Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Nudix Hydrolase 21 (NUDT21, also known as CFIm25) is a master regulator of alternative polyadenylation. Previous studies have revealed that NUDT21 is significantly decreased in systemic sclerosis (SSc) skin and that its downregulation in fibroblasts potentiates both skin and lung fibrosis (Weng T et al. J Clin Invest. 2019 & J Exp Med 2020). This study aims to investigate the upstream mechanisms that lead to NUDT21 repression in skin fibrosis.
Methods: NUDT21 levels in cells treated with different cytokines were determined by western blot and RT-qPCR. Dual-luciferase assays were performed to determine the micro RNA (miRNA) regulation of NUDT21. MiR-181a and -181b mimics and inhibitors were injected subcutaneously 10 days after the initial subcutaneous bleomycin treatment to determine their effects on skin fibrosis (n≥ 5 per group).
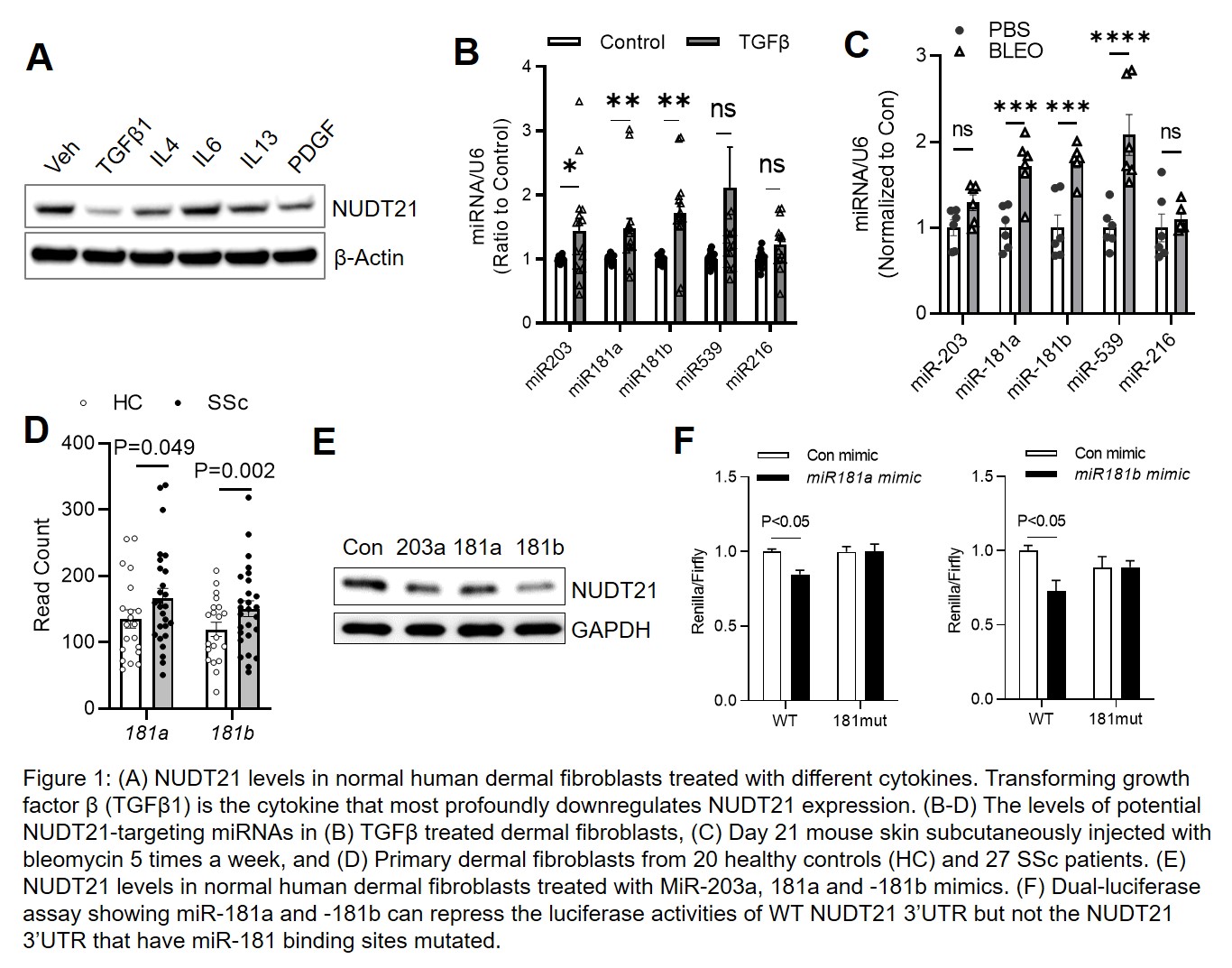
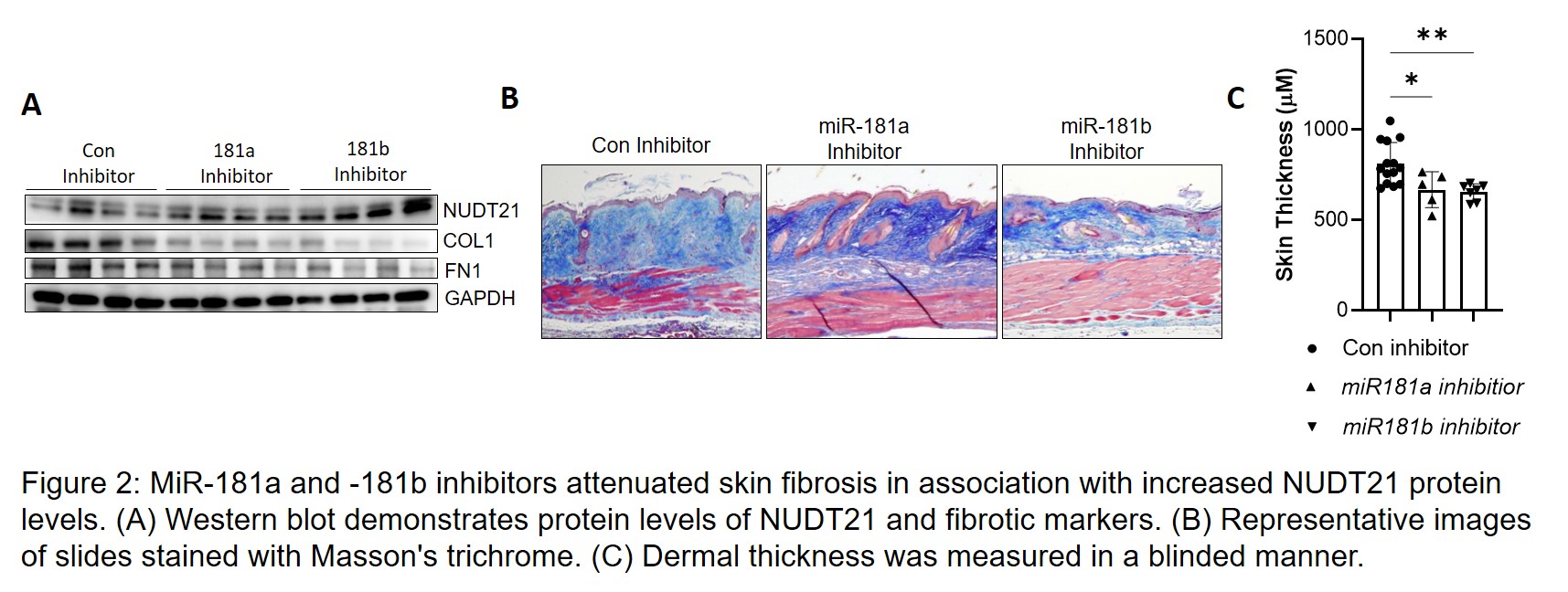
Results: In comparison to IL4, IL6, IL13, and PDGF, transforming growth factor β (TGFβ1) led to a stronger downregulation of NUDT21 in healthy control (HC) dermal fibroblasts (Fig. 1A). Further investigation showed that TGFβ did not downregulate NUDT21 transcript until 48 hours after treatment, suggesting that it regulated NUDT21 through an indirect mechanism such as miRNA induction. Screening potential NUDT21 targeting miRNAs revealed that miR-181a and -181b were elevated in TGFβ1 treated human dermal fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis in mice (Fig. 1B-C). Consistent with these findings, miR-181a and -181b were both significantly increased in primary dermal fibroblasts from 27 patients with early diffuse SSc compared to fibroblasts obtained from 20 matched HCs while the levels of other NUDT21 targeting miRNAs were not increased (Fig. 1D). Both miR-181a and -181b could directly bind NUDT21 3’UTR to repress NUDT21 expression in skin fibroblasts (Fig. 1E-F). Functional studies demonstrated that miR-181a and -181b inhibitors attenuated bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis murine models in association with decreased NUDT21 expression (Fig.2), while miR-181a and -181b mimics exaggerated bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis.
Conclusion: Taken together, these findings suggest miR-181a/b play a role in SSc pathogenesis and are potential therapeutic options for skin fibrosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mills T, Wu M, Puente H, Alonso J, charles J, Mayes M, Assassi S. Unraveling the Role of MiR-181 in Skin Fibrosis Pathogenesis by Targeting NUDT21 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unraveling-the-role-of-mir-181-in-skin-fibrosis-pathogenesis-by-targeting-nudt21/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unraveling-the-role-of-mir-181-in-skin-fibrosis-pathogenesis-by-targeting-nudt21/