Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M102 ACR Abstract: Misc Rheum & Inflam DZ I: DADA2, Cardiac Sarcoid,Cancer Immunotherapy(1911–1916)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: To analyze the efficacy of steroids and immunosuppressive drugs in the prevention of relapse in cardiac sarcoidosis.
Methods: In this monocentric retrospective study, all consecutive patients with histologically proven sarcoidosis hospitalized from January 2012 to December 2016 were considered. All patients admitted for treatment of symptomatic cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) were included. Patients received either steroids or steroids plus immunosuppressive (IS) drugs for CS treatment. The efficacy of each treatment strategy (steroids vs steroids + IS) was assessed by the cardiac relapses rate during follow up.
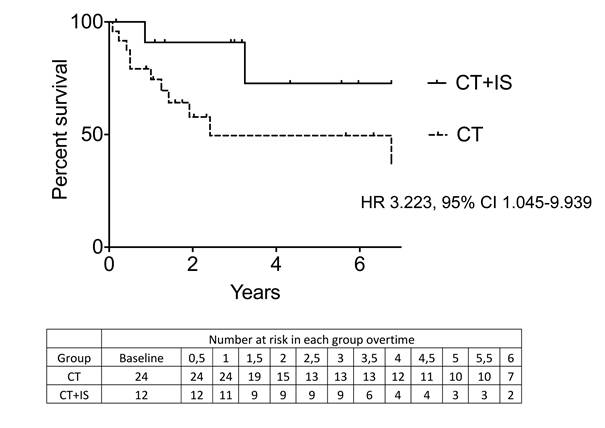
Results: 326 consecutive patients with histologically proven sarcoidosis were screened. Among them, 36 (11%) were admitted for symptomatic cardiac sarcoidosis (20 (55.5%) men, median age at diagnosis 48.5 [22.8-76]). 24 patients received steroids and 12 received steroids + IS (azathioprine n=5, methotrexate n=5, cyclophosphamide n=2). Over a median follow up of 3.6 [1-15.2] years, 13 (36.1%) patients suffered a cardiac relapse including third degree heart block (n=3), reduced left ventricular ejection fraction <50% (n=3), left ventricular dyskinesia (n=2) and ventricular tachycardia (n=2). The rate of cardiac relapse was 45.8% in the steroids group and 16.7% in the steroids+IS group (p=0.048). The median time to relapse did not significantly differ between groups (1.5 [0.5-6.8] vs 1.5 [1-3.2] years). Severe infection occurred in 4 patients under steroids alone and in 2 patients under steroids + IS therapy (p=ns)
Conclusion: In cardiac sarcoidosis relapses occur frequently. The association of steroids with immunosuppressive drugs appears to reduce the risk of cardiac relapse, as compared to steroids alone.
Characteristic of patients
|
|
All (n=36) |
Steroids (n=24) |
Steroids and IS (n=12) |
p |
|
Age at diagnosis of sarcoidosis, years |
48.5 [22.8-76] |
46 [22.8-66.3] |
50.6 [27.2-76] |
ns |
|
Male, n (%) |
20 (55.5) |
14 (58.3) |
6 (50) |
ns |
|
African American, n (%) |
26 (72.2) |
14 (58.3) |
12 (100) |
ns |
|
Organ involvement, n (%) |
||||
|
Lungs |
36 (100) |
24 (100) |
12 (100) |
ns |
|
Skin |
12 (33.3) |
8 (33.3) |
4 (33.3) |
ns |
|
Ear, nose, and throat |
11 (30.6) |
6 (25) |
5 (41.7) |
ns |
|
Eyes |
7 (19.4) |
5 (20.8) |
2 (16.7) |
ns |
|
Liver |
6 (16.7) |
4 (16.7) |
2 (16.7) |
ns |
|
Brain |
4 (11.1) |
2 (8.3) |
2 (16.7) |
ns |
|
Kidney |
2 (5.6) |
2 (8.3) |
0 |
ns |
|
Cardiac Involvement, n (%) |
||||
|
Congestive heart failure |
2 (5.5) |
2 (8.3) |
0 |
ns |
|
Sustained AT/VT |
9 (25) |
5 (20.8) |
4 (33.3) |
ns |
|
Second/third degree heart block |
12 (33.3) |
9 (37.5) |
3 (25) |
ns |
|
Reduced LVEF (<50%) |
12 (33.3) |
6 (25) |
6 (50) |
ns |
|
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
7 (19.4) |
5 (20.8) |
2 (16.7) |
ns |
|
Late gadolinium enhancement on CMR |
24/34 (70.6) |
15/22 (68.2) |
9 (75) |
ns |
|
Myocardial FDG uptake on cardiac PET |
16/25 (64) |
10/17 (58.9) |
6/8 (75) |
ns |
|
Follow up |
||||
|
Delay to first relapse, years |
1.5 [0.5-6.8] |
1.5 [0.5-6.8] |
1.5 [1-3.2] |
ns |
|
Cardiac relapse, n (%) |
13 (36.1) |
11 (45.8) |
2 (16.7) |
0.048 |
|
Steroids at last follow up, n (%) |
30 (88.2) |
21 (87.5) |
9 (75) |
ns |
|
IS at last follow up, n (%) |
21 (58.3) |
11 (45.8) |
10 (83.3) |
ns |
|
Severe infection, n (%) |
6 (16.7) |
4 (1.7) |
2 (1.7) |
ns |
|
Death, n (%) |
3 (8.3) |
2 (8.3) |
1 (8.3) |
ns |
|
Follow up, years |
3.6 [1-15.2] |
4 [1-12.9] |
3.4 [1-15.2] |
ns |
Patients receiving steroids + immunosuppressive drugs (CT+IS) had a lower rate of cardiac relapse than patients receiving only steroids (CT)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ballul T, Borie R, Crestani B, Daugas E, Descamps V, Dieude P, Dossier A, Extramiana F, Papo T, Sacre K. Treatment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Comparative Study of Steroids Alone Versus Steroids Associated with Immunosuppressive Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-cardiac-sarcoidosis-a-comparative-study-of-steroids-alone-versus-steroids-associated-with-immunosuppressive-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/treatment-of-cardiac-sarcoidosis-a-comparative-study-of-steroids-alone-versus-steroids-associated-with-immunosuppressive-drugs/