Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) is a transmembrane adhesion molecule with oxidative deamination functionality, which is expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells. Under inflammatory conditions, VAP-1 rapidly translocates to the cell surface, facilitating leukocyte adhesion and migration via its interaction with Siglec-9, a ligand upregulated on neutrophils and monocytes during inflammation. A soluble form of VAP-1 (sVAP-1) contributes to the circulating monoamine oxidase activity in human blood and further influences leukocyte migration. The novel radiotracer [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9 may improve the assessment of giant cell arteritis (GCA), as only being upregulated in inflammation. This study is the first to evaluate the diagnostic value and investigate the role of Siglec-9 and sVAP-1 in patients with relapsing GCA.
Methods: Patients with relapsing GCA underwent [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9-PET/CT. Additionally, GCA patients and healthy controls underwent laboratory testing, including sVAP-1 determination and Siglec-9 expression analysis. sVAP-1 levels were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Siglec-9 expression was assessed via flow cytometry (FACS) on peripheral blood mononuclear cells, which included CD3+CD4+ (CD4 T cells), CD3+CD8+ (CD8 T cells), CD14+CD16- (classical monocytes), CD14+CD16+ (intermediate monocytes), CD14-CD16+ (non-classical monocytes), CD19-CD38+CD138+ (plasma cells), CD19+CD38+ (plasmablasts), CD19+CD38- (naive B cells), and CD38+CD16+ (NK cells). Comparisons of sVAP-1 levels and Siglec-9 expression between GCA relapse patients and healthy controls were performed. Furthermore, associations between the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of the aorta and subclavian/ axillary artery with sVAP-1 levels and Siglec-9 expression were analyzed.
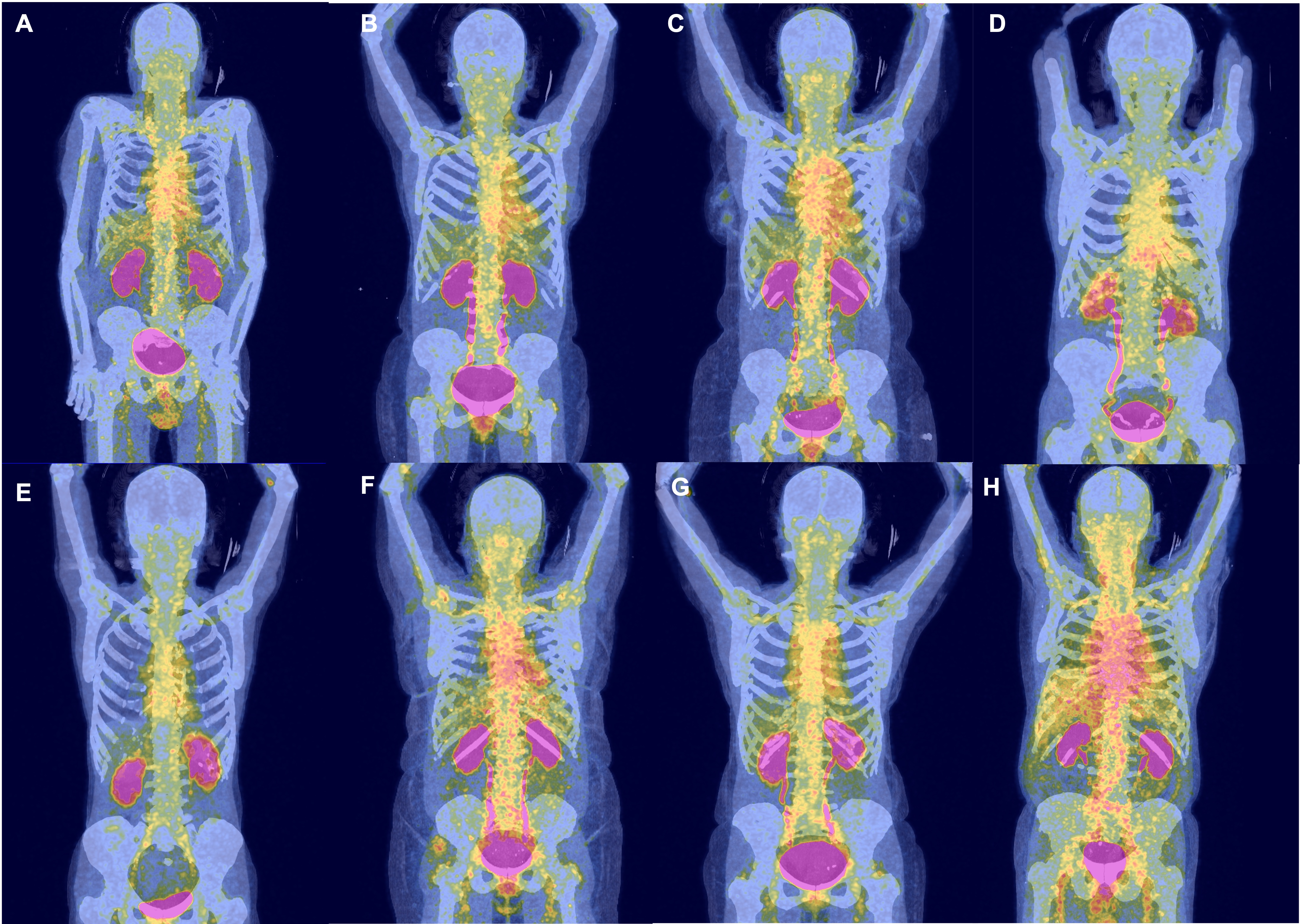
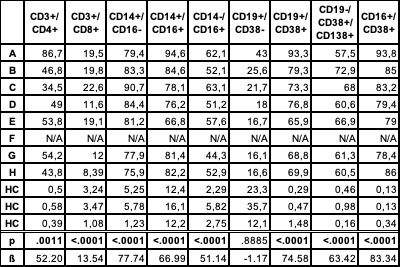
Results: Eight patients with relapsing GCA and eight healthy controls were enrolled (Tbl.1). The [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9 PET scan demonstrated increased localized SUVmax in the subclavian/ axillary artery and aorta (Fig. 1). ELISA showed significantly elevated sVAP-1 in GCA relapse patients compared to the control group (p = .0198). FACS revealed significantly increased Siglec-9 expression on CD4/ CD8 T cells, classical, intermediate, and non-classical monocytes, plasma cells, plasmablasts, and NK cells in relapsed patients compared to controls (p < .0001), while naïve B cells showed no difference (p = .8885) (Tbl. 2). No significant association was found between sVAP-1, Siglec-9 and tracer uptake (data not shown).
Conclusion: This study is the first to demonstrate that [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9-PET/CT can detect inflammatory activity in patients with relapsing GCA. The elevated levels of sVAP-1 and increased Siglec-9 expression on various immune cell subsets raise questions regarding their pathophysiological significance and potential roles as biomarkers in GCA. Further research is warranted to deepen our understanding of VAP-1 and Siglec-9 in GCA.
