Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
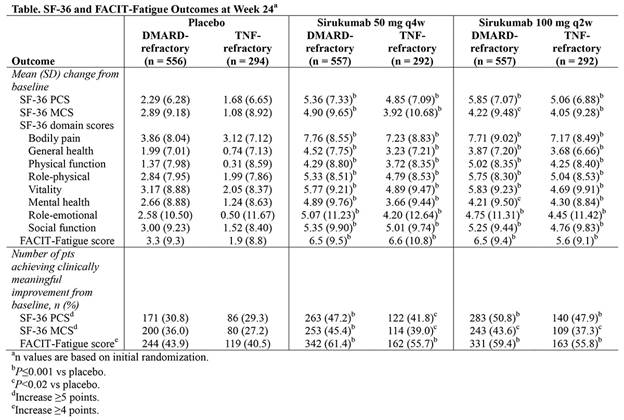
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) often experience both substantial fatigue and a decline in their health-related physical and emotional well-being. Sirukumab is a human anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the cytokine with high affinity, and is under development for RA and a number of other diseases. The effects of sirukumab on health-related physical and emotional well-being and fatigue were evaluated in 2 separate randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter global phase 3 studies in pts with RA refractory to conventional DMARDs (SIRROUND-D) or refractory or intolerant to anti-TNF therapy (SIRROUND-T). Pts may have been taking other biologics prior to both studies.
Methods: In both studies, eligible pts were randomized (1:1:1) to treatment with SC sirukumab 50 mg q4w, 100 mg q2w, or placebo q2w. The placebo-controlled portions of SIRROUND-D and -T were 52 and 24 wks, respectively; thus, results from both studies were examined at Wk 24 and are presented here. The primary objective of both studies was to evaluate the efficacy of sirukumab in the study-specific RA pt populations. Health-related physical and emotional well-being were evaluated as secondary endpoints using the SF-36 health survey, and fatigue evaluated using the FACIT-Fatigue scale. For SF-36 physical and mental component summary (PCS and MCS) scores, clinically meaningful improvement was defined as a ≥5-point increase from baseline (BL); for FACIT-Fatigue, clinically meaningful improvement was defined as a ≥4-point increase from BL.
Results: A total of 1,670 and 878 pts in SIRROUND-D and -T, respectively, had evaluable data. In both studies, increases (improvements) from BL at Wk 24 in mean SF-36 PCS and MCS scores and all 8 SF-36 domain scores were significantly greater with either sirukumab dose level (50 mg q4w or 100 mg q2w) versus placebo (all P<0.02; Table). Similarly across both studies, significantly greater mean increases (improvements) from BL at Wk 24 were observed in the FACIT-Fatigue score with sirukumab (either dose) versus placebo (all P<0.001 [not adjusted for multiplicity]; Table). Improvements in SF-36 and FACIT-Fatigue scores with both sirukumab doses versus placebo were observed at Wk 8 through all time points to Wk 24 in both studies. In addition, across studies, the percentages of pts who achieved clinically meaningful improvements from BL at Wk 24 in SF-36 PCS and MCS scores, and in FACIT-Fatigue score were significantly higher with sirukumab (either dose) versus placebo (all P<0.02).
Conclusion: Treatment with sirukumab was associated with significant and clinically meaningful improvements from BL in health-related physical and emotional well-being and fatigue for pts with active RA who had not responded adequately to prior treatment, regardless of whether prior treatment was with conventional DMARDs or TNF inhibitors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bingham C III, Tanaka Y, Karpouzas G, Takeuchi T, Aletaha D, Thorne C, Sheng S, Xu W, Rao R, Fei K, Hsu B, Agarwal P, Popik S, Kurrasch R, Peterson S, Ganguly R, Han C, McQuarrie K. Treatment with Sirukumab, an Anti-IL6 Cytokine Monoclonal Antibody, Improves Fatigue and Health-Related Physical and Emotional Well Being in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Refractory to Conventional or Biologic Therapy: Results of 2 Global, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-sirukumab-an-anti-il6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-improves-fatigue-and-health-related-physical-and-emotional-well-being-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-refractory-to-con/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-sirukumab-an-anti-il6-cytokine-monoclonal-antibody-improves-fatigue-and-health-related-physical-and-emotional-well-being-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-refractory-to-con/