Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite the expanding treatment landscape for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD), the lack of early and valid treatment response biomarkers (measurable in the circulation), may lead to delays in the initiation of effective therapies for SSc-ILD. The present study aimed to identify treatment response biomarkers for SSc-ILD by measuring changes in a select group of circulating biomarkers of inflammation, fibrosis, and epithelial injury after 12 months of therapy with either mycophenolate (MMF) or cyclophosphamide (CYC) and determining whether changes in these biomarkers predicted the likelihood of progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) during the following year.
Methods: Participants of Scleroderma Lung Study (SLS) II, which compared MMF versus CYC for SSc-ILD, who had blood samples at baseline and 12-months were included. Levels for C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-6, chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4), chemokine ligand 18 (CCL18) and Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6) were measured, and a logistic regression analysis was created to determine relationships between changes in these biomarkers and the development of PPF (based on physiologic, radiologic and symptomatic changes) by 24 months.
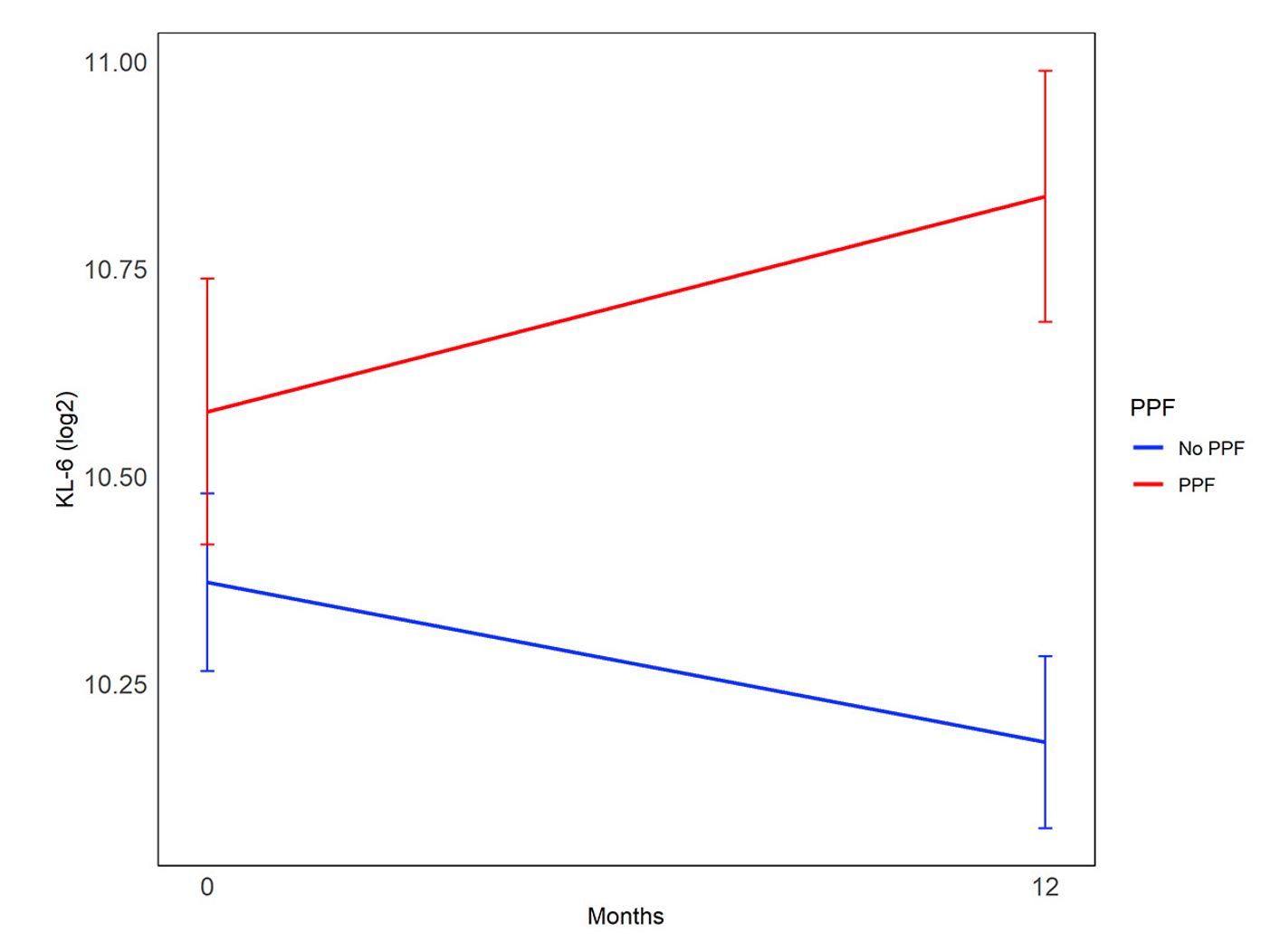
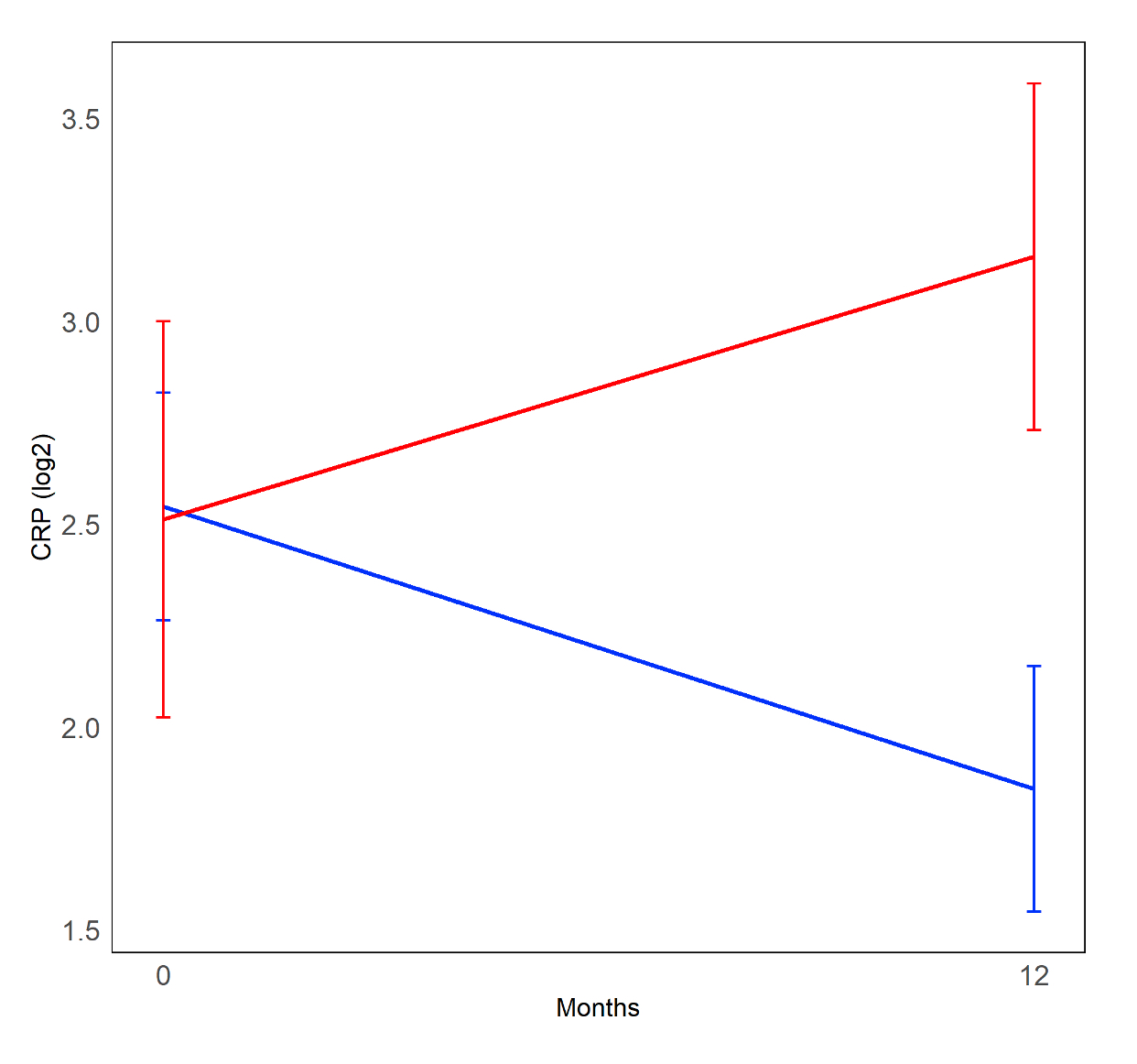
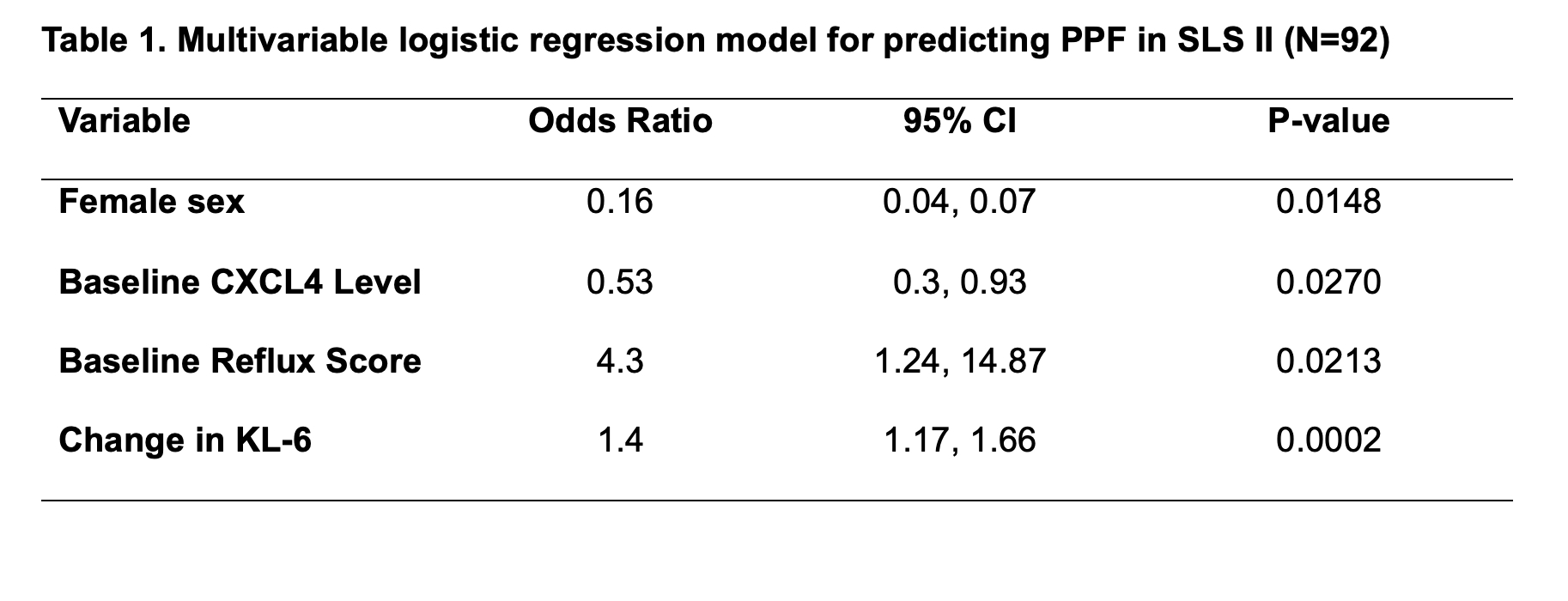
Results: Ninety-two of the 142 randomized participants had longitudinal biomarker measurements and the required clinical outcome data, with 19 (21%) meeting criteria for PPF. In the whole cohort, changes in KL-6 levels were significantly correlated with PPF. KL-6 increased in patients who developed PPF and decreased in patients who did not (Mean change 365.68 [SD 434.41]) vs -207.45 [SD 670.26]; P< 0.001; Figure 1). In the MMF alone arm, changes in CRP (Figure 2) and CXCL4 were also significantly correlated with PPF. When added to an existing prediction model based on baseline factors associated with PPF in this cohort (sex, baseline reflux severity and CXCL4 levels [1]), the change in KL-6 remained significantly associated with PFF (OR 1.4; P=0.0002), and sensitivity of the model improved from 68% to 95% (Table 1).
Conclusion: Changes in the circulating levels of KL-6 after treatment with MMF or CYC predicted PPF, even after adjusting for baseline factors associated with PPF. Measuring longitudinal KL-6 in patients with SSc-ILD may improve how we personalize therapy in patients with SSc-ILD.
References: 1. Volkmann ER, et al. ACR Open Rheumatol 2023.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Volkmann E, Wilhalme H, Tashkin D, Kim G, Goldin J, Haussmann A, Kuwana M, Roth M, Assassi S. Treatment Response Biomarkers for Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-response-biomarkers-for-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-response-biomarkers-for-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease/