Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)‑17F in addition to IL‑17A. BKZ was generally well tolerated by patients (pts) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in phase 2b/3 studies, according to previous pooled safety data.1 We present updated pooled safety data across integrated phase 2b/3 studies, with an additional one year of BKZ exposure from the ongoing phase 3 open-label extension (OLE) studies.
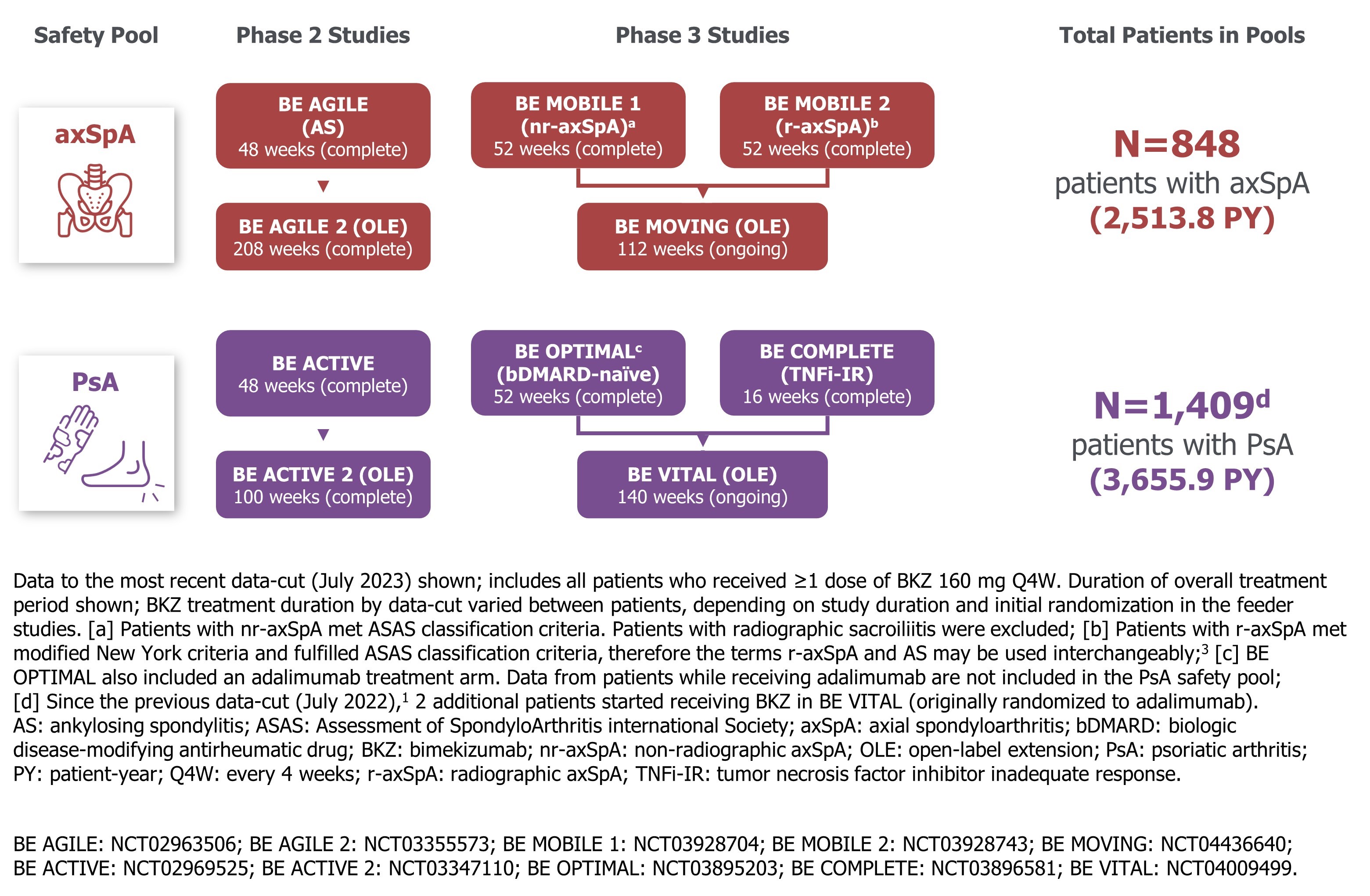
Methods: Safety data are reported for 2 pools, each comprising 3 phase 2b/3 studies and their OLEs, in patients with active axSpA (non-radiographic and radiographic) and active PsA, respectively (Figure).1 Exposure-adjusted incidence rates per 100 pt-years (EAIR/100 PY) are reported for treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) among those who received ≥1 dose of BKZ 160 mg every four weeks (wks) (Q4W). The n (%) of pts experiencing TEAEs are also presented. Data are reported to the data-cut (July 2023) across all treatment periods. All phase 2b/3 studies were complete by the data-cut, except the BE MOVING and BE VITAL OLEs, in which ongoing patients had reached ~104 wks of total study participation (Figure).
