Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Urine proteomic approaches have shown promise in identifying dynamic biological pathways in lupus nephritis (LN) which are not captured on renal histopathology or by measurement of proteinuria alone. We sought to investigate how the urine proteome changes with belimumab therapy and whether these changes might indicate any pathophysiologic explanations for the renal benefit of this drug.
Methods: Urine samples from 54 participants with biopsy-proven LN from the BLISS-LN trial (Furie et al., NEJM 2020) were collected at Week 0 (time of randomization), Week 24, and Week 52. A total of 1,000 urinary proteins were quantified using antibody microarrays (Raybiotech Kiloplex) at each time point and normalized using urine creatinine. The abundance of each urinary protein was compared in participants treated with belimumab (n = 28) versus standard of care (n = 26) at each time point using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test with Benjamini-Hochberg correction. Longitudinal fold change (e.g. fold change from Week 0 to 24) was also assessed for each protein in each treatment group.
Results: When comparing participants in the belimumab treatment group versus those in the standard of care group, there was no significant difference in the urine proteome at Week 0 per FDR threshold, as expected. At Week 24, five urinary proteins were found to be present at a significantly lower (CD23, Siglec-5) or higher (AIF, CRELD2, ROR2) level in those treated with belimumab (Figure 1). Numerically, lower CD23 and Siglec-5 (but not higher AIF, CRELD2, or ROR2) in the belimumab group persisted into Week 52, though this was no longer significant per FDR threshold (CD23 p = 0.002, q = 0.69; Siglec-5 p = 0.004, q = 0.69). Belimumab therapy was particularly associated with a negative fold change in CD23 between Week 0 and 24 (Figure 2). Specifically, the median fold change was -6.02 (IQR -14.42 to -3.82) in belimumab recipients versus -1.25 (IQR -2.60 to +1.56) in the standard of care arm (p = 0.0001, q = 0.12). With respect to longitudinal fold change, no other protein exhibited this behavior.
Conclusion: Significant reduction in urinary CD23 by Week 24 was most characteristic of belimumab therapy versus standard of care. CD23 is the low affinity receptor for IgE on B cells and also regulates IgE synthesis. CD23+ B cell-mediated antigen presentation of IgE-antigen complexes has been implicated in the enhancement of antibody and CD4+ T cell responses to said antigens. Anti-dsDNA IgE is common in SLE and is associated with active LN and worsened disease activity overall. Modulation of this CD23-mediated immune enhancement pathway might contribute to the added renal benefit of belimumab therapy versus standard of care alone. More generally, this work also provides evidence that treatment with specific medications can be detected in the urine proteome and could potentially be used for drug monitoring. We note that the full breadth of belimumab’s effect on the urine proteome may not be captured here, given that participants in BLISS-LN were treated with mycophenolate mofetil or cyclophosphamide-azathioprine for up to two months prior to randomization, thereby potentially blunting pro-inflammatory urinary signals that can only be seen before immunosuppression is started.
 Figure 1. Volcano plot of urinary proteins at Week 24 in the belimumab versus standard of care treatment arms. Points in orange represent proteins which were higher in those treated with belimumab and had an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. Points in blue represent proteins which were lower in those treated with belimumab with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. The dashed line is the p value threshold for a false discovery rate of 25% – this threshold was chosen given the relatively small sample size and exploratory nature of this work.
Figure 1. Volcano plot of urinary proteins at Week 24 in the belimumab versus standard of care treatment arms. Points in orange represent proteins which were higher in those treated with belimumab and had an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. Points in blue represent proteins which were lower in those treated with belimumab with an unadjusted p value of < 0.05. The dashed line is the p value threshold for a false discovery rate of 25% – this threshold was chosen given the relatively small sample size and exploratory nature of this work.
