Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: There are conflicting data regarding the effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) on radiographic spinal progression in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). The analysis of the first 2-year of the GErman SPondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (GESPIC) showed that higher NSAID intake may retard new bone formation in r-axSpA. It remained, however, unclear, whether cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors (COX2i) might have a stronger effect than non-selective (NS) ones and if the effect could be observed also in nr-axSpA. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of NSAIDs (COX2i and NS) intake on radiographic spinal progression in patients with r-axSpA and nr-axSpA.
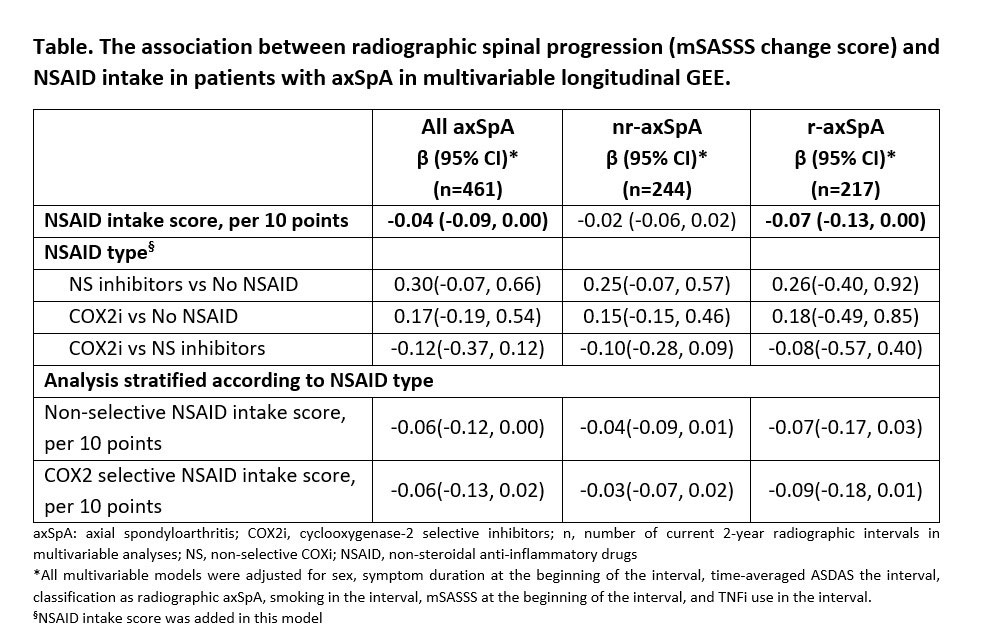
Methods: Based on the availability of at least two sets of spinal radiographs during 10-year follow-up, 243 patients with early axSpA (130 and 113 nr- and r-axSpA, respectively) from GESPIC were included in this analysis. The patients contributed a total of 540 2-year radiographic intervals. Radiographs were scored by 3 trained and calibrated readers according to the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS). Final mSASSS was calculated as a mean of 3 readers, and progression was defined as absolute mSASSS change score over 2 years. NSAID type, daily dose, and frequency of intake were recorded at visits. The ASAS index of NSAID intake (0-100) counting both dose and duration of intake was calculated for intervals. The association between NSAID intake (NSAID type and NSAID score) and radiographic spinal progression over 2 years was analyzed using longitudinal generalized estimated equations (GEE).
Results: At baseline, 161 (66.3%) patients were treated with NSAIDs. While 289 (53.5%) and 128 (23.7%) 2-year radiographic intervals were covered by NS and COX-2i respectively, 123 (22.8%) intervals were not covered by NSAID. A significant association between higher NSAID intake and retardation of radiographic spinal progression was found in adjusted multivariable longitudinal GEE analysis. This effect was mostly attributable to patients with r-axSpA (Table). mSASSS progression was numerically lower in patients taking COX2i (irrespectively of dose) as compared to patients treated with NS-NSAIDs; in stratified analysis, however, there was no clear dose-dependency (as reflected by NSAID index) in both groups (Figure, Table).
Conclusion: Higher NSAID intake is associated with lower radiographic spinal progression, particularly in r-axSpA patients. COX2i might possess a stronger inhibitory effect on radiographic progression as compared to NS-NSAIDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Torgutalp M, Rios-Rodriguez v, Dilbaryan A, Proft F, Protopopov M, Verba M, Rademacher J, Haibel H, Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Poddubnyy D. Treatment with Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Is Associated with Retardation of Radiographic Spinal Progression in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: 10-year Results from the GErman SPondyloarthritis Inception Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-is-associated-with-retardation-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-10-year-results-from-the-german-spondyl/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-with-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-is-associated-with-retardation-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-10-year-results-from-the-german-spondyl/