Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Glucocorticoids (GC) in high doses remain the first-line treatment for dermatomyositis (DM). One or more immunosuppressive agents are given concomitantly as steroid-sparing agents to prevent long term GC adverse effects. The objectives of this study were to describe the treatment patterns and GC doses used for patients with DM and to describe the evolution of the myositis core set measures (Physician Global Activity [PGA], Manual Muscle Testing 8 [MMT-8], and Extramuscular Global Assessment [EMGA]) while on treatment.
Methods: Newly diagnosed patients with probable or definite DM (according to Bohan and Peter criteria) between 2000 and 2020 were selected from the University of Pittsburgh Myositis Center Registry. The index date was the first visit to the Myositis Center. Patients were followed from the index date until either their last center visit or July 27, 2021. The frequency of dispensed prescriptions and changes in GC dosing were described. The evolution of PGA (scale from 0 [no activity] to 10 [high activity]), MMT-8 (scored from 0 to 150, lower scores indicate more muscle weakness), and EMGA (scale from 0 [no activity] to 10 [high activity]) in treated patients was described for groups with at least 50 patients. Continuous variables are presented using medians and interquartile ranges.
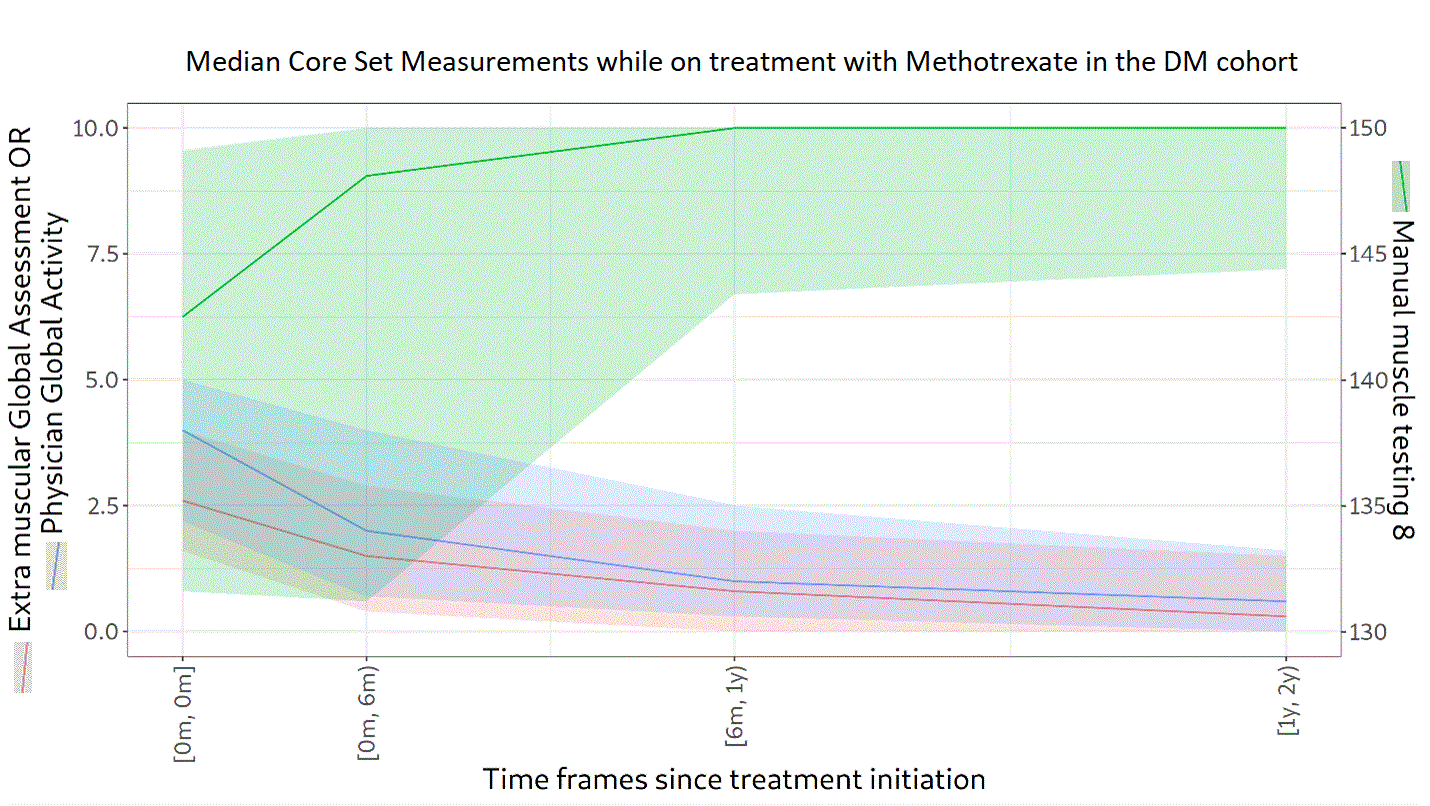
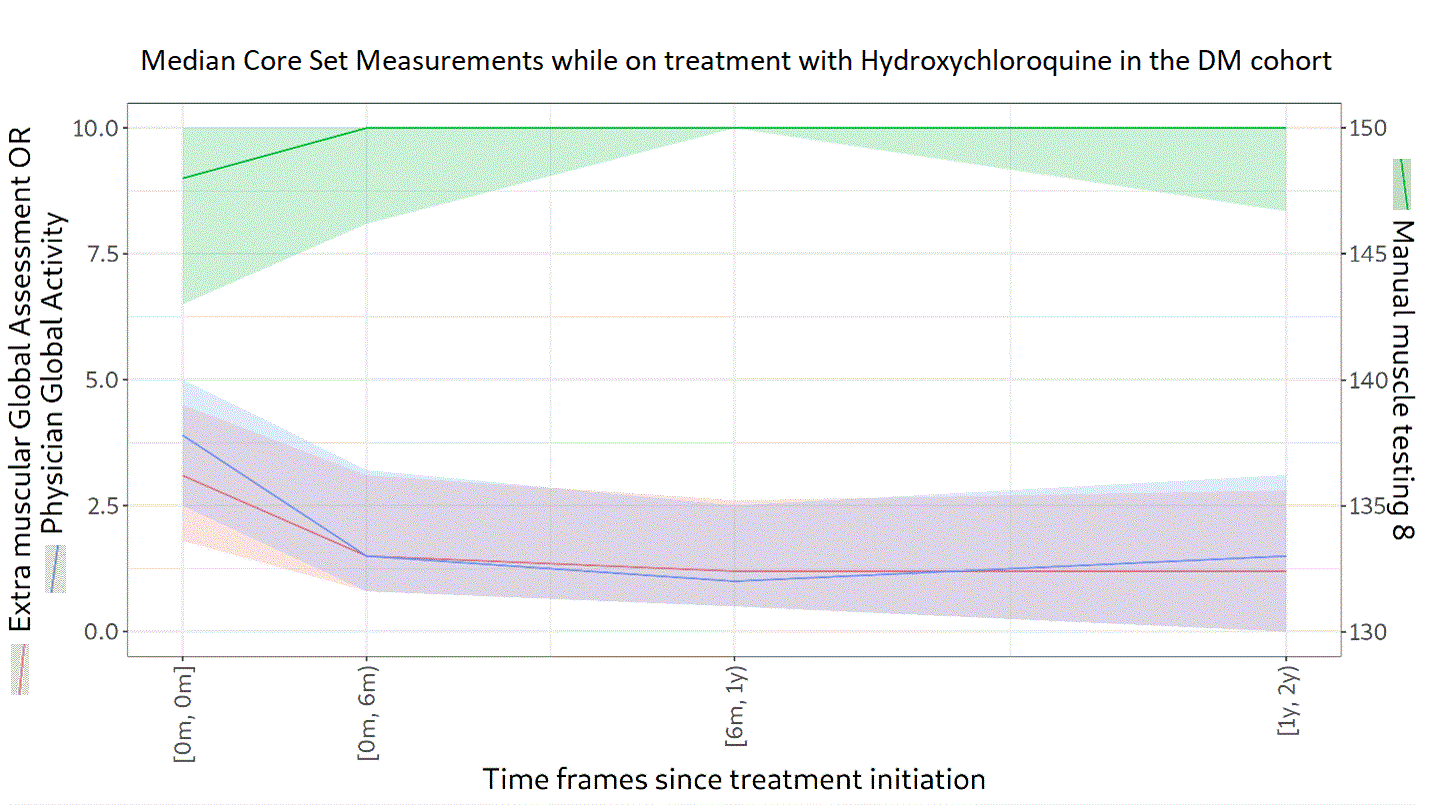
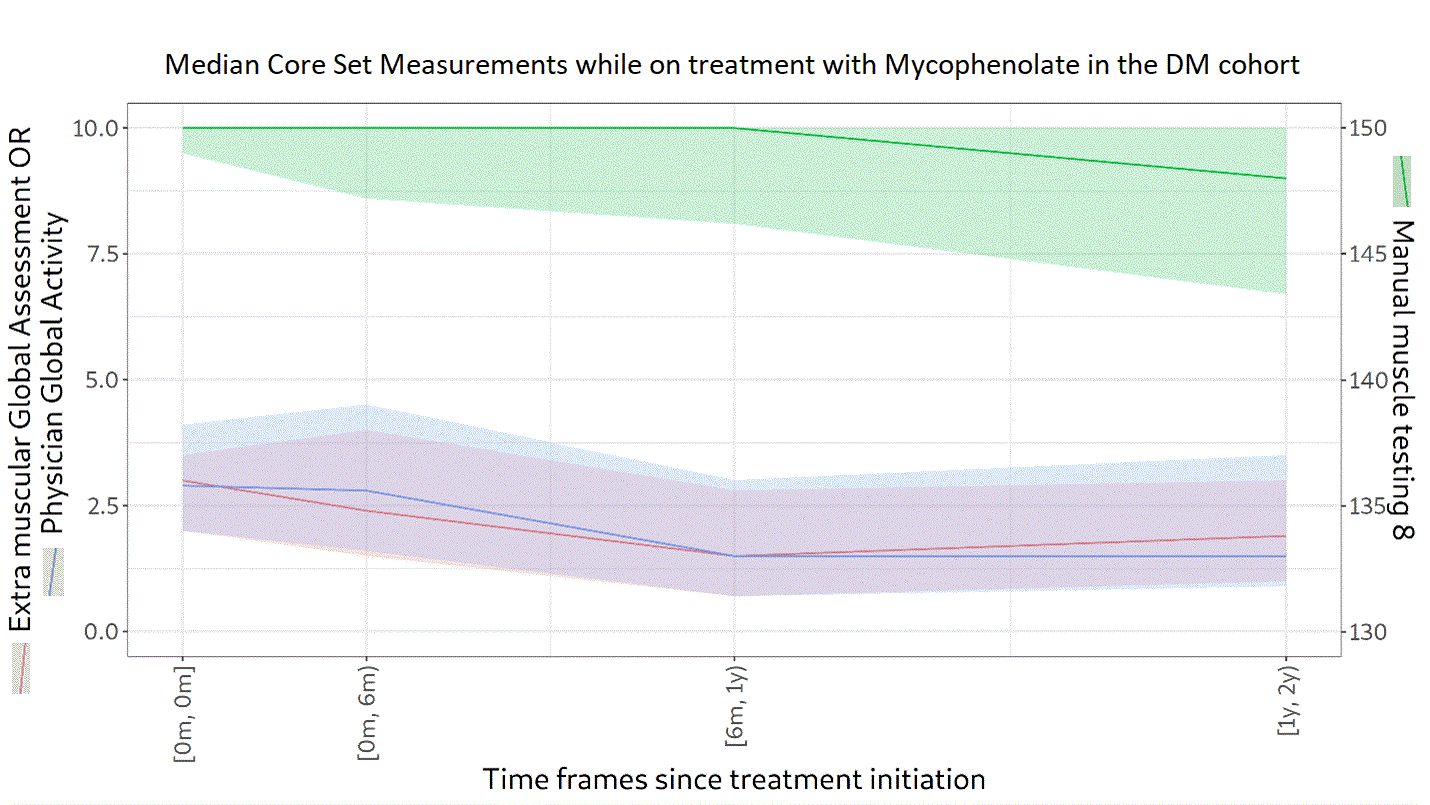
Results: A total of 174 patients with DM were included. Of these, 66% were female and 89% were White, with a median age of 54 years (45‒63). Over a follow-up of 4.0 years (1.3‒7.3), 94% received GC. The median (range) starting dose was 25.8 mg (15.0‒40.0). In the third year, GC was being used in 76% of patients at a dose of 5.0 mg (4.0‒10.0). A high proportion (68%) of patients were still on GC in the fifth year following the index date, at a dose of 5.0 mg (4.0–7.5). In addition to GC, 54% of patients received methotrexate, 37% mycophenolate, 32% hydroxychloroquine, 27% azathioprine, and 21% intravenous immunoglobulin. Median scores at the index date were 3.5 (1.9‒5.0) for PGA, 146 (137‒150) for MMT-8, and 2.7 (1.5‒4.0) for EMGA. PGA, MMT-8, and EMGA improved overtime while on treatment with methotrexate (n=94 patients), hydroxychloroquine (n=56), or mycophenolate (n=65), as depicted in Figures 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Median time between IIM diagnosis and treatment initiation was 34 days (1‒140) for methotrexate, 55 days (1‒326) for hydroxychloroquine, and 395 days (23‒1105) for mycophenolate. In the second year of treatment, 50 patients were still followed in the methotrexate group, 25 in the hydroxychloroquine group, and 21 in the mycophenolate group. Even after two years of treatment, PGA and EMGA remained greater than 0 in some patients, suggesting active disease.
Conclusion: Despite use of immunosupressants, a significant proportion of DM patients remained on GC for several years, many at doses known to be associated with long-term side effects ( >5 mg/day). These findings highlight the unmet medical need for alternative and GC-sparing therapies for patients with DM.
Medical editing support was provided by Bioscript Group.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oddis C, Feifel J, Ascherman D, Koontz D, Foch C, Henkel L, Muir J, Denis D, Aggarwal R. Treatment Patterns and Glucocorticoid Burden of Dermatomyositis Patients: A Cohort Study in the University of Pittsburgh’s Myositis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-patterns-and-glucocorticoid-burden-of-dermatomyositis-patients-a-cohort-study-in-the-university-of-pittsburghs-myositis-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-patterns-and-glucocorticoid-burden-of-dermatomyositis-patients-a-cohort-study-in-the-university-of-pittsburghs-myositis-registry/