This figure illustrates [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9-PET/CT imaging results from eight patients experiencing a relapse of giant cell arteritis. Patient-specific tracer uptakes are revealed in the aorta and subclavian/ axillary artery. The patients are ordered ascendingly based on their aortic tracer uptake. The labels A-H correspond to the patient numbers listed in Table 1.
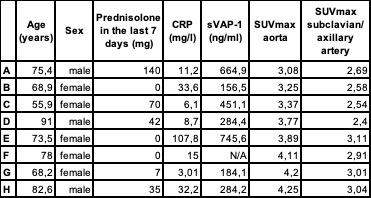
This table presents the demographic, clinical, and laboratory data of eight patients experiencing relapses of giant cell arteritis. It includes age, sex, administered prednisolone dose in the 7 days prior to the scan, CRP level, sVAP_1 levels, and relative tracer uptake in [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9-PET/CT in the aorta and subclavian/ axillary artery. The labels A-H correspond to the patient numbers listed in Figure 1. Abbreviations: mg: milligram; CRP: C-reactive protein; sVAP_1: soluble vascular adhesion protein_1; ng: nanogram; l: liter; SUV: standard uptake value.
This table presents the relative Siglec-9 expression on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in eight patients and three healthy controls. The cell lines examined include CD3+CD4+ (CD4 T cells), CD3+CD8+ (CD8 T cells), CD14+CD16- (classical monocytes), CD14+CD16+ (intermediate monocytes), CD14-CD16+ (non-classical monocytes), CD19-CD38+CD138+ (plasma cells), CD19+CD38+ (plasmablasts), CD19+CD38- (naïve B cells), and CD38+CD16+ (NK cells) Siglec-9 expression was significantly higher on CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, classical, intermediate, and non-classical monocytes, plasma cells, plasmablasts, and NK cells in relapsed patients compared to controls, while naïve B cells showed no significant difference. The labels A-H correspond to the patient numbers listed in Figure 1. Statistical significance (p-values) and estimates (ß) for the differences between patients and healthy controls are provided. Abbreviations: CD: cluster of differentiation, HC: healthy control.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Petzinna S, Küppers J, Schemmer B, Kernder A, Bauer C, Karakostas P, Bruci D, Morar A, Winklbauer A, Essler M, Schäfer V. Unveiling of a New Molecular Imaging Biomarker? Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-Siglec-9 PET/CT in Detecting Giant Cell Arteritis Relapse [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unveiling-of-a-new-molecular-imaging-biomarker-vascular-adhesion-protein-1-and-68gaga-dota-siglec-9-pet-ct-in-detecting-giant-cell-arteritis-relapse/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unveiling-of-a-new-molecular-imaging-biomarker-vascular-adhesion-protein-1-and-68gaga-dota-siglec-9-pet-ct-in-detecting-giant-cell-arteritis-relapse/