Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a rare autoimmune disorder that predominantly affects the skin and muscles in children under the age of sixteen. Literature on the clinical profiles and outcomes of JDM from India is scarce. This study aims to analyze the clinical features, laboratory findings, therapeutic measures, and outcomes of JDM in an Indian cohort.
Methods: Data on JDM patients were collected from inpatient records and the multicentric MyoIn cohort from NIMS Hyderabad over the past five years. Study parameters included demographic details, clinical features, laboratory findings such as enzyme levels and autoantibody profiles, and therapeutic interventions. Treatment outcomes were measured using the Total Improvement Score (TIS) with the IMACS-TIS calculator during the six-month follow-up visit.
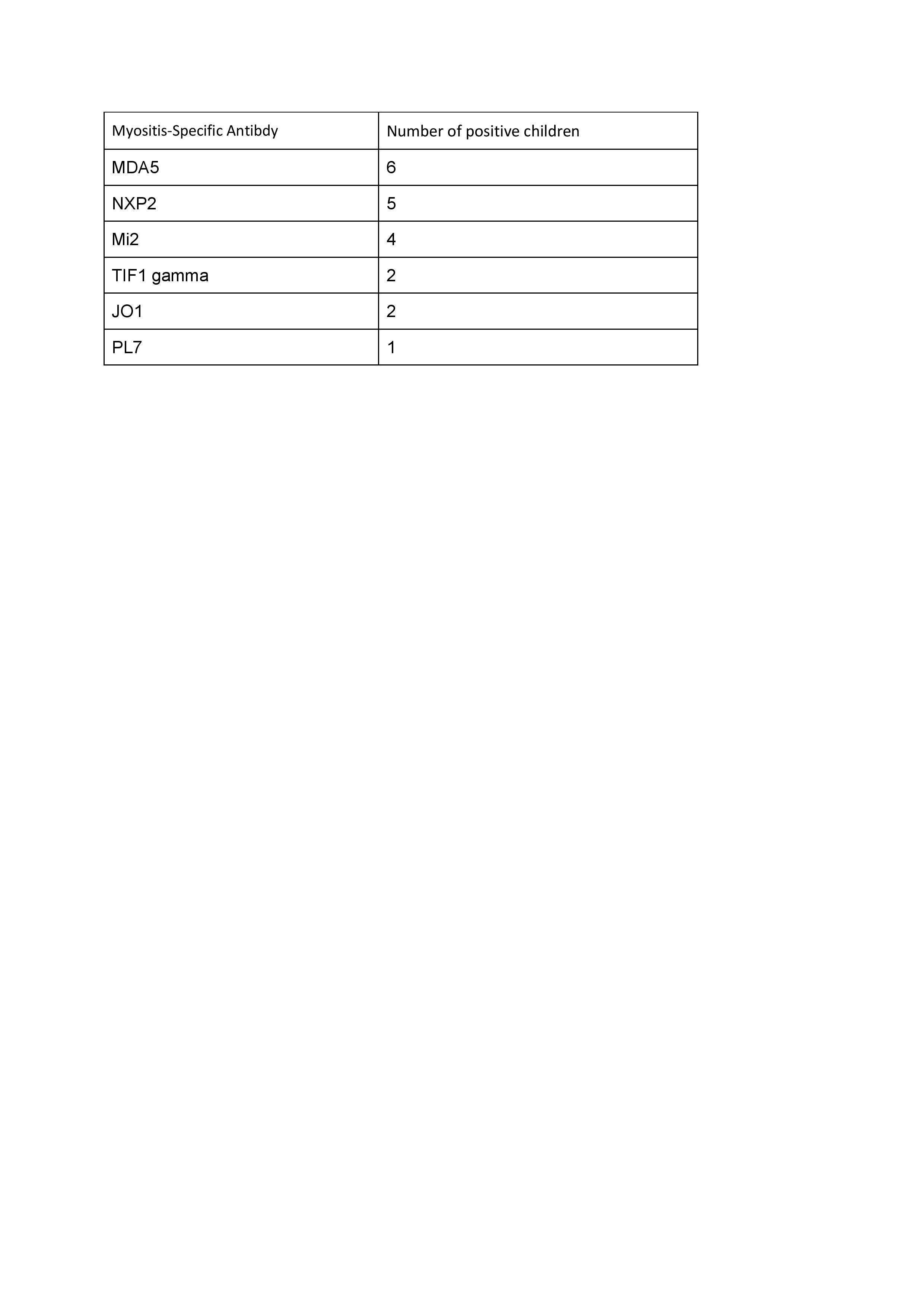
Results: Thirty patients (female:male = 3:1) with JDM were included. The mean age was 10.02 ± 5.08 years, with the youngest patient being two years old. The mean time from the onset of the first symptom to treatment was 7 ± 6 months, and the mean duration of follow-up was 2.5 ± 0.9 years. Constitutional features were present in 25 children. Twenty-four exhibited cutaneous manifestations, which included Gottron’s sign, heliotrope rash, and Gottron papules. The mean Manual Muscle Testing 8 (MMT8) score was 48 ± 6. Extramuscular manifestations, including arthritis, calcinosis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, digital gangrene, and interstitial lung disease (ILD), were present in 5, 3, 1, 1, and 2 patients, respectively. The mean creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were 230 (±128) mg/dL and 537 (±406) IU/L, respectively. Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) by immunofluorescence were negative in eight patients. Myositis specific antibodies were present in 20 patients of which MDA 5 being the commonest (6 patients ).Myositis-associated antibodies were present in 18 children, of whom 17 exhibited anti-Ro52 and one anti-PM-SCL positivity. Methotrexate was used as initial immunosuppression in all children; subsequently, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was used in five,, cyclophosphamide in two, rituximab in four, and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) in three children. Four patients died—one due to diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, one due to rapidly progressive ILD, and two due to infections.The statistical results for the Total Improvement Score (TIS) for Follow-up Visit 1 (F1) using the IMACS-TIS calculator indicate that most of the 15 patients experienced moderate improvements. TIS scores ranged from 30 (minimal improvement) to 70 (major improvement). Specifically, 6.7% of patients showed major improvement, 46.7% showed moderate improvement, 20% showed minimal improvement, and 20% experienced worsening conditions.
Conclusion: In our cohort, MDA5 was the most common antibody detected, and the majority of patients experienced moderate TIS improvement. The outcomes underscore the severity of the disease, with three fatalities highlighting the need for timely diagnosis, aggressive treatment, and close monitoring.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
yerram k, devarasetti p, Rajasekhar L. Unlocking Insights into Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Clinical and Demographic Profiles Paired with Total Improvement Scores at a Tertiary Center [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unlocking-insights-into-juvenile-dermatomyositis-clinical-and-demographic-profiles-paired-with-total-improvement-scores-at-a-tertiary-center/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/unlocking-insights-into-juvenile-dermatomyositis-clinical-and-demographic-profiles-paired-with-total-improvement-scores-at-a-tertiary-center/