Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Glucocorticoids (GC) are the mainstay therapy in Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA), initially at high doses (40-60 mg/day) followed by gradual glucocorticoid tapering. This treatment, especially in older patients, is associated with numerous adverse effects (AE). In addition, there are frequent relapses. Therefore, conventional synthetic immunosuppressants such as methotrexate (MTX), leflunomide, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate, have been used with controversial results. Studies with biological immunosuppressants, such as TNFi have been ineffective; in contrast, tocilizumab (TCZ) has obtained positive results and was approved for the treatment of GCA.
In the ARTESER study we describe a) treatment with GC, synthetic or biological immunosuppressants and concomitant treatments; b) AE of CG; and c) evolution.
Methods: ARTESER is a retrospective observational study sponsored by the Spanish Society of Rheumatology. 26 Spanish centers participated and all new patients diagnosed with GCA from June 1, 2013 to March 29, 2019 were included. Data on GC and immunosuppressants were collected at the beginning and during the follow-up of GCA patients. For the calculation of the cumulative dose of GC, an application was developed that, by including the periods of time, dose and type of GC received during follow-up, performs the automatic calculation in mg of prednisone.
Results: Of the 1675 patients included, GC treatment was adequately recorded in 1650 patients (Table 1). All received oral treatment, being prednisone the most frequently drug used (N=1602, 97.09%). In addition, 426 (25.82%) patients received at least one iv pulse of methylprednisolone, being the 1000 mg regimen the most frequent (n=217; 50.9%). The total mean duration of GC treatment was 22.65 months. The mean cumulative dose per patient at the end of follow-up was 8514.98 mg of prednisone.
The most prescribed concomitant treatment at the time of diagnosis of GCA was calcium (n=1281, 76.9%), vitamin D (n=1258, 75.6%) and bisphosphonates (n=831, 50.1%). The most widely used immunosuppressant was MTX both at diagnosis (n=165; 9.9%) and during follow-up (n=532; 31.8%), followed by TCZ, at diagnosis (22; 1.3%) and at follow-up (153; 9.1%).
AE with GC were described in 393 patients (23.8%), highlighting serious infections (n=67; 10.03%) followed by diabetes mellitus (n=63; 9.43%), steroid myopathy (n=53; 7.9%), vertebral fractures (n=47; 7.04%), non-vertebral fractures (n=36; 5.39%), heart failure (n=36; 5.39%), arterial hypertension (n=34; 5.09%) and neuropsychiatric alterations (n=27; 4.04%).
During the follow-up, 334 (19.9%) patients had relapses, 532 (31.8%) were hospitalized on some occasion, and 142 patients (8.48%) died. The main cause of death were infections (n=44; 30.99%), neoplasms (n=23; 16.2%), cardiovascular (n=15; 10.56%), and cerebrovascular (n=10; 7.04%).
Conclusion: The main treatment for GCA was oral GC, which were required for almost two years on average, in a quarter of patients associated with IV pulses. The cumulative steroid dose was high as well as the side effects. MTX was the most widely used immunosuppressant and TCZ was prescribed in 10%. Relapses and admissions at the hospital were relatively frequent.
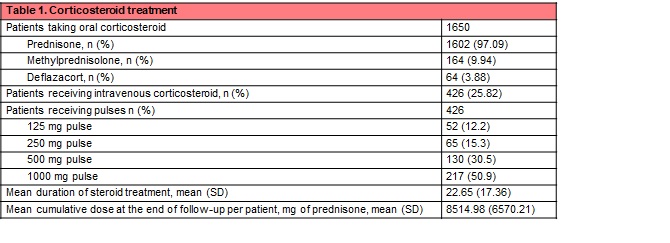 Table 1. Corticosteroid treatment
Table 1. Corticosteroid treatment
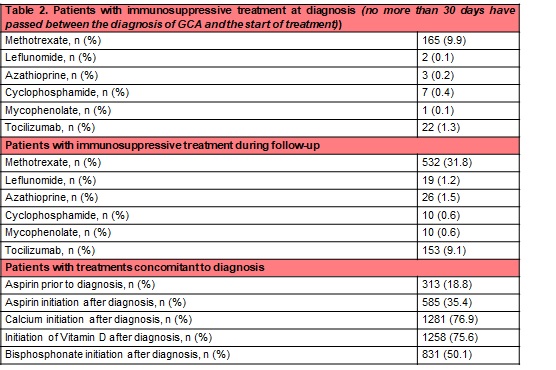 Table 2. Immunosuppressant and concomitant treatments
Table 2. Immunosuppressant and concomitant treatments
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sánchez-Costa J, Hernández-Rodríguez I, Fernández-Fernández E, Silva-Diaz M, Valero-Jaimes J, González-Fernández I, Sánchez J, Lluch J, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Mendizábal-Mateos J, Lois Bermejo P, Loricera J, Muñoz A, Valero-Martínez C, Moya P, Larena-Grijalba C, Navarro-Angeles V, Calvet-Fontova J, Casafont I, Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Labrada-Arrabal S, Calvo-Alén J, Iñiguez-Ubiaga C, Hernández V, Campos-Fernández C, Alcalde-Villar M, Juan-Mas A, De Miguel E, Narvaez J, gonzalez-Gay M, Garrido-Puñal N, Estrada-Alarcon P, Blanco R. Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis in the ARTESER Multicenter Study of 1675 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-in-the-arteser-multicenter-study-of-1675-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-giant-cell-arteritis-in-the-arteser-multicenter-study-of-1675-patients/