Results: The axSpA and PsA safety pools included 848 pts (2,513.8 PY) and 1,409 pts (3,655.9 PY), respectively.
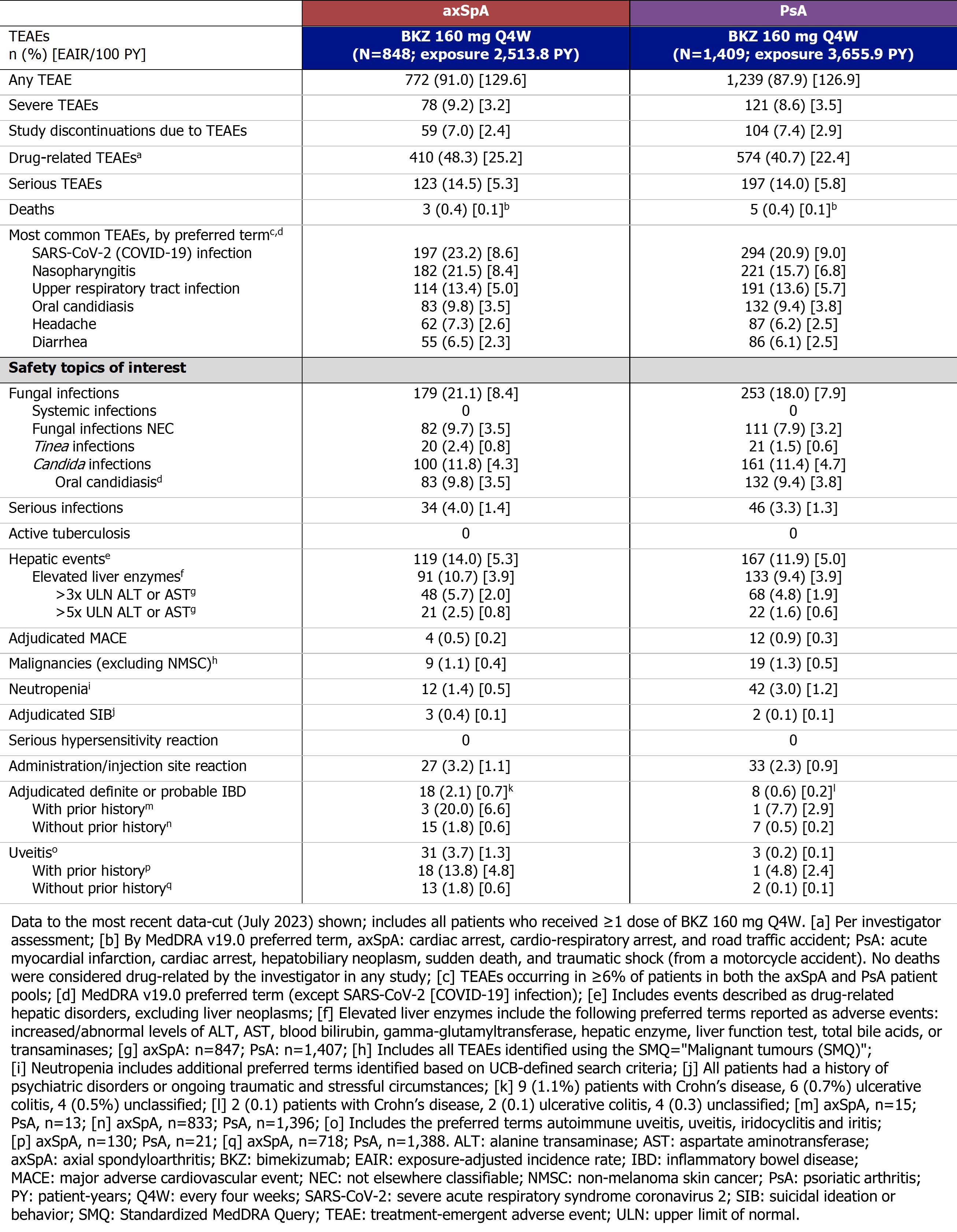
Since the previous data-cut,1 the EAIR for the majority of TEAEs remained stable with longer exposure to BKZ. The 3 most frequently reported TEAEs in pts with axSpA and PsA were SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection (Table).