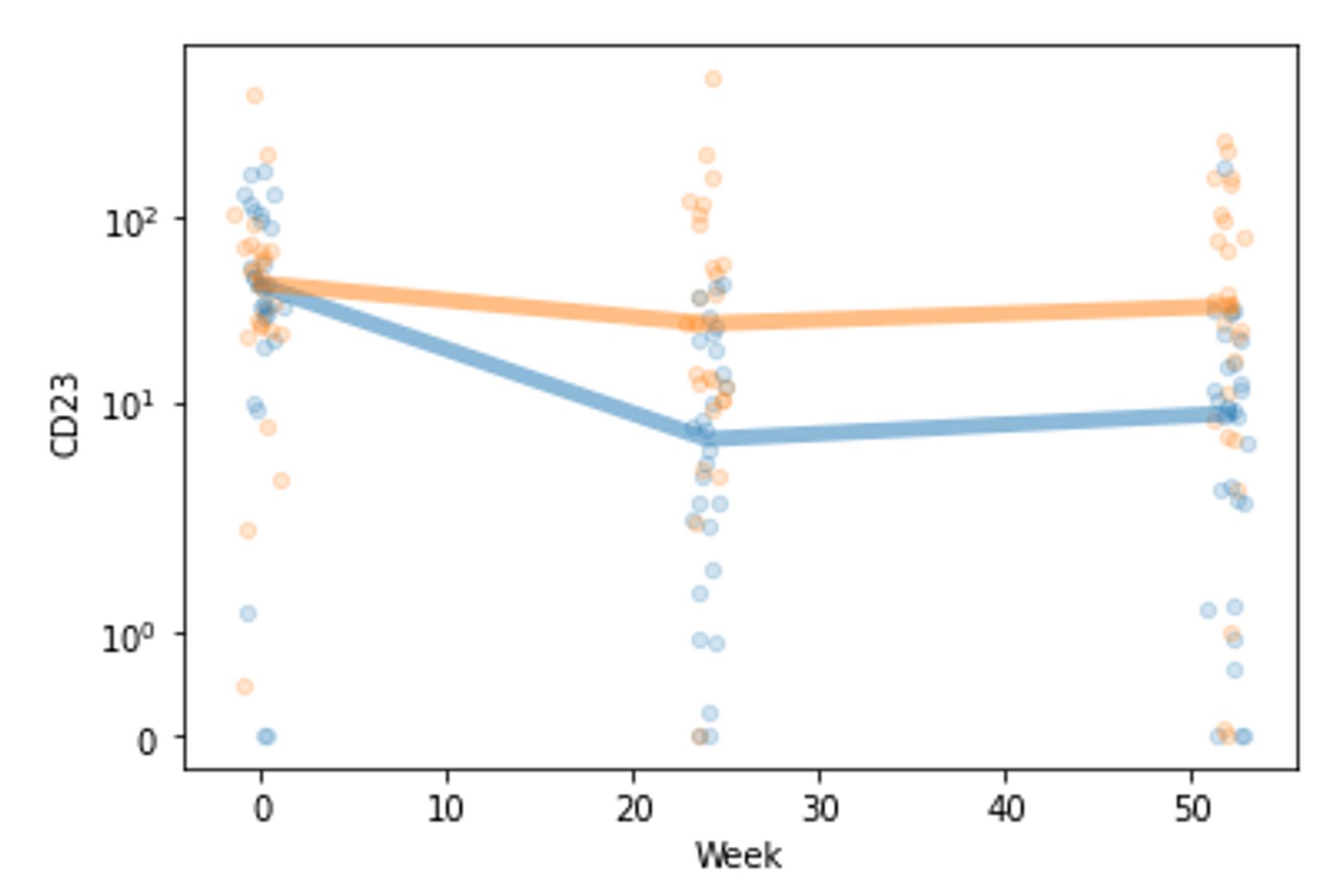 Figure 2. Abundance of CD23 over time in the belimumab (blue) and standard of care (orange) treatment groups. Each small circle represents one participant’s CD23 value at the given time, and the thick lines represent the median CD23 value per group at each time point.
Figure 2. Abundance of CD23 over time in the belimumab (blue) and standard of care (orange) treatment groups. Each small circle represents one participant’s CD23 value at the given time, and the thick lines represent the median CD23 value per group at each time point.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weeding E, Fava A, Mohan C, Goldman D, Petri M. Treatment of Lupus Nephritis with Belimumab Is Associated with Reduction in Urinary CD23 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-lupus-nephritis-with-belimumab-is-associated-with-reduction-in-urinary-cd23/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-lupus-nephritis-with-belimumab-is-associated-with-reduction-in-urinary-cd23/
