy. Median age: 30.0 (18–49) years. Median follow-up (range): 181.0 (7–488) days. Four and 15 pts had BILAG A cardiorespiratory and BILAG A renal involvement, respectively, and had refractory disease despite multiple prior therapies (median [range]: 7.0 [4–11]). Lower frequency and grade (gr) of adverse events were observed in DL1 vs DL2. Gr 3/4 neutropenia occurred in 46.2% (DL1) versus 83.3% (DL2); all events resolved. There were no gr 3/4 thrombocytopenia or prolonged cytopenias at either DL. Low gr cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 61.5% at DL1 (Table) versus 100% at DL2; no gr ≥3 CRS events were observed at either DL. Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) was not observed at DL1; 2 gr 3 ICANS events occurred at DL2. All CRS and ICANS were brief and reversible. DL1 was selected for expansion in Part B based on the improved safety profile at DL1 in Part A.After BMS-986353 administration, most evaluable pts experienced a substantial improvement in disease activity as assessed by a significant reduction in SLEDAI-2000K (2K) and Physician’s Global Assessment (PGA) scores; with 6 months of follow-up, DL1 pts had a median 9 point reduction in SLEDAI-2K score (Fig 1) and a 90% improvement in PGA. No clinically meaningful differences in efficacy outcomes were observed between DLs. Double-stranded DNA and serum complement (C3 or C4) had significant titer reduction or normalized over time for pts with abnormal values at screening. All pts showed robust CAR T cell expansion compared with liso-cel and complete peripheral blood B-cell depletion at both DLs with primarily naive repopulating B cells (Fig 2).
Conclusion: These data show a manageable safety profile and preliminary clinical benefit of BMS-986353 for pts with severe, treatment-resistant SLE, suggesting BMS-986353 may be a potential therapeutic option. Reference: 1. Schett G, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2024;76(suppl 9).Medical writing: Alexus Shirk, PhD (Caudex, an IPG Health Company), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb.
 CRS and ICANS at Part B expansion dose.
CRS and ICANS at Part B expansion dose.
.jpg) Figure 1. Total SLEDAI-2K score following BMS-986353 treatment in the SLE efficacy-evaluable population at DL1.
Figure 1. Total SLEDAI-2K score following BMS-986353 treatment in the SLE efficacy-evaluable population at DL1.
DL, dose level; M, month; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; SLEDAI-2K, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000.
.jpg) Figure 2. Median transgene PK profiles (A) and peripheral B cell concentration and phenotype (B) following BMS-986353 treatment in the SLE population.
Figure 2. Median transgene PK profiles (A) and peripheral B cell concentration and phenotype (B) following BMS-986353 treatment in the SLE population.
PK were analyzed using droplet PCR and pharmacodynamics were evaluated via flow cytometry.
DL, dose level; DN, double negative; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PK, pharmacokinetics; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schett G, Simon D, Wiesendanger M, Askanase A, Majithia V, Kramer N, Morel J, Mease P, De Langhe E, Saxena A, Farge d, Lescoat A, Desai A, McTume G, Handy W, Das S, Thorpe J, Melton A, Koegel A, Littlejohn E. Updated Phase 1 Trial Data Assessing the Tolerability, Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of BMS-986353 (CC-97540), a CD19-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Using a Next-Generation Process for Severe, Refractory SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/updated-phase-1-trial-data-assessing-the-tolerability-efficacy-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-bms-986353-cc-97540-a-cd19-directed-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-therapy-using-a-next/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/updated-phase-1-trial-data-assessing-the-tolerability-efficacy-pharmacokinetics-and-pharmacodynamics-of-bms-986353-cc-97540-a-cd19-directed-chimeric-antigen-receptor-t-cell-therapy-using-a-next/