Safety topics of interest are reported in Table. The EAIR/100 PY of serious infections was 1.4 in pts with axSpA and 1.3 in pts with PsA. For fungal infections, the EAIR/100 PY was 8.4 in pts with axSpA and 7.9 in PsA. Most fungal infections were mucocutaneous and mild/moderate in severity, including oral candidiasis infections. Permanent discontinuation of BKZ due to oral candidiasis was infrequent (axSpA: 0.2/100 PY; PsA: 0.4/100 PY). No systemic fungal infections were reported.
The EAIR/100 PY of hepatic events was 5.3 in pts with axSpA and 5.0 in PsA; most were transient liver enzyme abnormalities (Table; no confirmed cases of Hy’s law). For adjudicated definite/probable IBD, the EAIR/100 PY was 0.7 in axSpA and 0.2 in PsA, consistent with the higher background comorbidity of IBD often seen in axSpA compared with PsA.2 Uveitis occurred at an EAIR/100 PY of 1.3 in axSpA and 0.1 in PsA. No cases of active tuberculosis or completed suicide were reported in any study; rates of suicidal ideation/behavior and major adverse cardiac events are shown in Table.
During the studies, there were 3 deaths reported among pts with axSpA and 5 deaths among pts with PsA (further details in Table). No deaths were considered drug-related by the investigators.
Conclusion: With an additional year of exposure, the long-term safety profile of BKZ in pts with axSpA and PsA remained consistent with prior studies; no new safety signals or concerns were raised.1
References: 1. Mease PJ. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75(suppl 9). Abstract 0511; 2. Mease PJ. Rheumatol Ther. 2019;6:529–42; 3. Van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83:547–9.
Disclosures: P. Mease: AbbVie, 2, 5, Aclaris Therapeutics, 2, 5, Aclyrin, 2, 5, Amgen, 2, 5, Boehringer Ingelheim, 2, 5, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, 5, CorEvitas, 2, 5, Galápagos, 2, 5, Gilead, 2, 5, Inmagene, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, 5, Lilly, 2, 5, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, 2, 5, Novartis, 2, 5, Pfizer Inc, 2, 5, Sun Pharma, 2, 5, UCB, 2, 5; D. Poddubnyy: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Biocad, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Gilead, 2, MSD, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Samsung Bioepis, 2, UCB, 2, 6; R. Bajracharya: UCB Pharma, 3, 11; B. Ink: AbbVie, 11, GSK, 11, UCB Pharma, 3, 11; A. Marten: UCB Pharma, 3; U. Massow: UCB Pharma, 3; V. Shende: UCB Pharma, 3; M. Manente: UCB Pharma, 3, 11; L. Peterson: UCB Pharma, 3, 12, Shareholder; K. White: UCB Pharma, 3, 11; P. Nash: AbbVie, 5, 6, BMS, 5, 6, Boehringer Ingelheim, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, Gilead/Galapagos, 5, 6, GSK, 5, 6, Janssen, 5, 6, Novartis, 5, 6, Pfizer, 5, 6, Samsung, 5, 6, Sanofi, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 5, 6; L. Gensler: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Acelyrin, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Fresenius Kabi, 2, Janssen, 2, MoonLake, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, UCB, 2, 5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Poddubnyy D, Bajracharya R, Ink B, Marten A, Massow U, Shende V, Manente M, Peterson L, White K, Nash P, Gensler L. Updated Long-Term Safety and Tolerability of Bimekizumab in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis: Pooled Results from Phase 2b/3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/updated-long-term-safety-and-tolerability-of-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-results-from-phase-2b-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/updated-long-term-safety-and-tolerability-of-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-results-from-phase-2b-3-studies/